[1] BILGIC SN, DOMANIKU A, TOLEDO B, et al. EDA2R-NIK signalling promotes muscle atrophy linked to cancer cachexia. Nature. 2023;617(7962):827-834.
[2] YIN L, LI N, JIA W, et al. Skeletal muscle atrophy: From mechanisms to treatments. Pharmacol Res. 2021;172:105807.
[3] ANDRIEUX P, CHEVILLARD C, CUNHA-NETO E, et al. Mitochondria as a Cellular Hub in Infection and Inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11338.
[4] BELLANTI F, LO BUGLIO A, VENDEMIALE G. Muscle Delivery of Mitochondria-Targeted Drugs for the Treatment of Sarcopenia: Rationale and Perspectives. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(12):2588.
[5] 李伟,尹洪涛,孙永晨,等.线粒体移植治疗肌少症的潜力[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(13):2842-2848.
[6] LEDUC-GAUDET JP, HUSSAIN SNA, BARREIRO E, et al. Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitophagy in Skeletal Muscle Health and Aging. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8179.
[7] SULKSHANE P, RAM J, THAKUR A, et al. Ubiquitination and receptor-mediated mitophagy converge to eliminate oxidation-damaged mitochondria during hypoxia. Redox Biol. 2021;45:102047.
[8] IMBERECHTS D, KINNART I, WAUTERS F, et al. DJ-1 is an essential downstream mediator in PINK1/parkin-dependent mitophagy. Brain. 2022;145(12):4368-4384.
[9] WANG H, LUO W, CHEN H, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy: Molecular structure, orchestrating mechanism and related disorders. Mitochondrion. 2024;75:101847.
[10] CHRISTIAN CJ, BENIAN GM. Animal models of sarcopenia. Aging Cell. 2020;19(10): e13223.
[11] PIPER MDW, PARTRIDGE L. Drosophila as a model for ageing. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864(9 Pt A):2707-2717.
[12] DEMONTIS F, PICCIRILLO R, GOLDBERG AL, et al. Mechanisms of skeletal muscle aging: insights from Drosophila and mammalian models. Dis Model Mech. 2013;6(6):1339-1352.
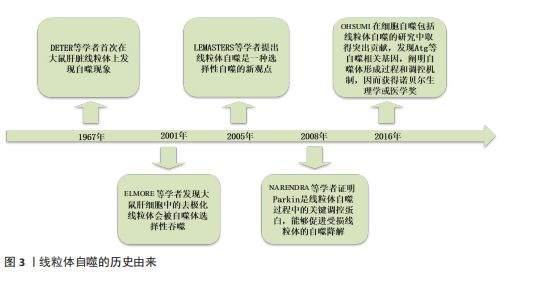
[13] DETER RL, DE DUVE C. Influence of glucagon, an inducer of cellular autophagy, on some physical properties of rat liver lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1967;33(2):437-449.
[14] ELMORE SP, QIAN T, GRISSOM SF, et al. The mitochondrial permeability transition initiates autophagy in rat hepatocytes. FASEB J. 2001;15(12):2286-2287.
[15] LEMASTERS JJ. Selective mitophagy, or mitophagy, as a targeted defense against oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. Rejuvenation Res. 2005;8(1):3-5.
[16] NARENDRA D, TANAKA A, SUEN DF, et al. Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol. 2008;183(5):795-803.
[17] OHSUMI Y. Historical landmarks of autophagy research. Cell Res. 2014;24(1):9-23.
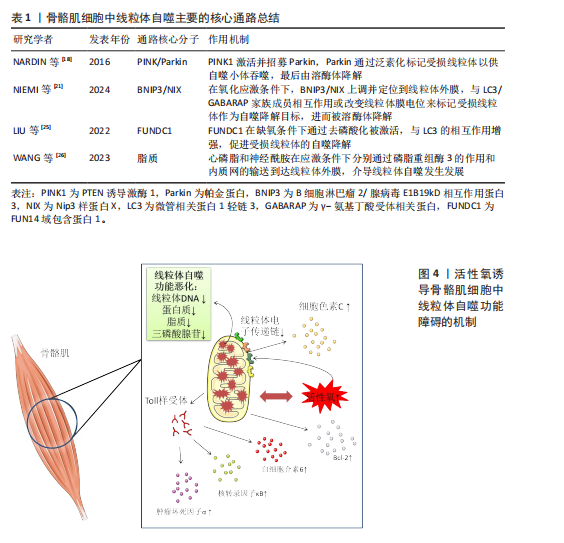
[18] NARDIN A, SCHREPFER E, ZIVIANI E. Counteracting PINK/Parkin Deficiency in the Activation of Mitophagy: A Potential Therapeutic Intervention for Parkinson’s Disease. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14(3):250-259.
[19] LI A, GAO M, LIU B, et al. mitophagy: molecular mechanisms and implications for cardiovascular disease. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(5):444.
[20] LI J, YANG D, LI Z, et al. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;84:101817.
[21] NIEMI NM, FRIEDMAN JR. Coordinating BNIP3/NIX-mediated mitophagy in space and time. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024;52(5): 1969-1979.
[22] ADRIAENSSENS E, SCHAAR S, COOK ASI, et al. Reconstitution of BNIP3/NIX-mediated autophagy reveals two pathways and hierarchical flexibility of the initiation machinery. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024:2024.08.28.609967.
[23] SUN Y, CAO Y, WAN H, et al. A mitophagy sensor PPTC7 controls BNIP3 and NIX degradation to regulate mitochondrial mass. Mol Cell. 2024;84(2):327-344.e9.
[24] CHEN M, CHEN Z, WANG Y, et al. Mitophagy receptor FUNDC1 regulates mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy. Autophagy. 2016;12(4):689-702.
[25] LIU H, ZANG C, YUAN F, et al. The role of FUNDC1 in mitophagy, mitochondrial dynamics and human diseases. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;197:114891.
[26] WANG S, LONG H, HOU L, et al. The mitophagy pathway and its implications in human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):304.
[27] WANG R, WANG G. Autophagy in Mitochondrial Quality Control. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1206:421-434.
[28] LU Y, LI Z, ZHANG S, et al. Cellular mitophagy: Mechanism, roles in diseases and small molecule pharmacological regulation. Theranostics. 2023;13(2):736-766.
[29] SU L, ZHANG J, GOMEZ H, et al. Mitochondria ROS and mitophagy in acute kidney injury. Autophagy. 2023;19(2):401-414.
[30] NOLFI-DONEGAN D, BRAGANZA A, SHIVA S. Mitochondrial electron transport chain: Oxidative phosphorylation, oxidant production, and methods of measurement. Redox Biol. 2020;37:101674.
[31] WANDEROY S, HEES JT, KLESSE R, et al. Kill one or kill the many: interplay between mitophagy and apoptosis. Biol Chem. 2020;402(1):73-88.
[32] SLITER DA, MARTINEZ J, HAO L, et al. Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation. Nature. 2018;561(7722): 258-262.
[33] NYBERG KG, CARTHEW RW. CRISPR-/Cas9-Mediated Precise and Efficient Genome Editing in Drosophila. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2540:135-156.
[34] ZHANG S, POINTER B, KELLEHER ES. Rapid evolution of piRNA-mediated silencing of an invading transposable element was driven by abundant de novo mutations. Genome Res. 2020;30(4):566-575.
[35] YAP ZY, PARK YH, WORTMANN SB, et al. Functional interpretation of ATAD3A variants in neuro-mitochondrial phenotypes. Genome Med. 2021;13(1):55.
[36] KARUNENDIRAN A, NGUYEN CT, BARZDA V, et al. Disruption of Drosophila larval muscle structure and function by UNC45 knockdown. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2021; 22(1):38.
[37] WU Z, WU A, DONG J, et al. Grape skin extract improves muscle function and extends lifespan of a Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease through activation of mitophagy. Exp Gerontol. 2018;113:10-17.
[38] BHATTACHARYA MRC. A Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Model in Drosophila melanogaster. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2143:301-310.
[39] CHECHENOVA M, STRATTON H, KIANI K, et al. Quantitative model of aging-related muscle degeneration: a Drosophila study. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023:2023.02.19.529145.
[40] KOMLÓS M, SZINYÁKOVICS J, FALCSIK G, et al. The Small-Molecule Enhancers of Autophagy AUTEN-67 and -99 Delay Ageing in Drosophila Striated Muscle Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):8100.
[41] REN Y, WANG K, WU Y, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide mitigates high-fat-diet-induced skeletal muscle atrophy by promoting AMPK/PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025;301:140488.
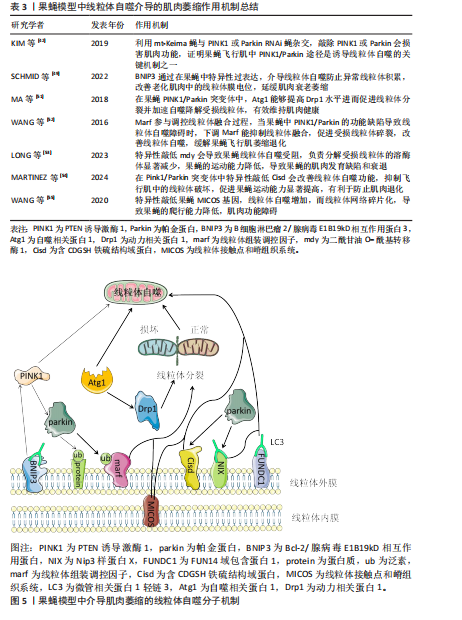
[42] KIM YY, UM JH, YOON JH, et al. Assessment of mitophagy in mt-Keima Drosophila revealed an essential role of the PINK1-Parkin pathway in mitophagy induction in vivo. FASEB J. 2019;33(9):9742-9751.
[43] BERNARDO G, PRADO MA, DASHTMIAN AR, et al. USP14 inhibition enhances Parkin-independent mitophagy in iNeurons. Pharmacol Res. 2024;210:107484.
[44] PARK J, LEE SB, LEE S, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Drosophila PINK1 mutants is complemented by parkin. Nature. 2006;441(7097):1157-1161.
[45] GREENE JC, WHITWORTH AJ, KUO I, et al. Mitochondrial pathology and apoptotic muscle degeneration in Drosophila parkin mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(7):4078-4083.
[46] CORNELISSEN T, VILAIN S, VINTS K, et al. Deficiency of parkin and PINK1 impairs age-dependent mitophagy in Drosophila. Elife. 2018;7:e35878.
[47] VOIGT A, BERLEMANN LA, WINKLHOFER KF. The mitochondrial kinase PINK1: functions beyond mitophagy. J Neurochem. 2016;139 Suppl 1:232-239.
[48] SUNG H, TANDARICH LC, NGUYEN K, et al. Compartmentalized Regulation of Parkin-Mediated Mitochondrial Quality Control in the Drosophila Nervous System In Vivo. J Neurosci. 2016;36(28):7375-7391.
[49] SCHMID ET, PYO JH, WALKER DW. Neuronal induction of BNIP3-mediated mitophagy slows systemic aging in Drosophila. Nat Aging. 2022;2(6):494-507.
[50] ZHANG T, XUE L, LI L, et al. BNIP3 Protein Suppresses PINK1 Kinase Proteolytic Cleavage to Promote Mitophagy. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(41):21616-21629.
[51] MA P, YUN J, DENG H, et al. Atg1-mediated autophagy suppresses tissue degeneration in pink1/parkin mutants by promoting mitochondrial fission in Drosophila. Mol Biol Cell. 2018;29(26):3082-3092.
[52] WANG ZH, CLARK C, GEISBRECHT ER. Drosophila clueless is involved in Parkin-dependent mitophagy by promoting VCP-mediated Marf degradation. Hum Mol Genet. 2016;25(10):1946-1964.
[53] LONG M, MCWILLIAMS TG. Lipid droplets promote efficient mitophagy. Autophagy. 2023;19(2):724-725.
[54] MARTINEZ A, SANCHEZ-MARTINEZ A, PICKERING JT, et al. Mitochondrial CISD1/Cisd accumulation blocks mitophagy and genetic or pharmacological inhibition rescues neurodegenerative phenotypes in Pink1/parkin models. Mol Neurodegener. 2024;19(1):12.
[55] WANG LJ, HSU T, LIN HL, et al. Drosophila MICOS knockdown impairs mitochondrial structure and function and promotes mitophagy in muscle tissue. Biol Open. 2020;9(12):bio054262.
[56] DAMSCHRODER D, RICHARDSON K, COBB T, et al. The effects of genetic background on exercise performance in Drosophila. Fly (Austin). 2020;14(1-4):80-92.
[57] MUNNIK C, XABA MP, MALINDISA ST, et al. Drosophila melanogaster: A platform for anticancer drug discovery and personalized therapies. Front Genet. 2022;13:949241.
[58] PANDEY UB, NICHOLS CD. Human disease models in Drosophila melanogaster and the role of the fly in therapeutic drug discovery. Pharmacol Rev. 2011;63(2):411-436.
[59] DENG J, GUAN XX, ZHU YB, et al. Reducing the Excess Activin Signaling Rescues Muscle Degeneration in Myotonic atrophy Type 2 Drosophila Model. J Pers Med. 2022;12(3):385.
[60] ZHANG Z, WANG Y, ZHAO J, et al. High-Throughput Small Molecule Drug Screening For Age-Related Sleep Disorders Using Drosophila melanogaster. J Vis Exp. 2023; (200). doi: 10.3791/65787.
[61] GUMENI S, PAPANAGNOU ED, MANOLA MS, et al. Nrf2 activation induces mitophagy and reverses Parkin/Pink1 knock down-mediated neuronal and muscle degeneration phenotypes. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(7):671.
[62] GRAHAM P, PICK L. Drosophila as a Model for Diabetes and Diseases of Insulin Resistance. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017;121: 397-419.
[63] 杨天爱,夏志,张舵,等.运动经线粒体自噬途径改善衰老性骨骼肌萎缩研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2024,43(10): 835-843.
[64] MAYNERIS-PERXACHS J, CASTELLS-NOBAU A, ARNORIAGA-RODRÍGUEZ M, et al. Microbiota alterations in proline metabolism impact depression. Cell Metab. 2022;34(5):681-701.e10.
[65] MATHER LM, CHOLAK ME, MORFOOT CM, et al. Inducible Reporter Lines for Tissue-specific Monitoring of Drosophila Circadian Clock Transcriptional Activity. J Biol Rhythms. 2023;38(1):44-63.
[66] LI L, WAZIR J, HUANG Z, et al. A comprehensive review of animal models for cancer cachexia: Implications for translational research. Genes Dis. 2023; 11(6):101080.
[67] XUE J, LI G, JI X, et al. Drosophila ZIP13 over-expression or transferrin1 RNAi influences the muscle degeneration of Pink1 RNAi by elevating iron levels in mitochondria. J Neurochem. 2022;160(5):540-555.
[68] SU Y, WANG T, WU N, et al. Alpha-ketoglutarate extends Drosophila lifespan by inhibiting mTOR and activating AMPK. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(12):4183-4197.
|