中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (26): 4242-4246.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.26.027
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
防旋髓内钉和InterTan固定A3型股骨转子间骨折:生物力学变化的有限元分析
刘建斌1,刘 敏2,马 林2,崔忠宁2,刘 明2,郭惠康2
- 1山西医科大学第一临床医学院,山西省太原市 030001;2山西晋城煤业集团总医院,山西省晋城市 048006
Liu Jian-bin, Studying for master’s degree, First Clinical Medical College, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
Liu Jian-bin1, Liu Min2, Ma Lin2, Cui Zhong-ning2, Liu Ming2, Guo Hui-kang2
- 1First Clinical Medical College, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2General Hospital, Jincheng Anthracite Mining Group, Jincheng 048006, Shanxi Province, China)
摘要:
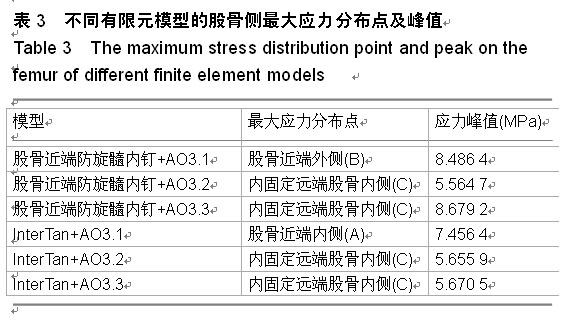
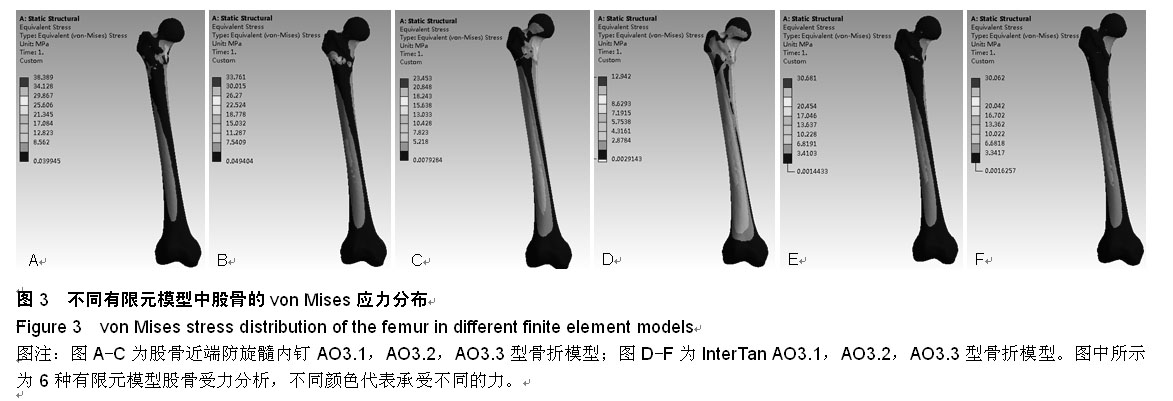
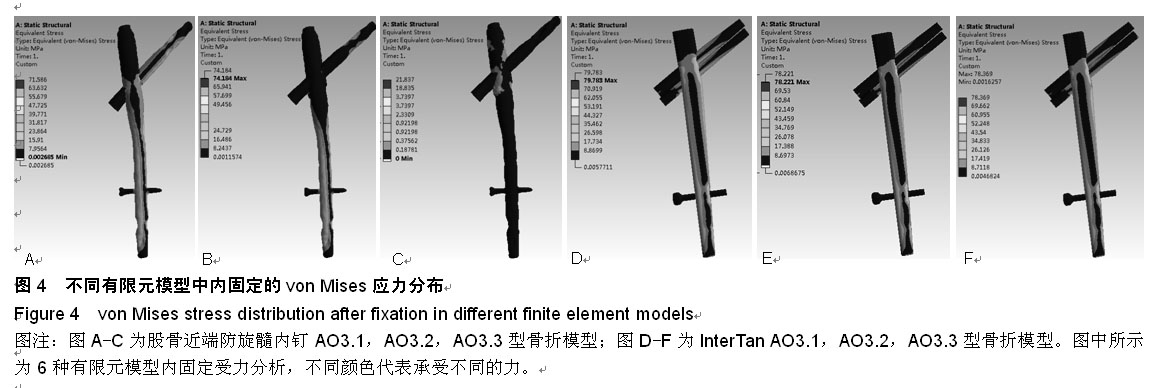
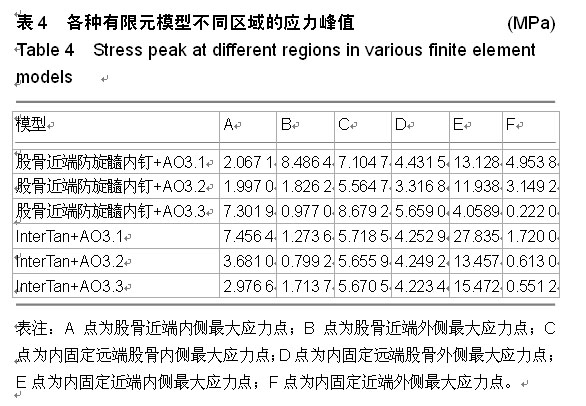
背景:股骨转子间骨折是髋部常见骨折之一,伴随着老年骨质疏松以及高能量伤,骨折线常常下移导致A3型股骨转子间骨折,治疗困难。常见的髓内固定包括股骨近端防旋髓内钉和InterTan等,由于其具有较高的稳定性和微创性,得到了广泛的应用。 目的:通过有限元分析的方法比较股骨近端防旋髓内钉和InterTan修复股骨转子间A3型骨折的生物力学稳定性。 方法:分别建立AO3.1,3.2,3.3型股骨转子间骨折及股骨近端防旋髓内钉和InterTan两种内固定的三维有限元模型,按骨科要求予以固定,观察不同模型股骨、内固定的应力分布,比较股骨及内固定模型不同区域的应力峰值,分析其生物力学稳定性。 结果与结论:AO3.1型骨折股骨近端防旋髓内钉组股骨侧应力集中在股骨近端外侧,InterTan组股骨侧应力集中在股骨近端内侧;AO3.2型骨折两种内固定系统股骨侧各个区域均无明显应力集中;AO3.3型骨折股骨近端防旋髓内钉组股骨侧应力集中在股骨近端内侧及内固定远端内侧,InterTan组股骨侧无明显应力集中。6种模型内固定远端应力均集中在内侧,其中股骨近端防旋髓内钉组应力大于InterTan组;内固定远端内外侧应力差值股骨近端防旋髓内钉组大于InterTan组;除股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定AO3.3型骨折外,其余5种模型应力峰值均位于头钉与主钉交叉处内侧。提示AO3.1和AO3.3型骨折中,InterTan比股骨近端防旋髓内钉具有更好的稳定性,AO3.2型骨折中,二者稳定性无明显差异;采用InterTan修复股骨转子间骨折时股骨端应力分布更加合理。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)