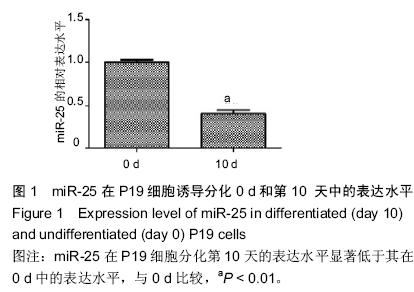
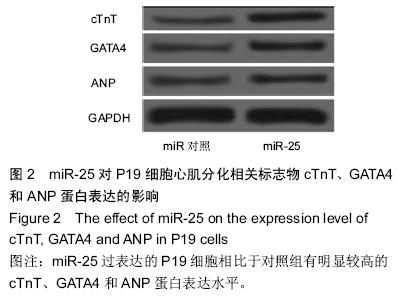
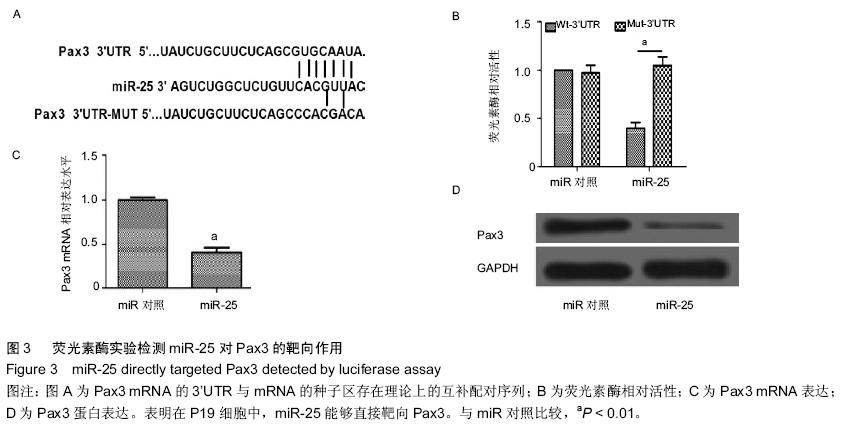
| [1] 吴云英. 460 例胎儿超声心动图分析[J].中国医药导刊,2012;14(12):2202.[2] Hoffman JI, Kaplan S. The incidence of congenital heart disease.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39(12): 1890-1900.[3] Hoffman J.Incidence of congenital heart disease: II.Prenatal incidence.Pediatr Cardiol. 1995;16(4): 155-165.[4] Miyazono K, Kamiya Y,Morikawa M.Bone morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction. J Biochem.2010;147(1):35-51.[5] Ambros V.The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431(7006):350-355.[6] 何卓晶, 洪艳.病毒 miRNA 研究进展概述[D]. 2011 年浙江省医学会医学病毒学分会, 医学微生物与免疫学分会学术年会. 2011.[7] Yuan J, Xiao G, Peng G,et al.MiRNA-125a-5p inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation and promotes cell differentiation by targeting TAZ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;457(2):171-176.[8] 朱莎莎, 刘雪华, 余章斌,等.miR-20b 过表达对 P19 细胞增殖和细胞分化的影响[J].发育医学电子杂志,2014,2(2):87-92.[9] Shiah S, Peng H, Jin S,et al. Cytokine induces MIR-424 expression and modulates SOCS2/STAT5 signaling pathway in oral cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2014; 50:147-147.[10] Valastyan S,Reinhardt F,Benaich N,et al.Retraction Notice to: A Pleiotropically Acting MicroRNA, miR-31, Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cell. 2015;161(2): 417.[11] Chaoxiong Z,Mingjian Z,Fu G,et al.Down regulation of miR-203in radiation-induced thymic lymphoma promoted cells proliferation and inhibited apoptosis. Chinese Journal of Radiological Medicine and Protection. 2015;35(1): 28-34.[12] Li Y, Liu S, Zhang F,et al.Expression of the microRNAs hsa-miR-15a and hsa-miR-16-1 in lens epithelial cells of patients with age-related cataract. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(2):2405-2410.[13] Li X, Yang Y, Wang L, et al.Plasma miR-122 and miR-3149 Potentially Novel Biomarkers for Acute Coronary Syndrome. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(5): e0125430.[14] Huang JB, Mei J, Jiang LY,et al. MiR-196a2 rs11614913 T> C Polymorphism is Associated with an Increased Risk of Tetralogy of Fallot in a Chinese Population. Acta Cardiologica Sinica.2015;31(1): 18-23.[15] Kabaria S,Choi DC,Chaudhuri AD,et al.Inhibition of miR-34b and miR-34c enhances α-synuclein expression in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS letters. 2015; 589(3):319-325.[16] Taipaleenmäki H, Browne G, Akech J,et al.Targeting of Runx2 by miR-135 and miR-203 Impairs Progression of Breast Cancer and Metastatic Bone Disease.Cancer research. 2015;75(7):1433-1444.[17] Hoss AG, Labadorf A, Latourelle JC,et al.miR-10b-5p expression in Huntington’s disease brain relates to age of onset and the extent of striatal involvement. BMC medical genomics. 2015;8(1):10.[18] Roderburg C, Benz F, Vargas Cardenas D,et al. Elevated miR‐122 serum levels are an independent marker of liver injury in inflammatory diseases.Liver International.2015;35(4):1172-1184.[19] Doridot L, Houry D, Gaillard H,et al. miR-34a expression, epigenetic regulation, and function in human placental diseases. Epigenetics. 2014;9(1): 142-151.[20] Liangju C, Ming Y, Yan C,et al. Roles of miR-15b in endothelial cell function and their relevance to vascular diseases. Yi chuan= Hereditas/Zhongguo yi chuan xue hui bian ji.2015;37(2):121-127.[21] Li Q, Song XW, Zou J,et al.Attenuation of microRNA-1 derepresses the cytoskeleton regulatory protein twinfilin-1 to provoke cardiac hypertrophy. Journal of cell science. 2010;123(14):2444-2452.[22] Wagh V, Pomorski A, Wilschut KJ,et al. MicroRNA-363 negatively regulates the left ventricular determining transcription factor HAND1 in human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014; 5(75):10.1186.[23] Ventura A, Young AG, Winslow MM,et al. Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17 through 92 family of miRNA clusters.Cell. 2008;132(5):875-86.[24] Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM,et al. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation.Nature genetics. 2006; 38(2):228-233.[25] Morton SU, Scherz PJ, Cordes KR,et al. microRNA-138 modulates cardiac patterning during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(46):17830-17835.[26] Wen J, Xia Q, Lu C,et al. Proteomic analysis of cardiomyocytes differentiation in mouse embryonic carcinoma P19CL6 cells. J Cell Biochem. 2007; 102(1):149-160.[27] Razumilava N, Bronk SF, Smoot RL,et al. miR‐25 targets TNF‐related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptor‐4 and promotes apoptosis resistance in cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology.2012;55(2): 465-475.[28] Zhang H, Zuo Z, Lu X,et al. MiR-25 regulates apoptosis by targeting Bim in human ovarian cancer. Oncology reports. 2012;27(2):594-598.[29] Zhao H, Wang Y, Yang L,et al. MiR-25 promotes gastric cancer cells growth and motility by targeting RECK. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;385(1-2):207-213.[30] 徐晓慧. miR-25 在食管鳞癌中通过抑制 CDH1 的表达促进细胞的侵袭和转移[D].北京协和医学院,2012.[31] 邱刚,房保栓,辛国宏,等. miR-25 靶向 RECK 促进宫颈癌 HeLa 细胞的增殖[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2015, (1):40-43.[32] Hu DL, Liu YQ, Chen FK,et al. Differential expression of microRNAs in cardiac myocytes compared to undifferentiated P19 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2011;28(1): 59-64.[33] 李贤慧,贾竹青,崔庆华,等. 稳定转染MiR-499对P19CL 6细胞向心肌细胞分化的影响[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2011,(4):316-322.[34] 郭励京,张志,刘紫东,等. miR-122 靶向调控心肌样细胞诱导分化过程中GATA4基因的表达[J].天津医药,2014, 42(4):333-336.[35] 兰贝蒂,张玉顺. 肺动脉高压合并小缺损先天性心脏病的认识与研究进展[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志. 2010,2(3):181-183.[36] Trojnarska O, Grajek S, Katarzyński S, et al. Predictors of mortality in adult patients with congenital heart disease. Cardiology journal. 2009;16(4):341-347.[37] Weber DG, Casjens S, Rozynek P,et al.Assessment of mRNA and microRNA stabilization in peripheral human blood for multicenter studies and biobanks. Biomarker insights. 2010;5:95.[38] Brase JC, Johannes M, Schlomm T,et al. Circulating miRNAs are correlated with tumor progression in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(3):608-616.[39] 刘学红, 张泳. Cx43和Pax3 蛋白在人胚胎胃发育过程中的表达及意义[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009,25(11): 2211-2213.[40] 刘学红, 张金萍, 何淑英, 等. Cx43和Pax3在人胚胎早期小肠肌层中的表达及其意义[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2008,28(4):634-636.[41] 刘学红,张泳,张金萍. nNOS, Pax3和Cx43蛋白在人胚胎早期脊髓中的表达及意义[J]. 解剖学报,2008, 39(4): 594-597.[42] Li Q, Le May M, Lacroix N,et al.Induction of Pax3 gene expression impedes cardiac differentiation. Sci Rep. 2013;3:2498. |
.jpg)