| [1] Black CR, Goriainov V, Gibbs D, et al. Bone Tissue Engineering. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 2015;1(3):132-140.[2] Jayasuriya AC, Shah C, Ebraheim NA, et al. Acceleration of biomimetic mineralization to apply in bone regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2008;3(1): 015003.[3] Lao L, Wang Y, Zhu Y, et al. Poly (lactide-co- glycolide)/hydroxyapatite nanofibrous scaffolds fabricated by electrospinning for bone tissue engineering.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(8): 1873-1884.[4] Abousleiman RI, Sikavitsas VI. Bioreactors for tissues of the musculoskeletal system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;585:243-259.[5] Schulz RM, Zscharnack M, Hanisch I,et al. Cartilage tissue engineering by collagen matrix associated bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Mater Eng. 2008;18(1 Suppl):S55-70.[6] Godara P,Nordon RE, McFarland CD, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in tissue engineering. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2008; 83(4): 397-407.[7] Nazirkar G, Singh S, Dole V, et al. Effortless effort in bone regeneration: a review.J Int Oral Health. 2014; 6(3):120-124.[8] Wang J, Cui X, Zhou Y, et al. Core-shell PLGA/collagen nanofibers loaded with recombinant FN/CDHs as bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Connect Tissue Res. 2014;55(4):292-298.[9] Pilipchuk SP, Plonka AB, Monje A, et al. Tissue engineering for bone regeneration and osseointegration in the oral cavity. Dent Mater. 2015;31(4):317-338.[10] Amini AR, Laurencin CT, Nukavarapu SP. Bone tissue engineering: recent advances and challenges. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2012;40(5):363-408.[11] Hollister SJ. Porous scaffold design for tissue engineering. Nat Mater. 2005;4(7):518-524.[12] Lacroix D, Chateau A, Ginebra MP, et al. Micro-finite element models of bone tissue-engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2006;27(30):5326-5334. [13] Liu Q, Cheng S, Li Z, et al. Characterization, biodegradability and blood compatibility of poly[(R)-3- hydroxybutyrate] based poly(ester-urethane)s. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;90(4):1162-1176.[14] Volova T, Goncharov D, Sukovatyi A, et al. Electrospinning of polyhydroxyalkanoate fibrous scaffolds: effects on electrospinning parameters on structure and properties. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2014;25(4):370-393.[15] 马敏先,周祥文,王永,等.鼠骨髓间充质干细胞诱导的成骨细胞与3-羟基丁酸-3-羟基己酸共聚物的体外相容性[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2013,33(3):614-616.[16] Yang G, Cai ZJ. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-4- Hydroxybutyrate)Nanofiber Menbranes. Advanced Materials Research. 2011;332-334:1527-1530.[17] Ou W, Qiu H, Chen Z, et al. Biodegradable block poly(ester-urethane)s based on poly(3- hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) copolymers. Biomaterials. 2011;32(12):3178-3188.[18] 郭静,张欣,胡成女.聚(3-羟基丁酸酯-co-4-羟基丁酸酯)研究进展[J].合成纤维工业,2012,35(3):370-393.[19] Chen X, Yang X, Pan J, et al. Degradation behaviors of bioabsorbable P3/4HB monofilament suture in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;92(2):447-455.[20] Chanprateep S, Buasri K, Muangwong A, et al. Biosynthesis and biocompatibility of biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2010;95(10): 2003-2012. [21] 李楠,王雪明,齐宏,等.电纺丝聚乳酸、聚3羟基丁酸酯共聚4羟基丁酸酯和聚碳酸亚丙酯纳米纤维的制备及表面亲水性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(12): 2273-2276. [22] 刘伟,刘萌,祝劲松,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞的体外培养、鉴定及成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(14): 2515-2519.[23] Gusi? N, Ivkovi? A, VaFaye J, et al. Nanobiotechnology and bone regeneration: a mini-review. Int Orthop. 2014; 38(9):1877-1884.[24] De Long WG Jr, Einhorn TA, Koval K, et al. Bone grafts and bone graft substitutes in orthopaedic trauma surgery. A critical analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89(3):649-658. [25] Kurien T, Pearson RG, Scammell BE. Bone graft substitutes currently available in orthopaedic practice: the evidence for their use. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(5): 583-597.[26] Inzana JA, Olvera D, Fuller SM, et al. 3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2014;35(13): 4026-4034. [27] Luo Y, Lode A, Wu C, et al. Alginate/nanohydroxyapatite scaffolds with designed core/shell structures fabricated by 3D plotting and in situ mineralization for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(12):6541-6549.[28] Gusi? N, Ivkovi? A, VaFaye J, et al. Nanobiotechnology and bone regeneration: a mini-review. Int Orthop. 2014; 38(9):1877-1884. [29] Ye C, Hu P, Ma MX, et al. PHB/PHBHHx scaffolds and human adipose-derived stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 200930(26):4401-4406.[30] 张弢,何志旭,叶川,等. 聚羟基丁酸/戊酸酯共聚物膜与的体外生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(12): 1920-1925.[31] Qiu H, Li D, Chen X, et al. Synthesis, characterizations, and biocompatibility of block poly(ester-urethane)s based on biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co- 4-hydroxybutyrate) (P3/4HB) and poly(ε-caprolactone). J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(1):75-86.[32] Siew EL, Rajab NF, Osman AB, et al. In vitro biocompatibility evaluation of poly(3- hydroxybutyrate- co-4-hydroxybutyrate) copolymer in fibroblast cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;81(2):317-325.[33] Rao U, Kumar R,Balaji S,et al. A Novel Biocompatible Poly (3-hydroxy-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) Blend as a Potential Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. Journal of Bioactive & Compatible Polymers. 2010;25(4):419-436. [34] Xu XY, Li XT, Peng SW, et al. The behaviour of neural stem cells on polyhydroxyalkanoate nanofiber scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2010;31(14):3967-3975. [35] Luo L, Wei X, Chen GQ. Physical properties and biocompatibility of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co- 3-hydroxyhexanoate) blended with poly(3- hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2009;20(11):1537-1553.[36] Wang X,Sang L,Wei Z, et al. Facile preparation and cytocompatibility of poly(lactic acid)/ poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) hybrid fibrous scaffolds. Polymer Engineering & Science. 2014; 54(12): 2902-2910.[37] Walmsley GG, McArdle A, Tevlin R, et al. Nanotechnology in bone tissue engineering. Nanomedicine. 2015;11(5):1253-1263.[38] Sikavitsas VI, Temenoff JS, Mikos AG. Biomaterials and bone mechanotransduction. Biomaterials. 2001; 22(19):2581-2593.[39] Burg KJ, Porter S, Kellam JF. Biomaterial developments for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2000;21(23):2347-2359.[40] Karageorgiou V, Kaplan D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis.Biomaterials. 2005;26(27): 5474-5491.[41] Wilson CE, de Bruijn JD, van Blitterswijk CA, et al. Design and fabrication of standardized hydroxyapatite scaffolds with a defined macro-architecture by rapid prototyping for bone-tissue-engineering research.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;68(1):123-132. |
.jpg)

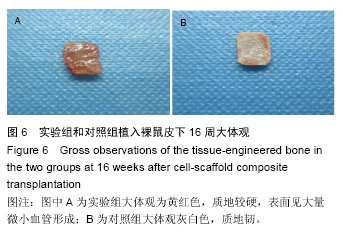
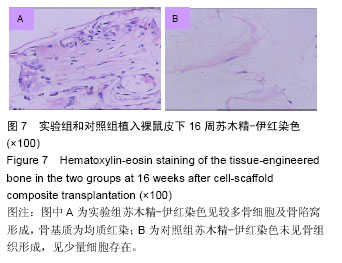
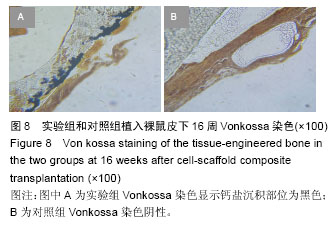
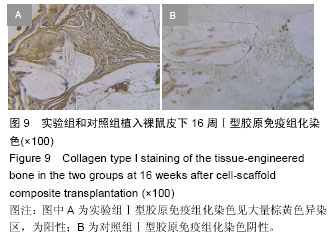
.jpg)