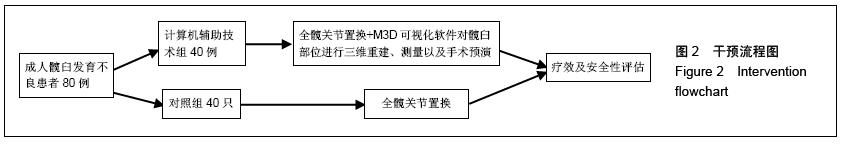
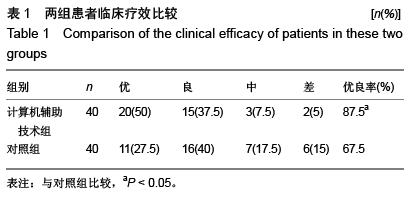
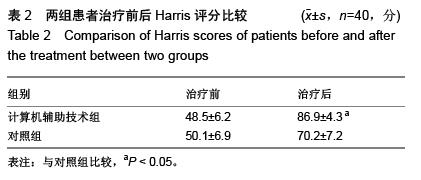
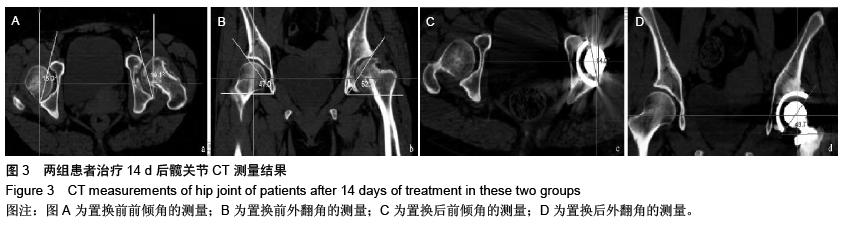
| [1] Aksoy C, Yilgor C, Demirkiran G, et al. Evaluation of acetabular development after Dega acetabuloplasty in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2013;22(2):91-95.[2] Bracken J, Tran T, Ditchfield M. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: controversies and current concepts. J Paediatr Child Health. 2012;48(11):963-973.[3] Bozek M, Bielecki T, Nowak R, et al. Arthroplasty in patients with congenital hip dysplasia-early evaluation of a treatment method. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2012;15(1):49-59.[4] Li H, Wang L, Dai K, et al. Autogenous impaction grafting in total hip arthroplasty with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Arthrop. 2013;28(4):637-643.[5] Antoniades J, Pellegrini Jr VD. Cross-sectional anatomy of the ilium: implications for acetabular component placement in total hip arthroplasty. Clinical Orthop Related Res. 2012; 470(12): 3537-3541.[6] Murayama T, Ohnishi H, Okabe S, et al. 15-ear comparison of cementless total hip arthroplasty with anatomical or high cup placement for Crowe I to III hip dysplasia. Orthopedics. 2012; 35(3):183.[7] 卢伟杰,金大地,李之琛,等.全髋关节置换后髋臼假体外倾角的临床研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2012,30(2):233-236.[8] Wong J, Abrishami A, El Beheiry H, et al. Topical application of tranexamic acid reduces postoperative blood loos in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled tril. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;15:2503-2513.[9] 傅峥,张健,姚海.氨甲环酸对全髋关节置换隐性失血的影响[J].重庆医科大学学报,2012,37(4):359-361.[10] Imbuldeniya AM, Walter WL, Zicat BA, et al. Cementless total hip replacement without femoral osteotomy in patients with severe developmental dysplasia of the hip: minimum 15-year clinical and radiological results. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(11): 1449-1454.[11] 向珊珊,陈艺,傅明,等.髋臼旋转截骨术时髋臼后上方植骨前后髋关节生物力学的改变及其对比[J/CD].中华关节外科杂志:电子版, 2012,6(3):68-71.[12] 郑卓肇.关节影像诊断系列讲座(三)股骨髋臼撞击综合征[J/CD].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2011,5(5):658-659.[13] 陈凯,蔡俊丰,秦玉星,等.髋臼发育不良全髋关节置换髋臼旋转中心原位固定与上移的比较研究[J/CD].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2014,8(1):56-59.[14] 孔刚,马卫华.全髋关节置换治疗成人髋关节发育不良的研究进展[J/CD].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2015,9(1):110-113.[15] 张卫红,龚春柱.全髋关节置换治疗髋关节发育不良的疗效观察[J].局解手术学杂志,2013,1(2):204-205.[16] 杨国志,李振武,李志安.成人髋关节发育不良的全髋关节置换治疗分析[J].中国当代医药,2012,19(28):182-184.[17] 秦宏敏,殷光义,赵良虎.全髋关节置换治疗成人髋关节发育不良的疗效分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2012,6(4):26-28.[18] 马海萍,姚剑英,吴林艳.成人先天性髋关节发育不良患者全髋关节置换围术期护理[J].实用临床医学(江西),2012,13(8):113-114.[19] 孙艺娟,罗辉,黄希照,等.不同剂量右美托咪定预防妇科腹腔镜手术患者全麻后寒战的临床观察[J].实用医学杂志, 2014,30(12): 1976-1978.[20] Robinson M, Bornstein L, Mennear B, et al. Effect of restoration of combined offset on stability of large head THA. Hip Int. 2012;22(3):248-253.[21] Little NJ, Busch CA, Gallagher JA, et al. Acetabular polyethylene wear and acetabular inclination and femoral offset. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(11):2895-2900.[22] 肖瑜,张福江,马信龙,等.全髋关节置换后股骨偏距减小与聚乙烯内衬磨损的关系[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(9):849-854.[23] 吴硕雄,王志萍,过伟,等.不同剂量舒芬太尼对全身麻醉下老年患者关节置换后苏醒质量的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志, 2013, 29(10): 951-954.[24] 杨晓凌,梁吉文.舒芬太尼在老年全髋关节置换后静脉自控镇痛的临床应用[J].实用疼痛学杂志,2011,7(4):274-275. [25] ang C,Li L,Shen B,et al. A multicenter randomized double-blind prospective study of the postoperative patient controlled intravenous analgesia effects of dezocine in elderly patients. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(3):530-539.[26] Langton DJ, Joyce TJ, Jameson SS, et al. Adverse reaction to metal debris following hip resurfacing: the influence of component type, orientation and volumetric wear. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(2):164-167.[27] Takamura KM, Yoon J, Ebramzadeh E, et al. Incidence and significance of femoral neck narrowing in the first 500 Conserve? Plus series of hip resurfacing cases: a clinical and histologic study. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(2):181-193.[28] Ho KK, Beazley J, Parsons N, et al. Narrowing of the femoral neck after resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip: a comparison of cemented and uncemented femoral components. Hip Int. 2010;20(4):542-546.[29] 蒋志勇,茹江英,胡玉华,等.全髋表面置换后发生股骨颈狭窄非手术相关危险因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(17): 1702-1707.[30] Prosser GH, Yates PJ, Wood DJ, et al. Outcome of primary resurfacing hip replacement: evaluation of risk factors for early revision. Acta Orthop. 2010;81(1):66-71.[31] Lu CH, Chen JL, Wu CT, et al. Effect of epidural neuraxial blockade-dependent sedation on the Ramsay Sedation Scale and the composite auditory evoked potentials index in surgical intensive care patients. J Formos Med Assoc. 2010; 109(8):589-595.[32] Amstutz HC, Wisk LE, Le Duff MJ. Sex as a patient selection criterion for metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Athroplasty. 2011;26(2):198-208.[33] 蒋志勇,茹江英,胡玉华,等.全髋表面置换后发生股骨颈狭窄非手术相关危险因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(17): 1702-1707.[34] Stulberg BN,Fitts SM,Bowen AR,et al. Early return to function after hip resurfacing: is it better than contemporary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(5):748-753.[35] Tan TL, Ebramzadeh E, Campbell PA, et al. Long-term outcome of a metal-on-polyethylene cementless hip resurfacing. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(4):802-807.[36] 马立峰,郭艾.金属对金属髋关节表面置换的研究进展[J/CD].中华损伤与修复杂志:电子版,2014,9(5):537-540.[37] Jia J, Li L, Zhang L, et al. Three dimensional-CT evaluation of femoral neck anteversion, acetabular anteversion and combined anteversion in unilateral DDH in an early walking age group. Int Orthop. 2012;36(1):119-124.[38] Tréguier C, Chapuis M, Branger B, et al. Pubo-femoral distance: an easy sonographic screening test to avoid late diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(3):836-844.[39] Arti H, Mehdinasab SA, Arti S. Comparing results of clinical versus ultrasonographic examination in developmental dysplasia of hip. J Res Med Sci. 2013;18(12):1051-1055.[40] Li LY, Zhang LJ, Li QW, et al. Development of the osseous and carti-laginous acetabular index in normal children and those with developmental dysplasia of the hip: a crosssectional study using MRI. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012; 94(12):1625-1631. |
.jpg)
.jpg)