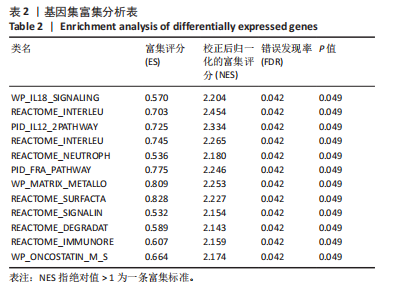
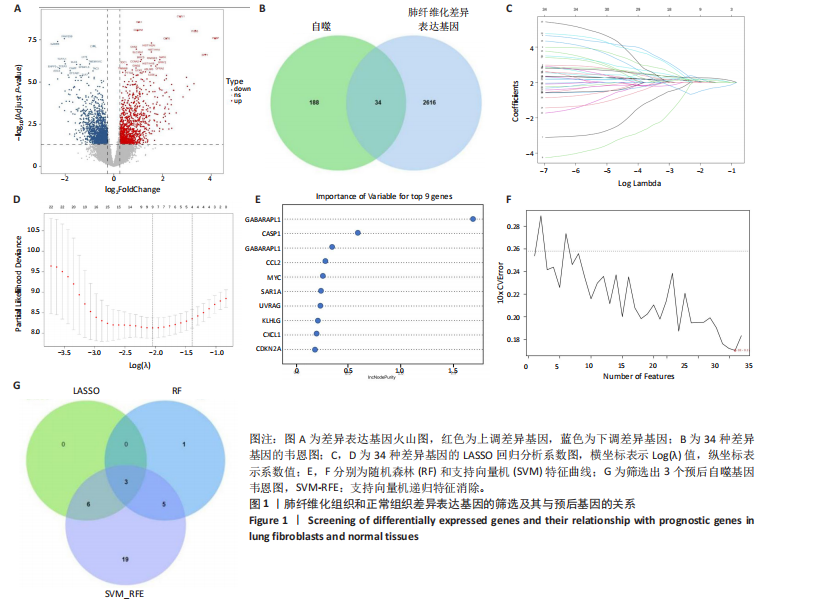
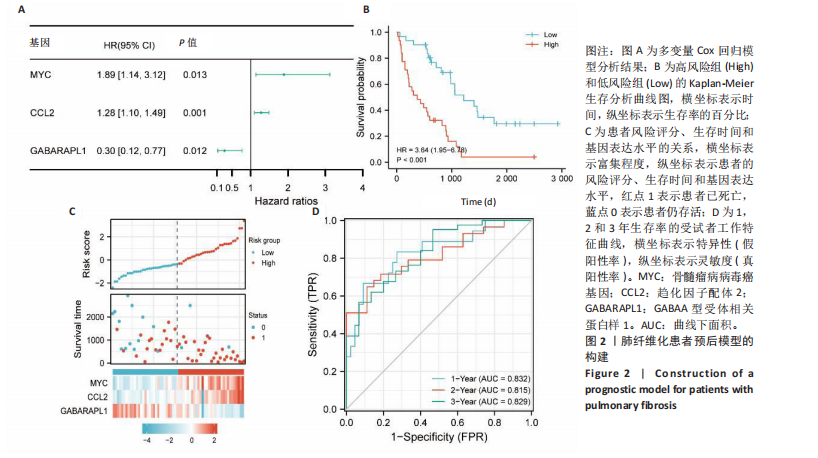
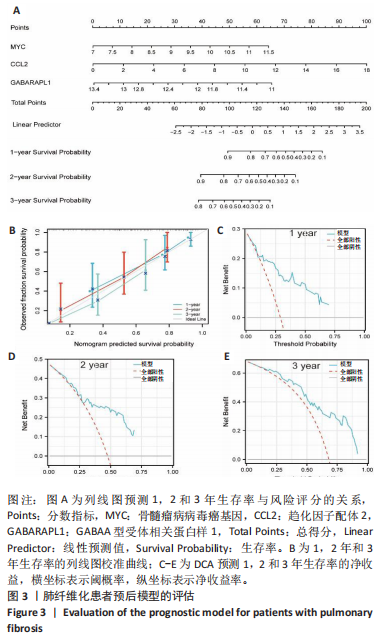
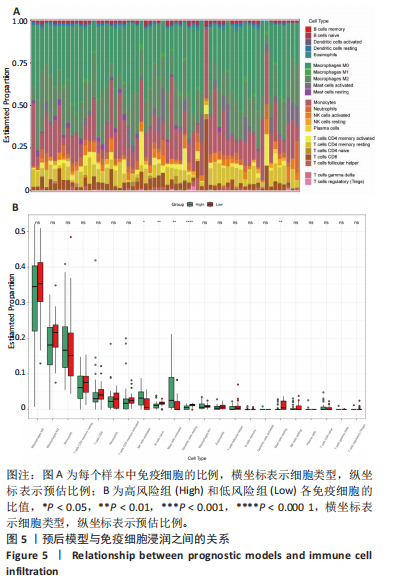
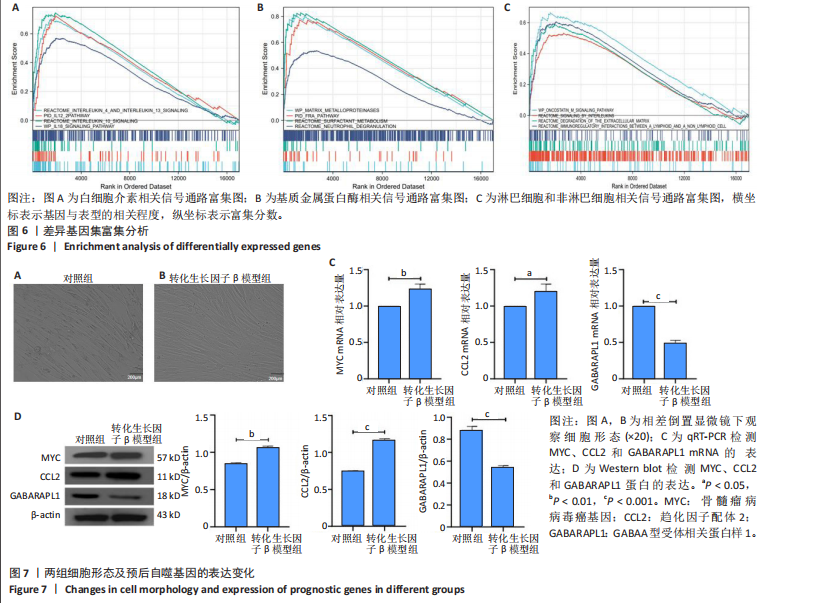
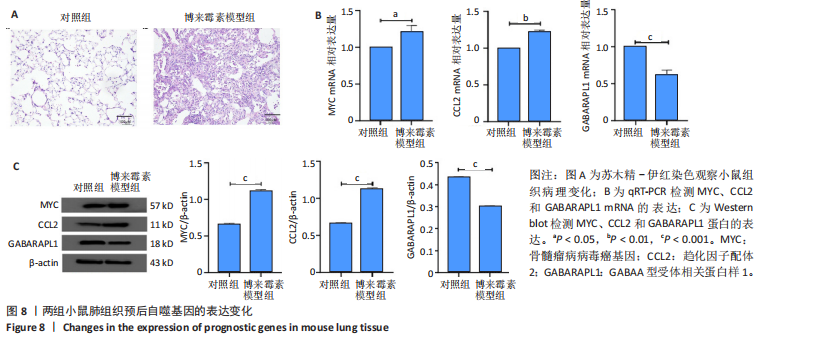
[1] CHANDA D, OTOUPALOVA E, SMITH SR, et al. Developmental pathways in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. Mol Aspects Med. 2019;65:56-69.
[2] LI X, WANG Y, LIANG J, et al. Bergenin attenuates bleomycin‐induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice via inhibiting TGF-β1signaling pathway. Phytother Res. 2021;35(10):5808-5822.
[3] GAO Q, CHANG X, YANG M, et al. LncRNA MEG3 restrained pulmonary fibrosis induced by NiO NPs via regulating hedgehog signaling pathway-mediated autophagy.Environ Toxicol. 2022;37(1):79-91.
[4] YAO Y, JIANG P, CHAO B, et al. GIMAP6 regulates autophagy, immune competence, and inflammation in mice and humans. J Exp Med. 2022; 219(6):e20201405.
[5] HEUKELS P, MOOR CC, VON DER THÜSEN JH, et al. Inflammation and immunity in IPF pathogenesis and treatment. Respir Med. 2019;147:79-91.
[6] ZHENG D, GUO J, LIANG Z, et al. Supramolecular Nanofibers Ameliorate Bleomycin‐Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Restoring Autophagy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(28):e2401327.
[7] WANG B, WANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. ROS-induced lipid peroxidation modulates cell death outcome: mechanisms behind apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Arch Toxicol. 2023;97(6):1439-1451.
[8] LEE C, KWAK S H, HAN J, et al. Repositioning of ezetimibe for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2024;63(5):2300580.
[9] DUAN JX, GUAN XX, YANG HH, et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide attenuates bleomycin-induced murine pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition: restoring autophagy in alveolar epithelial cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;101(Pt B):108211.
[10] TANG Q, XING C, LI M, et al. Pirfenidone ameliorates pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in a rat silicosis model by inhibiting macrophage polarization and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;244:114066.
[11] ZHOU Z, JIANG X, LIU D, et al. Autophagy is involved in influenza A virus replication. Autophagy. 2009;5(3):321-328.
[12] REED M, MORRIS SH, OWCZARCZYK AB, et al. Deficiency of autophagy protein Map1-LC3b mediates IL-17-dependent lung pathology during respiratory viral infection via ER stress-associated IL-1. Mucosal Immunol. 2015;8(5):1118-1130.
[13] HE Y, THUMMURI D, ZHENG G, et al. Cellular senescence and radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Transl Res. 2019;209:14-21.
[14] LI S, LI C, PANG X, et al. Metformin attenuates silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by activating autophagy via the AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:719589.
[15] LI X, HUANG K, LIU X, et al. Ellagic acid attenuates BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting Wnt signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:639574.
[16] TZOUVELEKIS A, GOMATOU G, BOUROS E, et al. Common pathogenic mechanisms between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. Chest. 2019;156(2):383-391.
[17] MU E, WANG J, CHEN L, et al. Ketogenic diet induces autophagy to alleviate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in murine models. Exp Lung Res. 2021;47(1):26-36.
[18] WYNN TA. Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J Exp Med. 2011;208(7):1339-1350.
[19] FU W, FANG X, WU L, et al. Neogambogic acid relieves myocardial injury induced by sepsis via p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2022;26(6):511-518.
[20] ZHAO J, WU Q, YANG T, et al. Gaseous signal molecule SO2 regulates autophagy through PI3K/AKT pathway inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improves myocardial fibrosis in rats with type II diabetes. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2022;26(6):541-556.
[21] 王晓旭. 羟基红花黄色素A通过自噬溶酶体途径缓解特发性肺纤维化机制研究[D].保定:河北大学,2024.
[22] 菅若男,甄华,郭晶晶.基于PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路激活自噬通路研究荜茇改善小鼠肺纤维化的机制[J].临床肺科杂志,2024, 29(5):675-682.
[23] 李鹏,牛璐,赵国静,等.基于自噬探究补肺活血胶囊对博莱霉素诱发小鼠肺纤维化的抑制作用[J].中成药杂志,2024,46(4):1337-1342.
[24] MENG Y, PAN M, ZHENG B, et al. Autophagy attenuates angiotensin II-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting redox imbalance-mediated NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome activation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019;30(4):520-541.
[25] SHANG C, HASSAN B, HAQUE M, et al. Crizotinib resistance mediated by autophagy is higher in the stem-like cell subset in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma, and this effect is MYC-dependent. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(2):181.
[26] LIU S, YANG Q, DONG B, et al. Gypenosides Attenuate Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting the AKT/mTOR/c-Myc Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12:806312.
[27] 阚泉,张岩,王海涛,等.抗氧化剂超氧化物歧化酶对大鼠肺巨噬细胞二氧化硅条件上清介导的肺成纤维细胞增殖及c-myc表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(14):2202-2206.
[28] JIN Y, QIU J, LU X, et al. C-MYC inhibited ferroptosis and promoted immune evasion in ovarian cancer cells through NCOA4 mediated ferritin autophagy. Cells. 2022;11(24):4127.
[29] ENTRIALGO-CADIERNO R, CUETO-UREÑA C, WELCH C, et al. The phospholipid transporter PITPNC1 links KRAS to MYC to prevent autophagy in lung and pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 2023;22(1):86.
[30] LIN HJ, LIU HH, LIN CD, et al. Cytolethal distending toxin enhances radiosensitivity in prostate cancer cells by regulating autophagy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017;7:223.
[31] KANMANI P, KIM H. Probiotics counteract the expression of hepatic profibrotic genes via the attenuation of TGF-β/SMAD signaling and autophagy in hepatic stellate cells. PLoS One. 2022;17(1):e0262767.
[32] DENG X, MERCER PF, SCOTTON CJ, et al. Thrombin induces fibroblast CCL2/JE production and release via coupling of PAR1 to Gαq and cooperation between ERK1/2 and Rho kinase signaling pathways. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19(6):2520-2533.
[33] XU H, WANG J, AL‐NUSAIF M, et al. CCL2 promotes metastasis and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non‐small cell lung cancer via PI3K/Akt/mTOR and autophagy pathways. Cell Prolif. 2024;57(3): e13560.
[34] GAO Y, CHEN S, JIAO S, et al. ATG5-regulated CCL2/MCP-1 production in myeloid cells selectively modulates anti-malarial CD4+ Th1 responses. Autophagy. 2024;20(6):1398-1417.
[35] NIINIKOSKI I, KOUKI S, KOHO N, et al. Evaluation of VEGF-A and CCL2 in dogs with brachycephalic obstructive airway syndrome or canine idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and in normocephalic dogs. Res Vet Sci. 2022;152:557-563.
[36] LU G, RAO D, ZHOU M, et al. Autophagic Network Analysis of the Dual Effect of Sevoflurane on Neurons Associated with GABARAPL1 and 2. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:1587214.
[37] KEULERS TG, LIBREGTS SF, BEAUMONT JEJ, et al. Secretion of proangiogenic extracellular vesicles during hypoxia is dependent on the autophagy-related protein GABARAPL1.J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(14):e12166.
[38] MENG J, XU L, MA B, et al. GABARAPL1 is essential for ACR-induced autophagic cell death of mouse Leydig cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025;289:117426.
|