中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (22): 3496-3502.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.22.011
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
颈椎后路植入物固定修复多节段脊髓型颈椎病:可改善症状但降低了颈椎活动度
赵 勇1,褚言琛2,李学森2,马金龙2,邹云雯2
- 1青岛大学,山东省青岛市 266003;2青岛大学附属医院脊柱外科,山东省青岛市 266003
-
收稿日期:2015-04-26出版日期:2015-05-28发布日期:2015-05-28 -
通讯作者:邹云雯,教授,青岛大学附属医院脊柱外科,山东省青岛市 266003 -
作者简介:赵勇,男,1987年生,汉族,硕士,主要从事脊柱外科方面的研究。 -
基金资助:山东省自然科学基金资助项目(ZR2011HM052)
Cervical posterior implant fixation for multi-segment cervical spondylotic myelopathy: improves symptoms but diminishes cervical range of motion
Zhao Yong1, Chu Yan-chen2, Li Xue-sen2, Ma Jin-long2, Zou Yun-wen2
- 1Qingdao University, Qingdao 266003, Shandong Province, China
2Department of Spine Surgery, the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266003, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2015-04-26Online:2015-05-28Published:2015-05-28 -
Contact:Zou Yun-wen, Professor, Department of Spine Surgery, the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266003, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Zhao Yong, Master, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266003, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2011HM052
摘要:
背景:颈椎后路单开门椎管成形单侧侧块内固定与全椎板切除双侧侧块内固定通过扩大椎管有效容积治疗脊髓型颈椎病,并且两种固定方法的疗效和安全性并不清楚。 目的:观察颈后路单开门椎管成形单侧侧块内固定与全椎板切除双侧侧块内固定治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病,植入物与宿主生物相容性。 方法:回顾性分析117例多节段(≥3个)脊髓型颈椎病患者病历资料,分为单开门组65例和全椎板切除组52例,分别采用单开门椎管成形单侧侧块内固定及全椎板切除双侧侧块内固定治疗。对两组患者固定前及末次随访进行JOA评分、估算恢复率,观察神经恢复情况,并通过侧位X射线片测量颈椎曲度指数和颈椎活动度进行评估。 结果与结论:两组平均随访时间28个月(12-59个月)。两组均无C5神经根麻痹患者。两组末次随访JOA评分均高于固定前(P < 0.01)。两组间JOA评分、恢复率、末次随访颈椎曲度指数比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。两组末次随访颈椎活动度均低于固定前(P < 0.01)。结果说明,颈后路单开门椎管成形单侧侧块内固定与全椎板切除双侧侧块内固定在改善神经功能、缓解疼痛、减少并发症上有相似的疗效,但一定程度上降低了颈椎活动度。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
赵 勇,褚言琛,李学森,马金龙,邹云雯. 颈椎后路植入物固定修复多节段脊髓型颈椎病:可改善症状但降低了颈椎活动度[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(22): 3496-3502.
Zhao Yong, Chu Yan-chen, Li Xue-sen, Ma Jin-long, Zou Yun-wen. Cervical posterior implant fixation for multi-segment cervical spondylotic myelopathy: improves symptoms but diminishes cervical range of motion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(22): 3496-3502.
Quantitative analysis of participants and baseline data
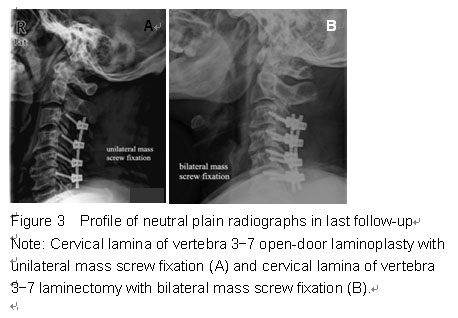
Of the original 216 patients, 117 with multi-segment CSM were eligible for participation. Sixty-five patients (45 men and 20 women) with a mean age of 62.2 years (range, 41-78 years) underwent open-door laminoplasty with unilateral mass screw fixation (Figure 3A). Fifty-two patients (32 men and 20 women) with a mean age of 62.2 years (range, 39-84 years) underwent laminectomy with bilateral mass screw fixation (Figure 3B). No statistical difference in sex, age, or operative levels was found between the two groups. The postoperative JOA scores, cervical curvature index, range of motion of the two groups were not significantly different (Table 3). The whole follow-up period lasted 28 months (range, 12-59 months). During the follow-up period, no C5 nerve root palsy occurred in the two groups. At the final follow-up, only 2 patients suffered axial symptoms, with an incidence of 1.7 % (2 of 117).
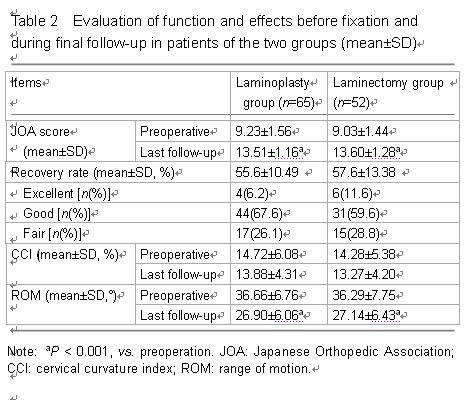
There were statistically significant differences between preoperative and final follow-up JOA scores in each group (P < 0.001; Table 2). The preoperative and final follow-up JOA scores were 9.23±1.56/13.51±1.16 in laminoplasty group, 9.03±1.44/13.60±1.28 in laminectomy group, respectively. No statistically significant difference was found in final follow-up JOA scores between two groups (Table 2). The neurological recovery was excellent in 4 (6.2%, laminoplasty group), 6 (11.5%, laminectomy group)
patients, good in 44 (67.7%, laminoplasty group, 30 (57.7%, laminectomy group), fair in 17 (26.1%, laminoplasty group), 16 (30.8%, laminectomy group) and there were no poor cases in two groups (Table 2). The recovery rate was 55.6±10.49 % in laminoplasty group, 57.6±13.38 % in laminectomy group in final follow-up, and no statistically significant differences between two groups (P < 0.001; Table 2).
No significant difference in preoperative and final follow-up cervical curvature index was found between the two groups (P > 0.05; Table 2, Figure 4). The cervical range of motion decreased from 36.66±6.76/36.29±7.75 (laminoplasty group/laminectomy group) preoperatively to 26.90±6.06/27.14±6.43 (laminoplasty group/laminectomy group) at the final follow-up (P < 0.001; Table 2, Figure 4).
No complications such as deep infection, pseudarthrosis, or screw loosening occurred. No closure of opened laminae was observed in laminoplasty group; and no screw extrusion, breakage, or nerve injury was observed in two groups.
| [1] Machino M, Yukawa Y, Hida T, et al. The prevalence of pre- and postoperative symptoms in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy treated by cervical laminoplasty. Spine. 2012,37:E1383-E1388. [2] Kim TJ, Bae KW, Uhm WS, et al. Prevalence of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine. Joint Bone Spine. 2008;75:471-474. [3] Fujimori T, Iwasaki M, Okuda S, et al. Long-term results of cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament with an occupying ratio of 60% or more. Spine. 2014;39:58-67. [4] Lao LF, Zhong GB, Li XF, et al. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy for multi-level cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a systematic review of the literature. J Orthop Surg Res 2013;8:45. [5] Fehlings MG, Arvin B. Surgical management of cervical degenerative disease: the evidence related to indications, impact, and outcome. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11: 97-100. [6] Kadanka Z, Mares M, Bednaník J, et al. Approaches to spondylotic cervical myelopathy conservative versus surgical results in a 3-year follow-up study. Spine. 2002; 27:2205-2211. [7] Kaminsky SB, Clark CR, Traynelis VC. Operative treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and radiculopathy. A comparison of laminectomy and laminoplasty at five year average follow-up. Iowa Orthop J. 2004;24:95-105. [8] Matz PG, Anderson PA, Holly LT, et al. The natural history of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11:104-111. [9] Nurick S. The pathogenesis of the spinal cord disorder associated with cervical spondylosis. Brain.1972,95:87-100. [10] Papadopoulos CA, Katonis P, Papagelopoulos PJ,et al. Surgical decompression for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: correlation between operative outcomes and MRI of the spinal cord. Orthopedics. 2004;27:1087-1091. [11] Della Pepa GM, Roselli R, La Rocca G et al. Laminoplasty is better of laminectomy in cervical stenotic myelopathy: myth or truth? 2014;18(Suppl 1):50-54. [12] Pal D, Bayley E, Magaji S, et al. Freehand determination of the trajectory angle for cervical lateral mass screws: how accurate is it? Eur Spine J. 2011;20:972-976. [13] Hirabayashi K, Miyakawa J, Satomi K, et al. Operative results and postoperative progression of ossification among patients with ossification of cervical posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine. 1981;6:354-364. [14] Takeshita K, Murakami M, Kobayashi A,et al. Relationship between cervical curvature index (Ishihara) and cervical spine angle (C2-7). Orthop Sci. 2001;6:223-226. [15] Ryken TC, Heary RF, Matz PG, et al. Cervical laminectomy for the treatment of cervical degenerative myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11:142-149. [16] Derenda M, Kowalina I. Cervical laminoplasty–review of surgical techniques, indications, methods of efficacy evaluation, and complications. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2006;40: 422-432. [17] Hale JJ, Gruson KI, Spivak JM. Laminoplasty: a review of its role in compressive cervical myelopathy. Spine J. 2006;6: 289S-298S. [18] Matsumoto M, Chiba K, Toyama Y. Surgical treatment of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and its outcomes: posterior surgery by laminoplasty. Spine. 2012;37: E303-E308. [19] Chen Y, Guo Y, Chen D, et al. Long-term outcome of laminectomy and instrumented fusion for cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Int Orthop. 2009;33: 1075-1080. [20] Hyun SJ, Riew KD, Rhim SC. Range of motion loss after cervical laminoplasty: a prospective study with minimum 5-year follow-up data. Spine J. 2013;13:384-390. [21] Yusof MI, Hassan E, Abdullah S. Predicted cervical canal enlargement and effective cord decompression following expansive laminoplasty using cervical magnetic resonance imaging. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011;33:109-115. [22] Sodeyama T, Goto S, Mochizuki M, et al. Effect of decompression enlargement laminoplasty for posterior shifting of the spinal cord. Spine. 1999;24(15):1527-1531. [23] Houten JK, Cooper PR. Laminectomy and posterior cervical plating for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: effects on cervical alignment, spinal cord compression, and neurological outcome. Neurosurgery. 2003;52:1081-1088. [24] Anderson PA, Matz PG, Groff MW, et al. Laminectomy and fusion for the treatment of cervical degenerative myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11:150-156. [25] Hostin RA, Wu C, Perra JH, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of three revision screw strategies for failed lateral mass fixation. Spine. 2008;33:2415-2421. [26] Duan Y, Zhang H, Min SX, et al. Posterior cervical fixation following laminectomy: a stress analysis of three techniques. Eur Spine J. 2011;20:1552-1559. 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
|
| [1] | 闵友江, 姚海华, 孙 洁, 周 璇, 余 航, 孙前谱, 洪恩四. 磁共振评价“三通针法”对脊髓损伤患者脑功能的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | 蒋红英, 朱 亮, 余 曦, 黄 靖, 向小娜, 兰正燕, 何红晨. 富血小板血浆干预脊髓损伤患者压力性损伤的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [3] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [4] | 孔德胜, 何晶晶, 冯宝峰, 郭瑞云, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, 吕 飞, 张舒涵, 张晓琳, 马 隽, 崔慧先. 间充质干细胞修复大动物模型脊髓损伤疗效评价的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [5] | 刘正蓬, 王雅辉, 张义龙, 明 颖, 孙志杰, 孙 贺. 3D打印椎间融合器置入治疗脊髓型颈椎病:颈椎曲度及椎间高度恢复的半年随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 849-853. |
| [6] | 吴 刚, 陈建文, 王世隆, 段笑然, 刘海军, 董建峰. 单纯HyProCure跗骨螺钉治疗青少年柔韧性平足合并痛性副舟骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 901-905. |
| [7] | 孔令宝, 吕 欣. 胫骨后外侧平台骨折手术治疗中植入物选择与入路对支撑作用的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 942-947. |
| [8] | 马斌祥, 何万庆, 周广超, 关永林. 雷公藤内酯醇改善大鼠脊髓损伤后的运动障碍[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [9] | 李兴平, 肖东琴, 赵 桥, 陈 硕, 白亦光, 刘 康, 冯 刚, 段 可. 钛表面载铜抗菌功能膜的制备及性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [10] | 吕家兴, 白磊鹏, 杨朝昕, 苗岳松, 金 宇, 李哲宏, 孙广普, 徐 莹, 张擎柱. 膝关节骨性关节炎老年股骨转子间骨折行股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [11] | 刘 畅, 韩树峰. 股骨近端联合拉力交锁髓内钉与股骨近端防旋髓内钉、亚洲型股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗老年转子间骨折的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| [12] | 吕泽祥, 吴居泰, 蒋 健, 冯 骁, 李腾飞, 王业华. 氨甲环酸联合卡络磺钠干预全膝关节置换的失血及安全性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 386-390. |
| [13] | 孙建威, 杨新明, 张 瑛. 孟鲁司特联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤模型大鼠[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [14] | 张德刚, 刘 栋, 李 朋, 王兆林, 张 锴, 张新军. 弹性髓内钉与钢板置入治疗移位锁骨中段B型骨折的短期随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3860-3864. |
| [15] | 徐伟龙, 左 媛, 辛大奇, 贺晨阳, 赵 鹏, 史 鸣, 周博源, 刘雅婷, 赵 岩. 急性钳夹型脊髓损伤模型大鼠造模方式的选择:一项网状Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(23): 3767-3772. |
for decompressing the spinal cord by expanding the space. Although some neurological function can be recovered after surgery, a degree of irreversible neurological damage is unfortunately unavoidable in patients with CSM. Until recently, cervical posterior operative method was performed as a common surgical procedure for multi-segment CSM; however, complications, such as postsurgical instability, kyphotic deformity, and restenosis by epidural scar, affect the postoperative result[11]. After laminectomy or laminoplasty without fixation, many cervical complications occurred, such as instability and curvature change. With the rapid development of fixation in the department of orthopedics, screw rod system has been widely applied to cervical posterior approach operation in the clinic, and the complications after operation have been greatly reduced. The cervical posterior operation with lateral mass screw fixation has become an effective method that can provide ample decompression and stability of cervical vertebra. Although the lateral mass screw fixation has been widely used in clinic, the therapeutic effectiveness that two operative methods treat multi-segment cervical spondylotic myelopathy by expanding the space available for the spinal cord and providing stability remains unclear.
.jpg) Design
Design A retrospective analysis.
The experiment was conducted in the Department of Spine surgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University in China from December 2014 to February 2015.
Clinical and radiological data from patients with multi-segment CSM who underwent open-door laminoplasty with unilateral mass screw fixation and laminectomy with bilateral mass screw fixation between January 2010 and December 2013 were reviewed.
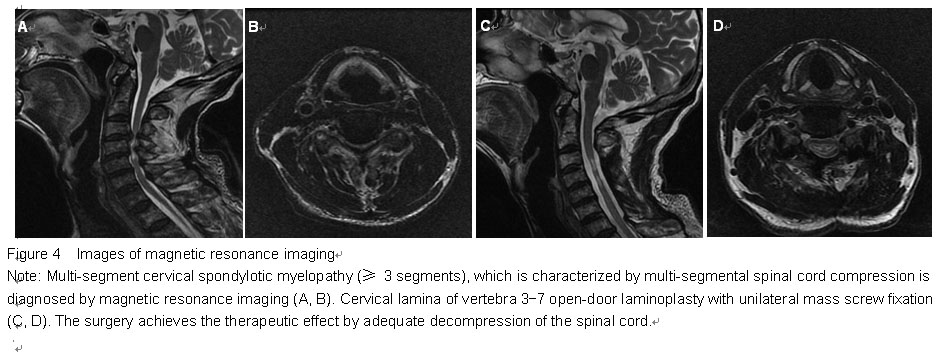
(1) A clear diagnosis made by history, physical examination, plain radiographs, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); (2) multi-segment CSM (≥ 3 segments); (3) a minimum of postoperative 12-month follow-up; (4) complete pre- and post-operative imaging and clinical data records.
(1) Patients lost to follow-up; (2) any history of rheumatoid arthritis, cerebral palsy, or tumors; (3) previous cervical surgery; (4) destructive spondyloarthritis caused by hemodialysis; (5) injuries; (6) severe kyphotic deformity and spinal fusion with instrumentation; (7) thoracic spondylotic myelopathy; and (8) lumbar spinal canal stenosis.
Of the original 216 patients, 117 with multi-segment CSM were eligible for participation. Of these, 117 patients who were observed for more than 12 months after surgery were enrolled in this study (follow-up rate, 91.1%). The 117 patients were divided into two groups according to procedure: the open-door laminoplasty with unilateral mass screw fixation (laminoplasty group) and the laminectomy with bilateral mass screw fixation (laminectomy group). The laminoplasty group comprised 45 males and 20 females with a mean age of 62.2 years (range, 41-78 years) and average disease duration of 26.32 months (range, 10-49 months). The laminectomy group comprised 32 males and 20 females with a mean age of 62.2 years (range, 39-84 years) and average disease duration of 28.16 months (range, 8-56 months). All patients presented with symptoms of myelopathy. Each patient whose clinical findings were consistent with the diagnosis of progressive cervical myelopathy was failed to respond to nonsurgical treatment. All patients had cord compression at three or more segments confirmed by radiography. There was no significant difference in gender, age, disease duration, type, and affected segments between the two groups (P > 0.05; Table 1).
.jpg)
Spinal implant
All patients underwent the internal fixation via posterior cervical pathway and fusion in Vertex system that was produced by American Medtronic Sofamor Danek Company.
Surgical procedure
The patients were placed in the prone position with the head holder under general anesthesia. A standard posterior midline exposure was performed for both procedures.
All patients were required to stay in bed for the first week after surgery, and thereafter walking was allowed with a cervical collar for 8 weeks.
The severity of myelopathy before and after surgery was evaluated according to a scoring system proposed by the Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) for CSM (JOA score). A perfect JOA score for CSM was 17 points. The improvements of neurological function in JOA scores were expressed as recovery rate. The recovery rate was determined as following formula originally suggested by Hirabayashi[13]: recovery rate (%)= (postoperative JOA score-preoperative JOA score)/[17 (normal functional score)-preoperative JOA score] × 100. The recovery rate for each patient was classified into 4 grades: those greater than 75% were categorized as excellent for activities of daily living, those that were 50%-74% were categorized as good, those that were 25%-49% were categorized as fair, and those that were less than 24% were categorized as poor.
Preoperative and final follow-up cervical alignments were measured in the profile of neutral plain radiographs by cervical curvature index as described by Ishihara[14] (Figure 1). Line segment A is drawn between the postero-inferior edge of the C2 and C7 spinal bodies. The four lines, a1-a4, are drawn perpendicular to line A from each postero-inferior edge of the C3, C4, C5, and C6 vertebral bodies. The cervical curvature index (Ishihara) is the percentage of the sum of the four segments divided by line segment A (Figure 1). Cervical range of motion was measured using the Cobb method for C2-C7 in flexion and extension on radiographs (Figure 2). These measurements were performed over three times by one of the authors and an independent experienced musculoskeletal radiologist to reduce the intra- and inter observer bias.
There were (1) JOA for cervical spondylotic myelopathy (JOA score); (2) recovery rate; (3) cervical curvature index as described by Ishihara; (4) cervical range of motion.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 18.0 software. An independent samples t-test was used to assess statistical significance of changes between last follow-up and preoperative parameters in two groups. A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
.jpg)
.jpg)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
widen the spinal canal without removing the dorsal elements of the cervical spine for multi-segmental CSM[16-17].
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||