中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (26): 3890-3896.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.26.014
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
不稳定股骨转子间骨折不同内固定方式的三维有限元分析
陈少明1,邱玉金2,卢 斌1,杨志强1,王宝九1,冯振东1
- 1昌邑市人民医院骨二科,山东省昌邑市 261300;2潍坊医学院附属医院骨科,山东省潍坊市 261031
Three-dimensional finite element analysis of unstable intertrochanteric fracture in different fixation ways
Chen Shao-ming1, Qiu Yu-jin2, Lu Bin1, Yang Zhi-qiang1, Wang Bao-jiu1, Feng Zhen-dong1
- 1Second Department of Orthopedics, Changyi Municipal People’s Hospital, Changyi 261300, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261031, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
动力髋螺钉:是修复股骨转子间骨折的主要固定装置,其操作简单,固定效果好,抗剪切应力比较大,不足为对骨质疏松患者固定效果不理想,没有抗旋转作用。
骨折有限元模型:可以从生物力学的角度研究骨折发生的机制,发现骨折的易发部位,从而有效预测和防止骨折的发生,并且可以对骨折进行生物力学分析,为临床骨折的治疗提供有效的依据。有限元对骨折固定装置的生物力学也有指导意义。
摘要
背景:由于不稳定型股骨转子间骨折骨骼的形态及力学传递比较复杂,普通的实验方法难以全面完整的分析其生物力学变化特点,并且普通实验成本高、周期长、重复性比较差等缺陷使其在生物力学方面的研究受到限制。
目的:应用三维有限元法分析不稳定股骨转子间骨折不同内固定方式的生物力学特点。
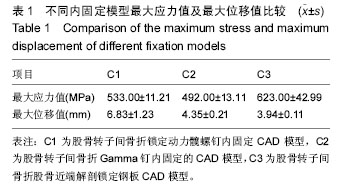
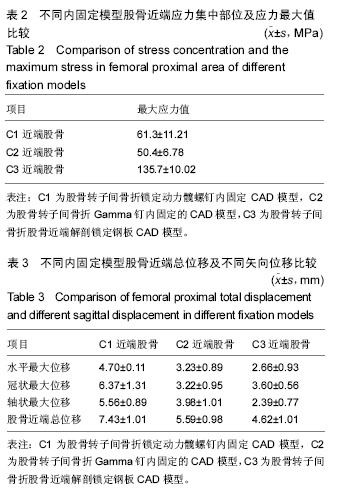
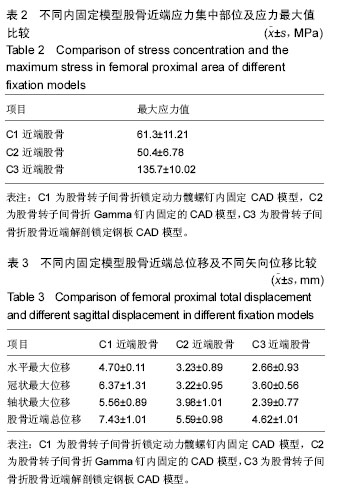
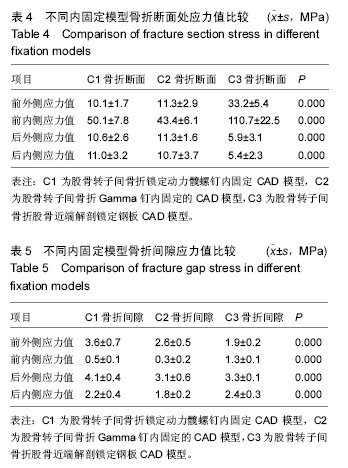
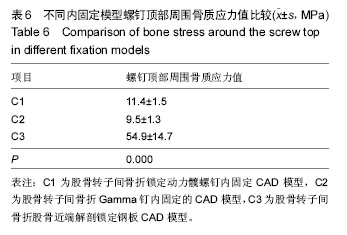
方法:建立股骨转子间骨折锁定动力髋螺钉内固定模型(C1)、Gamma钉内固定模型(C2)以及股骨近端解剖锁定钢板内固定模型(C3),将股骨远端固定,施加髋关节反作用力2 800 N及外展肌力分别为1 200 N。三维有限元法分析不稳定股骨转子间骨折3种内固定模型不同部位的应力分布、应力集中部位以及最大位移情况。
结果与结论:①骨折断面应力值:C3骨折断面前外侧应力值和前内侧应力值均最大,C3骨折断面后外侧应力值和后内侧应力值均最小,3组比较差异均有显著性意义(P均< 0.05)。②骨折间隙应力值:C1、C2和C3的前外侧应力值、前内侧应力值、后外侧应力值和后内侧应力值之间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。其中C1前外侧应力值明显大于C2前外侧应力值(P < 0.05),C3的前外侧应力值明显小于C1前外侧应力值和C2前外侧应力值(P < 0.05),C3的前内侧应力值明显小于C1前内侧应力值和C2前内侧应力值(P < 0.05);C1后外侧应力值明显大于C2后外侧应力值和C3后外侧应力值(P < 0.05),C1后内侧应力值明显大于C2后内侧应力值(P < 0.05),C3的后内侧应力值明显小于C1后内侧应力值和C2后内侧应力值(P < 0.05)。③螺钉顶部周围骨质应力值:3组之间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),其中C3的螺钉顶部周围骨质应力值明显大于C1和C2(P < 0.05)。④由此可见,锁定动力髋螺钉、Gamma钉和股骨近端解剖锁定钢板3种内固定方式修复不稳定股骨转子间骨折各有优缺点,可以根据需要选择合适的内固定装置。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID:0000-0001-6536-4671(陈少明)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)