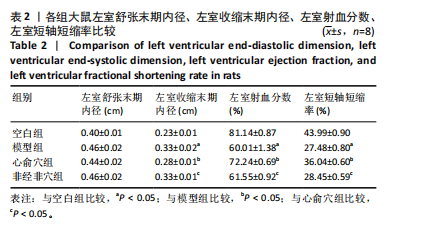
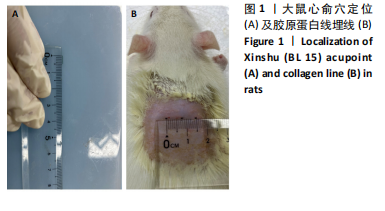
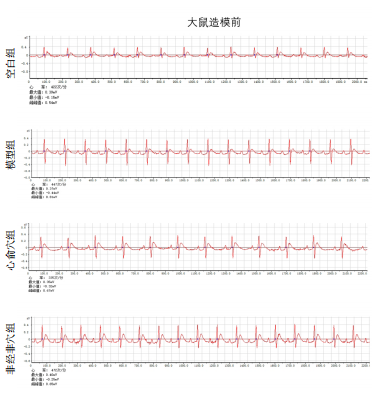
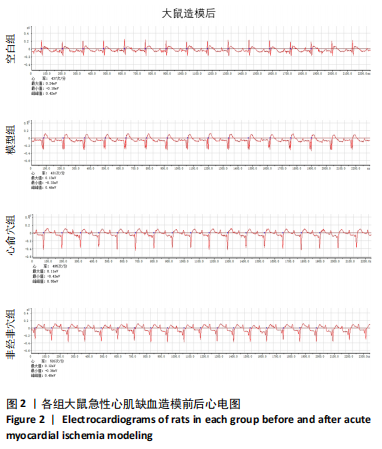
[1] Reyes-Retana JA, Duque-Ossa LC. Acute Myocardial Infarction Biosensor: A Review From Bottom Up. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2021;46(3): 100739.
[2] 国家心血管病中心.中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022[M].北京:科学出版社,2023.
[3] COSTA MA, PAIVA AE, AND REOTTI JP, et al. Peri-cytes constrict blood vessels after myocardial ischemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;116:1-4.
[4] 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022》概要[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2023,31(7):485-508.
[5] JORTVEIT J, PRIPP AH, LANGORGEN J, et al. Inci-dence, risk factors and outcome of young patients with myo-cardial infarction. Heart. 2020;106(18):1420-1426.
[6] 陈焱.中老年雌性大鼠心肌缺血再灌注后认知障碍与海马区自噬的相关性研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2023.
[7] ZHAO L, LI D, ZHENG H, et al. Acupuncture as Adjunctive Therapy for Chronic Stable Angina: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(10):1388-1397.
[8] 叶婷婷,梁欣,李丽红,等.羊肠线与聚乙丙交酯线埋入大鼠“足三里”穴区局部时效性刺激效应的机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(29):4605-4611.
[9] 袁静雪,刘金红,倪金霞,等.不同频次穴位埋线治疗脾虚湿阻型超重/肥胖:随机对照试验[J].中国针灸,2023,43(11):1229-1234.
[10] 曹靖先.穴位贴敷联合中药干预肾虚血瘀型EMs的IVF结局及卵泡液代谢组学研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2024.
[11] ZHU Y, WANG J, YAO L, et al. Electroacupuncture at BL15 attenuates chronic fatigue syndrome by downregulating iNOS/NO signaling in C57BL/6 mice. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2023;306(12):3073-3084.
[12] 邓雅方.电针对急性心肌缺血大鼠心俞穴区伤害性感受器P2X3/TRPV1/SP表达的影响[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2023.
[13] LI X, ZHOU J, HUANG K. Inhibition of the IncRNA Mirtl Attenuates Acute Myocardial Infarction by Suppressing NF-κB Activation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(3):1153-1164.
[14] JIN JL, LV RG, GUO J, et al. Improvement of Left Ventricular Remodelling by Inhibition of NF-κB in a Rat Model of Myocardial Infarction. Heart Lung Circ. 2016;25(10):1007-1012.
[15] 杨慧惠,刘慧敏,张子琪,等.从NF-κB信号通路探讨中药单体对糖尿病周围神经病变的保护作用[J].实用中医内科杂志,2024, 38(8):79-84+153.
[16] CHEN Y, XU Y, RAMAKRISHNA S. Electromagnetic-responsive targeted delivery scaffold technology has better potential to repair injured peripheral nerves: a narrative review. Adv Technol Neurosci. 2024;1(1):51-71.
[17] HAMID T, GUO SZ, KINGERY JR, et al. Cardiomyocyte NF-κB p65 promotes adverse remodelling, apoptosis, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;89(1):129-138.
[18] KIM SK, KIM YM, YEUM CE, et al. Rifampicin Inhibits the LPS-induced Expression of Toll-like Receptor 2 via the Suppression of NF-kappaB DNA-binding Activity in RAW 264.7 Cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;13(6):475-482.
[19] 卢圣锋,袁璟,丁亚娟,等.电针对大鼠缺血心肌组织中炎性物质和交感神经活性物质表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2019,44(5):313-318.
[20] KRISHNAMURTHY P, RAJASINGH J, LAMBERS E, et al. IL-10 inhibits inflammation and attenuates left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction via activation of STAT3 and suppression of HuR. Circ Res. 2009;104(2):e9-e18.
[21] 谭亚芳,潘诗婷,祁建勇,等.丹蒌片改善大鼠急性心肌缺血的作用研究[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2022,20(15):2743-2746.
[22] 卞镝,田辉,隋月皎,等.电针“内关”对缺血性心肌损伤大鼠钠离子通道相关蛋白的影响[J].中国针灸,2016,36(1):64-68.
[23] 李忠仁.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2013:327.
[24] 吴琼.按压心俞调控AMPK通路改善心肌缺血大鼠能量代谢的作用及机制研究[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2022.
[25] ZHU Y, WANG J, YAO L, et al. Electroacupuncture at BL15 attenuates chronic fatigue syndrome by downregulating iNOS/NO signaling in C57BL/6 mice. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2023;306(12):3073-3084.
[26] WANG J, ZHANG Q, YAO L, et al. Modulating activity of PVN neurons prevents atrial fibrillation induced circulation dysfunction by electroacupuncture at BL15. Chin Med. 2023;18(1):135.
[27] ZHAO TT, LIU JJ, ZHU J, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4-Mediated Stem Cell Mobilization Involved in Cardioprotective Effects of Electroacupuncture on Mouse with Myocardial Infarction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022; 2022:4455183.
[28] KAZEMI AH, ADEL-MEHRABAN MS, JAMALI DASTJERDI M, et al. A comprehensive practical review of acupoint embedding as a semi-permanent acupuncture: A mini review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024; 103(23):e38314.
[29] ZHANG H, GUO M, WANG T, et al. Enhancing postoperative analgesia in open orthopedic surgery through acupoint catgut embedding: A single-center randomized clinical trial. Chin Med J (Engl). 2024;137(23):2883-2885.
[30] 刘芳,董桦,李晓雯,等.中医非药物疗法治疗糖尿病前期的应用进展[J].内蒙古中医药,2024,43(4):153-155.
[31] 米婧,惠建荣,李彬锋,等.穴位埋线治疗疲劳综合征的机制研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2022,31(7):1019-1022.
[32] 邰萱,黄小楼,韦雪兰,等.心俞穴位埋线联合曲美他嗪对大鼠心肌梗死后能量代谢影响的研究[J].海南医学院学报,2024,30(19): 1451-1458.
[33] 韩芳,李焕芹,曹克刚,等.中医药临床研究中安慰剂选择与评价[J].北京中医药,2020,39(8):846-850.
[34] 杨旭光,李瑛,田小平, 等.国内外针灸研究中假穴选取方法评述[J].中医杂志,2009,50(8):748-750.
[35] FEI YT, CAO HJ, XIA RY, et al. Methodological challenges in design and conduct of randomised controlled trials in acupuncture. BMJ. 2022;376:e064345.
[36] 朱柯璇,李旭豪,范李想,等.安慰针刺在临床研究中的应用与设计[J/OL].上海针灸杂志,1-7[2024-11-18]. doi: 10.13460/j.issn.1005-0957.2024.13.4036
[37] 安琪,赵佳,刘佩东,等.电针联合丹参多酚酸盐对急性心肌梗死大鼠心功能及药物组织分布的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2022,42(3):334-340.
[38] 董亚琴,万隆,黄倩茹,等.TRPVs在预电针心俞穴调整急性心肌缺血大鼠心功能中的作用[J].时珍国医国药,2022,33(3):742-744.
[39] 王坤,张文强,李慧,等.丹参多酚酸盐通过SIRT3/β-catenin-PPARγ信号通路对心肌梗死大鼠的作用及机制研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2023,23(7):1225-1230.
[40] 孙千惠,古春凌,杨守亲,等.针刺治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤介入时机的研究探析[J].针灸临床杂志,2024,40(1):93-96.
[41] 李瑞瑞,张露文,张渺,等.皮质前额叶和海马PPAR-α通路参与N-棕榈酰乙醇胺抗大鼠抑郁样行为[J].天津医药,2022,50(3):248-253.
[42] YUAN L, DAI X, FU H, et al. Vaspin protects rats against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI) through the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;835:132-139.
[43] 蔡荣林,胡玲,余情,等.电针“内关”“心俞”对急性心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠血清白介素-1β、白介素-10含量及心肌组织NF-κB p65蛋白表达的影响[J].云南中医学院学报,2014,37(2):6-9. |