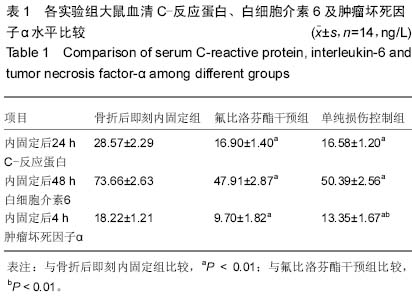
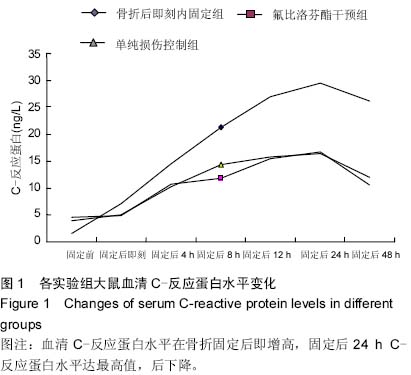
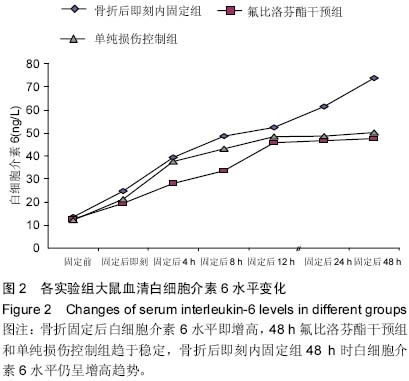
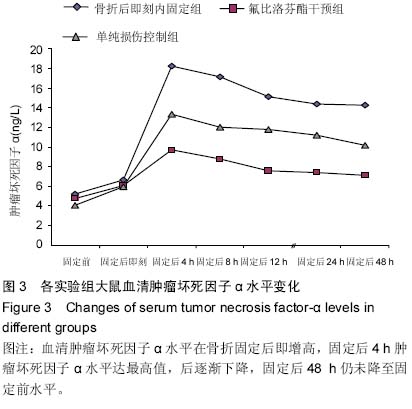
| [1] Rotondo MF, Schwab CW, McGonigal MD, et al. Damage control: an approach for improved survival in exsanguinating penetrating abdominal injury. J Trauma. 1993;35(3):375-383.
[2] Roberts CS, Pape HC,Jones AL,et al.Damage control orthopaedics:evolving concepts in the treatment of patients who have sustained orthopaedics truma. JBJS Instr Course Lect. 2005;54(2):447-462.
[3] Giannoudis PV, Hildebrand F, Pape HC.Inflammatory serum markers in patients with multiple trauma. Can they predict outcome? J Bone Joint Surg. 2004;3(3):313-323.
[4] Giannoudis PV. Current concepts of the inflammatory response after major trauma: an update. Injury. 2003;34(8): 397-404.
[5] Mokart D, Capo C, Blache JL, et al. Early postoperative compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome is associated with septic complications after major surgical trauma in patients with cancer. British J Surg. 2002;89(11): 1450-1456.
[6] Hildebrand F, Giannoudis P, Kretteck C,et al. Damage control: extremities. Injury. 2004;35(7):678-689.
[7] Pape HC, Giannoudis PV, Krettek C,et al. Timing of fixation of major fractures in blunt polytrauma: role of conventional indicators in clinical decision making. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19(8):551-562.
[8] Pape HC, van Griensven M, Rice J, et al. Major secondary surgery in blunt trauma patients and perioperative cytokine liberation: determination of the clinical relevance of biochemical markers. J Trauma. 2001;50(6):989-1000.
[9] 王晓伟,孙天胜,刘智,等.老年髋部骨折手术疗效的危险因素分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(9):811-816.
[10] 丁呈彪,丁洋洋,汤健,等.氟比洛芬酯对骨折急性疼痛患者多种炎性介质及疼痛评分的影响[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2013,17(5): 414-416.
[11] 王晓伟.炎性反应对老年髋部骨折后肺损害的作用及意义的基础研究[D].山西医科大学, 2009.
[12] 卢国林,林财珠,林献忠.氟比洛芬酯对大鼠急性痛的超前镇痛效果[J].福建医科大学学报,2008, 42(2):158-160.
[13] Xie HL, Ouyang WF, Wu BH, et al.A case-control study regarding tea consumption and risk of hip fractures in middle-aged and elderly Chinese. Chin J Epidemiol. 2013; 34(4):385-388.
[14] 韩亚军,帖小佳,伊力哈木•托合提.中国中老年人骨质疏松症患病率的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(7):1129- 1134.
[15] Cornwall R,Gilbert MS,Koval KJ,et al.Functional Outcomes and Mortality Vary among Different Types of Hip Fractures: A Function of Patient Characteristics. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;425:64-71.
[16] 郭永智,王晓伟,刘智,等.老年骨质疏松性髋部骨折风险预测[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012, 27(10):879-881.
[17] 俞越,刘畅,刘士嘉,等.北方地区115例中老年髋部骨折常见易患因素分析[J].中国老年保健医学, 2014, 12(4):57-57.
[18] 张桂芳. 骨质疏松性髋部骨折老年患者的临床治疗效果观察[J]. 中西医结合心血管病电子杂志, 2014, 2(2):16-17.
[19] 鲍宏玮,严力生,钮心刚,等. 80岁以上髋部骨折患者的围手术期处理[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2010, 25(4):323-324.
[20] Pape HC,Kolk M,Paffrath T,et al.Primary intramedullary femur fixation in multiple trauma patients with associated lung contusion-a cause of posttraumatic ARDS? J Trauma. 1993; 34(4):540-548.
[21] Hossain M, Neelapala V, Andrew JG. Results of non-operative treatment following hip fracture compared to surgical intervention. Injury. 2009;40(4): 418-421.
[22] 孙天胜.老年髋部骨折的损伤控制外科治疗[J].国际外科学杂志, 2011,38(11):721-723.
[23] Tegeder I, Pfeilschifter J, Geisslinger G. Cyclooxygenase- independent actions of cyclooxygenase inhibitors. FASEB J. 2001;15(12):2057-2072.
[24] Doraid J,Steven EW,Marc GJ,et al.Growth hormone attenuates the acute-phase response to thermal injury. Arch Surg. 2006;132(11):1171-1175.
[25] 丁雪梅.血糖、C反应蛋白、D-二聚体对SIRS病情预测的价值[J]. 山东医药,2014,54(29):66-68.
[26] Celebi OO, Celebi S, Canbay A, et al. The effect of sinus rhythm restoration on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels and their association with long-term atrial fibrillation recurrence after electrical cardioversion. Res Gate. 2011; 118(3):168-174.
[27] Henningsen KM, Therkelsen SK, Bruunsgaard H, et al. Prognostic impact of hs-CRP and IL-6 in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation treated with electrical cardioversion. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2009;69(3):425-432.
[28] Livingston DN, Mosenthal AC, Dietch EA.Sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome:a clinical- mechanistic overview. New Horizon. 2005;24(3):257-266.
[29] 李雅巍,王东信.炎症反应与术后认知功能并发症的关系研究进展[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2014, 39(8):673-677.
[30] 许永志,林月云,陈彬.严重创伤患者SIRS评分与葡萄糖、乳酸、CRP水平的相关性分析[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2014, 35(10): 1272-1274.
[31] Koch A, Gressner OA, Sanson E, et al. Serum resistin levels in critically ill patients are associated with inflammation, organ dysfunction and metabolism and may predict survival of non-septic patients. Critical Care. 2009; (3):R95.
[32] Jiang CY, Wang W, Tang JX, et al. The adipocytokine resistin stimulates the production of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 in pancreatic acinar cells via NF-κB activation. J Endocrinol Invest. 2013;36(11):986-992.
[33] 乐海浪,罗国强.创伤后早期炎症因子TNF-a、IL-1、IL-6的研究进展[J].现代诊断与治疗, 2014, 25(4):763-765.
[34] 杨峰,随福革,张勇,等.关节置换后血清白细胞介素6,8,10及C-反应蛋白表达与深静脉血栓形成[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(43):8031-8033.
[35] Chen JW, Chen YH, Lin SJ. Long-term exposure to oxidized low-density lipoprotein enhances tumor necrosis factor-alpha- stimulated endothelial adhesiveness of monocytes by activating superoxide generation and redox-sensitive pathways. Res Gate. 2006;40(5):817-826.
[36] 黄党生,韩溟,谢扬.血液炎症标记物在诊断小儿急性阑尾炎中的意义[J].南方医科大学学报,2012,32(8):1154-1156.
[37] Julius D, Basbaum AI. Molecular mechanisms of nocieption. Nature. 2001;413(6852):203-210.
[38] 王延炳,姜晓红.非甾体抗炎药和传统阿片类药物在术后镇痛中的效果比较[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2012,28(6):417-419.
[39] 高玉洁.非甾体抗炎药物的临床应用及安全性评价[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2009, 12(2):122-125.
[40] 谭妙娟,何炳洪,官碧琼,等.骨科医院门诊2011年非甾体抗炎药应用情况分析[J].中国现代医学杂志,2013,23(25):106-108.
[41] 崔旭蕾,郭向阳,任洪智.非甾体抗炎药临床应用的研究进展[J].国际麻醉学与复苏杂志,2007,28(2):122-125.
[42] 朱爱兵,何月,肖彬.氟比洛芬酯超前镇痛对妇科腹腔镜术后镇痛的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2008,24(5):416-417. |