中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (16): 4180-4192.doi: 10.12307/2026.716
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
中药有效成分治疗类风湿关节炎:基于核因子κB信号通路的机制
付 晓1,2,李纪高1,闫小楠1,2,宋 哲1,郭岳峻1,2,李韩冰1,2,周 全1
- 1河南中医药大学第一附属医院风湿病科,河南省郑州市 450003;2河南中医药大学第一临床医学院,河南省郑州市 450046
-
收稿日期:2025-07-29接受日期:2025-08-30出版日期:2026-06-08发布日期:2025-11-28 -
通讯作者:周全,博士,副教授,硕士生导师,河南中医药大学第一附属医院风湿病科,河南省郑州市 450003 -
作者简介:付晓,女,2001年生,河南省长垣市人,汉族,2026年河南中医药大学毕业,硕士,主要从事中医药防治风湿免疫疾病的研究。 -
基金资助:河南中医药重点(培育)学科-中西医结合临床(CZ0404-03);河南省中医药科学研究专项(2023ZXZX1071),项目负责人:李纪高;河南省中医药科学研究专项(2024ZY3032),项目负责人:宋哲
Traditional Chinese medicine effective ingredients for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: mechanism based on nuclear factor kappaB signaling pathway
Fu Xiao1, 2, Li Jigao1, Yan Xiaonan1, 2, Song Zhe1, Guo Yuejun1, 2, Li Hanbing1, 2, Zhou Quan1
- 1Department of Rheumatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China; 2The First Clinical School of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2025-07-29Accepted:2025-08-30Online:2026-06-08Published:2025-11-28 -
Contact:Zhou Quan, PhD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Rheumatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China -
About author:Fu Xiao, MS, Department of Rheumatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China; The First Clinical School of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Provincial Key (Cultivation) Discipline of Traditional Chinese Medicine - Clinical Integration of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, No. CZ0404-03; Henan Provincial Special Project on Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2023ZXZX1071 (to LJG); Henan Provincial Special Project on Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2024ZY3032 (to SZ)
摘要:
文题释义:
核因子κB:是细胞内关键的核因子,于1986年被首次发现参与到B细胞的发育和活化,影响细胞的增殖、迁移和凋亡等生命历程,并参与到炎症、癌症及自身免疫性疾病的发生发展中。
类风湿关节炎:是一种慢性自身免疫性疾病,主要以全身性炎症反应、软骨组织破坏、持续性滑膜炎和关节结构受损为特征,该病主要侵犯破坏全身小关节,引发软骨和骨骼的损伤,严重者可导致不可逆的残疾。
背景:研究表明,核因子κB信号通路在类风湿关节炎中高度表达,并通过调控细胞因子、血管内皮生长因子、内源性抗氧化酶等物质,促进类风湿关节炎的进展。
目的:总结分析核因子κB 信号通路对类风湿关节炎的作用机制,并对近5年来中药治疗类风湿关节炎的相关文献进行总结汇报,以期为类风湿关节炎的临床治疗提供新的参考依据。
方法:以“核因子κB,类风湿关节炎,中医药,骨损伤,中药单体,中药药对,中药复方,研究进展”为中文检索词,以“NF-κB,
Rheumatoid arthritis,Traditional Chinese Medicine,bone injury,TCM monomeric compounds,TCM herb pairs,TCM compound formulations,Research Progress”为英文检索词,检索2016年3月至2025年3月发表于中国知网和PubMed数据库的有关核因子κB与类风湿关节炎及中药单体、药对、复方干预调控的文献,最终纳入87篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①核因子κB在类风湿关节炎的发病中起着至关重要的作用;②核因子κB信号通路可以通过诱导炎性细胞聚集、产生活性氧物质、调控破骨细胞形成、介导血管异常增生等方式导致类风湿关节炎;③中药单体汉黄芩素等、中药药对制川乌-白芍等以及中药复方薏苡附子败酱散等可通过调控磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B/核因子κB、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/核因子κB、Toll样受体4/核因子κB等核因子κB相关信号通路,抑制类风湿关节炎疾病进展。
http://orcid.org/0009-0004-4752-7667(付晓)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
付 晓, 李纪高, 闫小楠, 宋 哲, 郭岳峻, 李韩冰, 周 全. 中药有效成分治疗类风湿关节炎:基于核因子κB信号通路的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(16): 4180-4192.
Fu Xiao, Li Jigao, Yan Xiaonan, Song Zhe, Guo Yuejun, Li Hanbing, Zhou Quan. Traditional Chinese medicine effective ingredients for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: mechanism based on nuclear factor kappaB signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4180-4192.
(核因子κB2)和p105/p50(核因子κB1)5个亚基组成,这些亚基高度保守,共享一个氨基末端Rel同源结构域,可形成不同形式的同源或异源二聚体,并与具有κB位点的相关DNA序列结合,调节基因表达[9]。
核因子κB信号通路的激活主要由两种途径,即经典通路和非经典通路,分别由不同的促炎信号介导。在经典路径中,IκB激酶(inhibitor of kappa B kinase,IKK)复合物(IκB激酶α、IκB激酶β、IκB激酶γ)在接收胞外刺激后使核因子κB抑制因子α(IκBα)发生磷酸化,并通过蛋白酶体降解进一步泛素化,形成由p65、p50、c-Rel 组成的核因子κB三聚体,三聚体裂解释放后被进一步翻译修饰,进入细胞核中,调控下游基因的转录[10]。非经典途径是核因子κB诱导激酶受肿瘤坏死因子受体超家族刺激后被激活并发生磷酸化,进而介导IκB激酶α诱导p100磷酸化,最终导致p100泛素化后被降解成p52,在细胞质中形成p52、RelB异源二聚体后,迁移至细胞核内,调节靶基因的转录,激活信号传导[11]。
2.2 核因子κB信号通路在类风湿关节炎中的作用机制
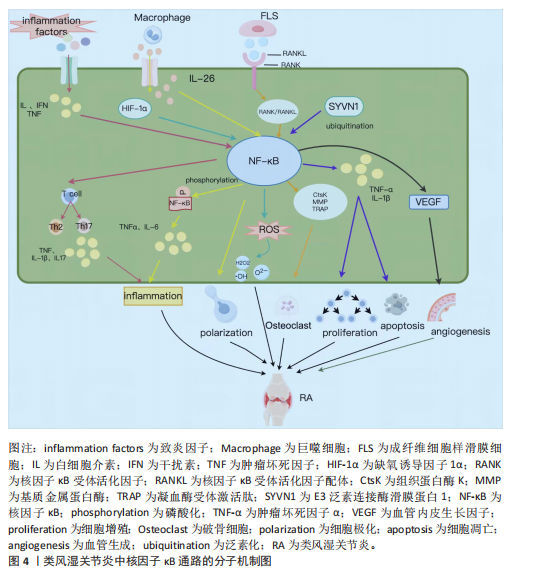
2.2.1 调节炎症因子 类风湿关节炎发病机制复杂,其发病与炎症直接相关[12]。白细胞介素、干扰素和肿瘤坏死因子等促炎细胞因子通过激活核因子κB进一步促进促炎细胞因子的分泌,加剧炎症反应[13]。激活的核因子κB信号通路诱导单核细胞和巨噬细胞产生促炎细胞因子、趋化因子或干扰素刺激基因,介导炎性细胞的募集,引起类风湿关节炎关节炎症的发生[14-15]。相关研究已证实,从中药防己中提取出来的粉防己碱可以下调核因子κB通路活性,从而抑制白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,发挥治疗类风湿关节炎的作用[16]。
2.2.2 调节氧化应激 氧化应激是机体内发生氧化与抗氧化体系失衡的一种病理状态,导致超氧阴离子(O2-)、过氧化氢基(H2O2)、羟基自由基(·OH)、过氧亚硝基阴离子(ONOO-)等活性氧的产生[17]。在类风湿关节炎中,促炎性M1巨噬细胞可诱导核因子κB和缺氧诱导因子1α之间的级联反应,从而产生过量活性氧并增强巨噬细胞M1型的表达,进一步加剧炎症进展[18]。研究表明,氢分子通过抑制核因子κB通路活性,增加超氧化物歧化酶水平,降低GSH水平,直接中和·OH和 ONOO-,改善类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞中氧化应激水平[19]。
2.2.3 调节免疫细胞 巨噬细胞是类风湿关节炎滑膜活检中最高表达的细胞类型[20]。关节滑膜在受到炎症浸润或已经发生损伤时,滑膜中的巨噬细胞通常会变为活化状态,这种现象称为巨噬细胞极化。极化后的巨噬细胞常表现为M1和M2两种表型,其中,M1型巨噬细胞产生促炎细胞因子介导滑膜组织损伤,为类风湿关节炎提供炎症微环境[21];M2型巨噬细胞产生抗炎细胞因子对损伤组织进行修复[22]。巨噬细胞产生的白细胞介素26在类风湿关节炎滑膜细胞中高度表达,能够通过上调白细胞介素1β诱导 CD4+ 记忆T细胞向Th17细胞的极化[23],而且能够诱导核因子κB 的磷酸化,促进M1型巨噬细胞的极化,上调肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6表达,加快类风湿关节炎病情进展[24]。
2.2.4 调控破骨细胞形成 破骨细胞分化是类风湿关节炎中关节破坏和骨质流失的重要因素[25]。在类风湿关节炎中,成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞表达核因子κB受体活化因子配体,与活化巨噬细胞细胞表面受体(核因子κB受体活化因子)结合,启动核因子κB受体活化因子/核因子κB受体活化因子配体通路,并与下游核因子κB信号通路发生级联反应,共同参与上调由破骨细胞产生的凝血酶受体激活肽(TRAP)、组织蛋白酶K(CtsK)和基质金属蛋白酶9的表达,促进破骨细胞生成[26]。研究表明,SN50作为核因子κB抑制肽可以靶向调控核因子κB p50亚基在骨髓单核巨噬细胞中的核易位,阻止破骨细胞形成[27]。
2.2.5 抑制增殖,促进凋亡 成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞的异常增殖是类风湿关节炎关节滑膜组织中最主要的病理表现,可以产生大量肿瘤坏死因子α、 白细胞介素6 ,介导炎症的发生,在类风湿关节炎关节滑膜炎症和骨损伤中发挥重大作用[28-29]。细胞凋亡是细胞为了抵抗外部刺激并维持内部环境的稳态,发生的程序性死亡[30]。在线粒体中,抗凋亡B细胞淋巴瘤2(B-cell lymphoma-2,Bcl-2)家族蛋白通过抑制BAX和BAK来防止caspase激活,从而调节细胞凋亡[31]。在类风湿关节炎进展中,E3泛素连接酶滑膜蛋白1经过泛素化,从而调控核因子κB信号通路,上调肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β等炎性细胞因子的数量,抑制胶原诱导性关节炎小鼠关节炎中滑膜细胞的凋亡,并显著促进滑膜细胞增殖[32]。
2.2.6 诱导血管新生 血管新生是类风湿关节炎早期主要的病理特征,在病情进展中发挥重要作用,血管内皮生长因子是一种同源二聚体糖蛋白,作用于类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞,参与调节血管新生[33]。血管内皮生长因子的启动子区域含有核因子κB反应元件 ,可以通过激活核因子κB信号通路诱导血管内皮生长因子表达,从而促进血管新生[34]。实验表明,BAY11-7082作为核因子κB抑制剂,可以浓度依赖性降低血管内皮生长因子水平,从而抑制类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞血管生成[35]。
综上所述,中医药可以通过调控核因子κB信号通路调节炎症因子水平和氧化应激能力,参与免疫细胞极化和破骨细胞形成,并诱导细胞凋亡、抑制细胞增殖和血管新生,在类风湿关节炎中发挥作用,主要作用及相互关系机制图详见图3,主要通路分子机制图详见图4。
2.3 中药通过核因子κB信号通路治疗类风湿关节炎 类风湿关节炎属祖国医学中“痹证”范畴,并在《素问·痹论》中记载:“所谓痹者,各以其时重感于风寒湿之气也”。《灵枢·百病始生》曰:“此必因虚邪之风,与其身形,两虚相得,乃客其形”,说明正气亏虚是导致类风湿关节炎的内在原因。以风寒湿为首的外邪袭击人体是发病的重要条件,并根据个人体质及所处环境的不同,疾病临床表现出
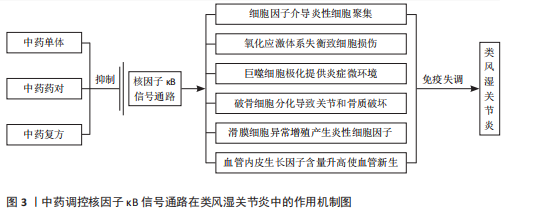
的寒、热、虚、实等症状也不尽相同。
近年来,中医药通过调控核因子κB信号通路以治疗类风湿关节炎的研究逐渐深入,现总结了近5年来发表于中国知网(CNKI)、PubMed数据库中的用于治疗类风湿关节炎的33个中药单体化合物、5个中药药对、11个中药方剂,以期为类风湿关节炎的中医药治疗提供新的参考价值和理论依据。
2.3.1 中药单体
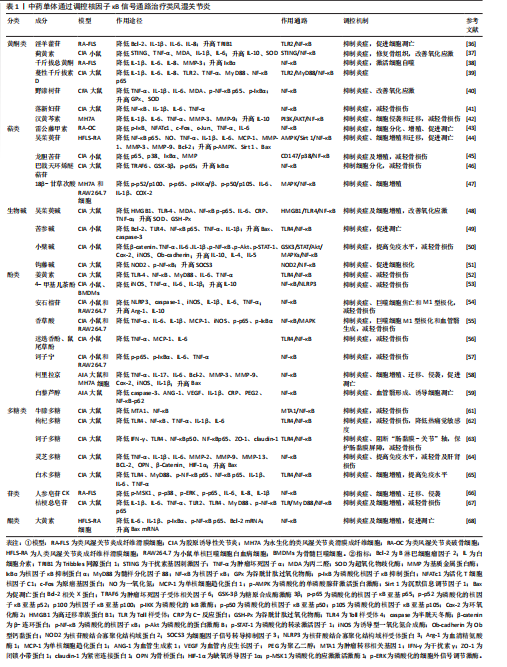
(1)黄酮类:淫羊藿苷是来源于中药淫羊藿中的具有活性的黄酮苷类化合物。实验表明,淫羊藿苷抑制Bcl-2、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素8和白细胞介素6释放的同时促进Tribbles同源蛋白1表达,抑制Toll样受体(Toll-like receptor,TLR)2/核因子κB信号通路,促进细胞凋亡,抑制炎症反应[36]。蓟黄素是从蓟属中提取出来的黄酮类化合物,能够抑制干扰素基因刺激因子(stimulator of interferon gene,STING)/核因子κB信号通路,增加白细胞介素10、减少肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β含量,减轻炎症,而且能够降低丙二醛、提高超氧化物歧化酶水平,改善体内氧化应激反应,促进骨组织修复[37]。千斤拔总黄酮提取自草药千斤拔,研究证实千斤拔总黄酮能够促进IκBɑ表达,进而调控核因子κB信号通路,激活类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞细胞自噬,并下调白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素8、基质金属蛋白酶3细胞因子水平,抑制炎症,减轻骨损伤[38]。此外,同产自千斤拔的蔓性千斤拔素D通过抑制Toll样受体2/髓样分化因子88 (myeloid differentiation factor 88,My D88)/核因子κB信号传导,降低白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、肿瘤坏死因子α水平,改善关节炎症[39]。野漆树苷源于芸香科柑橘属植物,现代研究表明野漆树苷可以降低核因子κB p65 、IκB-α磷酸化水平,下调肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6水平,改善炎症,并且能够上调关节软骨中谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶,下调丙二醛表达,发挥抗氧化应激功能[40]。落新妇苷是从土茯苓中分离出来的总黄酮类化合物,研究发现落新妇苷通过抑制核因子κB表达,显著降低白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平,抑制炎症反应,减轻骨损伤[41]。汉黄芩素是来源于中药黄芩干燥根中的天然化合物。研究结果显示,汉黄芩素通过抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/AKT/核因子κB信号通路,降低白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9表达,增加白细胞介素10表达,从而抑制炎症和MH7A细胞的侵袭与迁移,减轻骨破坏[42]。上述研究表明,淫羊藿苷、蓟黄素、千斤拔总黄酮、蔓性千斤拔素D、野漆树苷、落新妇苷、汉黄芩素均能通过抑制核因子κB通路,发挥抑制炎症、抗类风湿关节炎的效果,其中,蔓性千斤拔素D、蓟黄素、土茯苓落新妇苷、野漆树苷、汉黄芩素可以减轻骨损伤;淫羊藿苷、汉黄芩素能够抑制细胞增殖;蓟黄素、野漆树苷能够改善大鼠体内氧化应激反应;汉黄芩素还能够抑制MH7A细胞的侵袭与迁移以及肌原纤维分化;除此之外,野漆树苷可以拮抗大鼠关节炎所致的体质量减轻。
(2)萜类:雷公藤甲素是从雷公藤根部分离出来的二萜类化合物。研究表明,雷公藤甲素能够下调p-IκB表达,抑制核因子κB信号通路,降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6分泌,促进细胞凋亡,并且呈浓度依赖性抑制活化T-细胞核因子1 (NFATc1)、c-Fos、c-Junm表达,抑制细胞增殖和破骨细胞分化[43]。吴茱萸苷是提取自传统藏药翼首草中的一种环烯醚萜苷类化合物,可以抑制单磷酸腺苷激活蛋白激酶/沉默信息调节因子1/核因子κB信号通路,降低人类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞中趋化因子、细胞因子和基质金属蛋白酶水平,从而抑制炎症反应、细胞增殖和迁移,并通过升高Bax水平,降低Bcl-2水平,促进细胞凋亡[44]。龙胆苦苷是从中药龙胆中分离得到的环烯醚萜苷,通过抑制CD147/p38/核因子κB通路,下调p65、p38、IκBα水平,减少基质金属蛋白酶分泌,从而抑制炎症和细胞增殖,减轻骨损伤[45]。巴戟天环烯醚萜苷是茜草科植物巴戟天属中的主要化学成分,近年研究发现,巴戟天环烯醚萜苷能够降低肿瘤坏死因子受体关联因子6和糖原合酶激酶3β活性,抑制p65磷酸化,促进IκBα表达,从而抑制破骨细胞分化,减轻骨损伤[46]。
18β-甘草次酸(18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid,18β-GA)是从中药甘草根中提取出的五环三萜皂苷类化合物,研究表明,18β-甘草次酸通过调控丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/核因子κB信号通路,降低白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、环氧化酶2水平,发挥抗炎作用,并通过抑制G1/S期进程,干预细胞增殖[47]。由此得出,雷公藤甲素、吴茱萸苷、龙胆苦苷、巴戟天环烯醚萜苷、18β-甘草次酸能够调控核因子κB信号通路从而控制类风湿关节炎炎症反应,其中,雷公藤甲素、龙胆苦苷、巴戟天环烯醚萜苷均能抑制细胞分化,减轻骨损伤;吴茱萸苷、龙胆苦苷、18β-甘草次酸、巴戟天环烯醚萜苷能够抑制核因子κB p65磷酸化;巴戟天环烯醚萜苷雷公藤甲素还可阻止破骨细胞生成及骨吸收。
(3)生物碱:吴茱萸碱是从中药吴茱萸近干燥成熟果实中分离出来的吲哚生物碱。研究发现吴茱萸碱通过抑制高迁移率族蛋白B1/Toll样受体4/核因子κB通路,降低白细胞介素6、C-反应蛋白、肿瘤坏死因子α水平,从而抑制炎症、细胞增殖,同时促进超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶表达,改善抗氧化应激的能力[48]。苦参碱是从苦参中提取的活性化合物。周婷婷等[49]用人工气候箱建立风湿热痹型胶原诱导性关节炎小鼠模型,发现苦参碱能够抑制Toll样受体4、核因子κB p65 表达,调控Toll样受体4/核因子κB信号通路,下调肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β含量,减轻炎症反应,并降低Bcl-2,升高Bax、天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶(caspase)3含量,诱导细胞凋亡。小檗碱是存在于多种植物中的异喹啉生物碱。动物实验表明,小檗碱通过调控原合酶激酶3/信号转导和转录激活因子 3/蛋白激酶B/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/核因子κB信号转导相关蛋白表达,降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、环氧化酶2、诱导型一氧化氮合成酶等促炎因子,提高白细胞介素10等抗炎因子,抑制炎症,减轻骨损伤,并能够增加脾脏中T细胞数量,改善机体免疫能力[50]。钩藤碱是从钩藤的带钩枝条提取出来的生物碱。研究表明,钩藤碱通过抑制NOD2/核因子κB通路,促进巨噬细胞M2型极化,减轻关节滑膜炎症[51]。以上结果证实,吴茱萸碱、苦参碱、小檗碱、钩藤碱通过调控核因子κB通路抑制炎症,其调控机制不尽相同。其中,小檗碱可以抑制血管翳生成、促进脾脏内T细胞形成,钩藤碱能够诱导巨噬细胞极化,吴茱萸碱能够抑制体内氧化应激反应,吴茱萸碱、苦参碱均可通过抑制Toll样受体4受体活性以调节免疫反应。
(4)酚类:姜黄素是存在于姜科、天南星科植物根茎中的一类多酚类化合物。研究表明,姜黄素可以抑制Toll样受体4/核因子κB通路,降低白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α含量,抑制炎症反应和破骨细胞形成,减轻骨损伤[52]。4-甲基儿茶酚(4-Methyl Catechol,4-MC)是槲皮素代谢后产生的小酚类化合物,现代研究表明4-甲基儿茶酚作用于核因子κB/NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3信号通路,通过调控M1/M2巨噬细胞极化,促进白细胞介素10抗炎细胞因子分泌,抑制诱导型一氧化氮合成酶、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6等促炎细胞因子的分泌,改善炎症,减轻骨损伤,发挥治疗类风湿关节炎作用[53]。安石榴苷是从中药石榴皮果根中分离得到的化合物,研究表明,安石榴苷通过调控核因子κB信号通路,干预巨噬细胞焦亡和M1表型极化,从而抑制NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3、caspase-1 等促炎细胞因子表达,促进Arg-1和白细胞介素10抗炎细胞因子表达,减轻骨损伤[54]。香草酸是广泛存在于自然界植物中的一种酚酸类活性化合物,能够下调p65、IκBα的磷酸化水平,抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化,降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、诱导型一氧化氮合成酶炎症水平,从而抑制血管翳的生成,减轻骨损伤[55]。迷迭香中的两种酚性二萜类化合物迷迭香酚、鼠尾草酚,通过抑制Toll样受体4/核因子κB信号通路,降低肿瘤坏死因子α、单核细胞趋化蛋白1、白细胞介素6含量,改善炎症水平,减轻骨损伤[56]。诃子宁是从中药诃子成熟果实中提取出来的天然酚酸类化合物,现代研究已证实诃子宁通过下调p-p65、p-IκBα表达、抑制p65核易位,调控核因子κB信号通路,降低白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平,对小鼠炎症的改善和对骨质的修复起到良好效果[57]。柯里拉京(Corilagin)是从传统中药老鹳草提取出来的没食子酸单宁化合物。最近研究结果发现,柯里拉京通过调控核因子κB信号通路,降低Bcl-2、基质金属蛋白酶3、肿瘤坏死因子α等相关因子含量,促进Bax表达,从而抑制细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭,诱导细胞凋亡,改善体内炎症反应[58]。白藜芦醇是来源于桑葚、中药虎杖等多种天然植物的多酚类化合物,研究证实,白藜芦醇能够下调核因子κB p62的表达,减少白细胞介素1β、C反应蛋白、前列腺素E2炎症因子水平,下调caspase-3 、血管生成素1、血管内皮生长因子表达,从而缓解炎症反应,诱导细胞凋亡,抑制血管翳形成[59]。
以上结果表明,姜黄素、4-甲基儿茶酚、安石榴苷、香草酸、迷迭香酚、鼠尾草酚可下调核因子κB信号传导,其中,姜黄素、4-甲基儿茶酚均可以降低核因子κB蛋白的表达实现信号阻断,从而抑制炎症,减轻骨损伤,4-甲基儿茶酚、安石榴苷、香草酸可通过诱导巨噬细胞发生极化,调节免疫系;此外,香草酸还能够保护小鼠脾脏组织,改善自身免疫功能。诃子宁和柯里拉金均可以抑制核因子κB通路中p65的磷酸化,降低细胞内炎症反应,发挥抗炎抗风湿的效果。
(5)多糖类:多糖是普遍存在于植物中的活性大分子,具有多种药理作用。近年研究发现,中药多糖大多具备抗类风湿关节炎作用[60]。牛膝多糖是从草药牛膝中分离出来的水溶性果聚糖。研究表明,牛膝多糖可以下调转移相关蛋白1(MTA1)、核因子κB蛋白表达,从而抑制炎症、改善大鼠踝关节骨损伤[61]。枸杞多糖是从枸杞的成熟子实提取出的一种水溶性多糖。研究证实,枸杞多糖可抑制Toll样受体4/核因子κB信号通路,降低血清肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6水平,抑制炎症、减轻骨损伤,同时可以上调大鼠热痛阈及热刺激缩足反射潜伏期时间[62]。诃子多糖是从诃子的成熟果实中提取出来的一类活性成分,被广泛应用于藏药和蒙药,研究表明,诃子多糖能够抑制Toll样受体4/核因子κB信号通路,下调胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠滑膜内核因子κB p50、核因子κB p65含量,降低肠道和血清中干扰素γ、Toll样受体4表达,从而抑制关节炎症,减轻骨损伤。此外,诃子多糖通过调控该通路,阻断“肠黏膜-关节”轴,降低小肠组织中胞质紧密连接蛋白1 (ZO-1)、紧密连接蛋白1含量,改善类风湿关节炎大鼠肠黏膜水肿,保护胃肠道[63]。灵芝多糖是从灵芝水提物中提取出来的主要活性物质。研究结果显示,灵芝多糖可以降低基质金属蛋白酶、Bcl-2、骨桥蛋白、β-连环蛋白水平,减轻类风湿关节炎导致的骨损伤,下调缺氧诱导因子1α,抑制血管及滑膜形成,并通过降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6含量,升高Bax 蛋白含量,抑制炎症及细胞分化。此外,灵芝多糖还可以提高机体免疫功能,减少肝肾脏器损伤[64]。白术多糖多提取于菊科植物白术的干燥根茎中。研究发现,白术多糖通过下调Toll样受体4、髓样分化因子88、核因子κB p65水平,降低白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α细胞因子含量,抑制炎症及细胞增殖,同时可以降低胸腺和脾脏指数,提高机体免疫水平,发挥免疫调节作用[65]。由此观之,牛膝多糖、枸杞多糖、诃子多糖、灵芝多糖、白术多糖均能阻断核因子κB通路,抑制炎症反应,其中,牛膝多糖、枸杞多糖、诃子多糖、灵芝多糖可以减轻骨损伤;此外枸杞多糖可以提高实验大鼠的热痛阈,诃子多糖能够阻断“肠黏膜-关节”轴,保护类风湿关节炎大鼠肠道不受疾病影响。
(6)苷类:人参皂苷CK (GinsenosidecompoundK,GCK)是从人参中分离得到的四环三萜型化合物。研究发现,人参皂苷CK通过调控糖皮质激素受体与p65之间的相互作用,抑制核因子κB的转录活性,从而调控核因子κB相关信号通路,下调白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、白细胞介素1β表达,抑制炎症及细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,发挥抗类风湿关节炎功效[66]。桔梗总皂苷是从桔梗根部提取出的一类糖苷化合物,研究证实,桔梗总皂苷能够调控Toll样受体/髓样分化因子88/核因子κB通路中相关信号表达,减少白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α含量,抑制炎症及细胞增殖,减轻骨损伤[67]。纵观以上研究成果,发现在调控核因子κB通路时,人参皂苷可以通过糖皮质激素受体的转录激活和抑制两种途径来抑制细胞的增殖、迁移、侵袭,桔梗总皂苷则通过抑制滑膜组织内相关转录蛋白活性,发挥抗炎作用。
(7)醌类:大黄素是一种羟基蒽醌类化合物,在大黄、何首乌及虎杖等中草药中广泛存在。研究结果显示,人类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞经大黄素诱导后,可以呈浓度依赖性下调p-IκBα和p-NF-κB p65的表达,降低Bcl-2 mRNA、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1β含量,升高Bax mRNA,促进细胞凋亡,抑制细胞增殖,减轻炎症反应[68]。
中药单体通过调控核因子κB通路治疗类风湿关节炎的研究汇总,见表1。
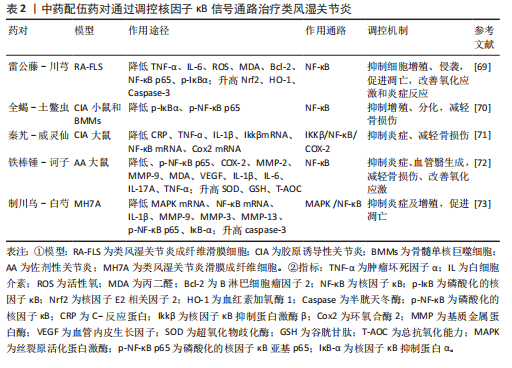
2.3.2 药对 雷公藤-川芎是治疗类风湿关节炎的常用配伍药,其中,雷公藤味苦辛,具有祛风除湿、消肿止痛作用,川芎味辛、温,为气中之血药,二者配伍相辅相成,在治疗中活血行气、祛风止痛,共同发挥抗风湿的强大疗效。研究发现,雷公藤-川芎可以显著阻止核因子κB信号通路,降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6含量,改善体内炎症水平,同时降低核因子E2相关因子2、血红素氧合酶(HO)-1、Bcl-2表达,升高Caspase-3表达,促进细胞凋亡,抑制细胞增殖、侵袭,并且能够下调细胞内活性氧、丙二醛,提高抗氧化应激能力,从而发挥治疗作用[69]。
全蝎-土鳖虫是经典的破血逐瘀药物配伍,全蝎搜络祛邪、活血祛瘀,土鳖虫祛风止痛、散结通络,二者均为虫类活血要药,二者相伍,祛瘀不伤正,具有显著治疗效果。赵呈雷等[70]
研究证实:全蝎-土鳖虫能够剂量依赖性下调核因子κB p65、IκBα磷酸化水平,抑制骨髓单核巨噬细胞增殖和分化,缓解炎症反应,改善骨损伤。
秦艽-威灵仙是治疗风湿痹病的一组常用中药药对,其中秦艽祛风除湿、舒筋止痛,威灵仙祛风散邪、通络除痹,二者配伍可缓解急性期风湿疼痛。葛珊等[71]对该药对中有效成分进行研究,发现二者配伍能够抑制IκB激酶β/核因子κB/环氧化酶2通路,下调IκB激酶β、Nfkb、环氧合酶2的mRNA水平,降低C-反应蛋白、肿瘤坏死因子ɑ、白细胞介素1β含量,改善体内炎症水平,减轻骨损伤。
铁棒锤-诃子配伍可以抑制核因子κB信号通路,升高AA大鼠体内超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽和总抗氧化能力(T-AOC),降低丙二醛,从而提高抗氧化应激能力,并通过下调白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素17A、肿瘤坏死因子α、环氧化酶2、基质金属蛋白酶2、基质金属蛋白酶9、血管内皮生长因子蛋白表达,发挥抗炎、抑制血管翳形成的作用[72]。
制川乌-白芍是《金匮要略》中乌头汤的中药组成成分,临床上也常用于寒湿痹阻型类风湿关节炎的治疗,体外实验表明,从制川乌、白芍中分别提取出来的有效成分苯甲酰乌头原碱、芍药苷,二者配伍能够协同强化抑制丝裂原活化蛋白激酶-核因子κB信号通路的激活,显著上调caspase-3含量,下调基质金属蛋白酶9、基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13、白细胞介素1β含量,从而改善炎症水平,抑制细胞增殖,促进细胞凋亡[73]。
中药配伍药对调控核因子κB信号通路治疗类风湿关节炎的研究模型及作用机制见表2。
由此观之,中药单体和配伍药对通过调控核因子κB信号通路,能够抑制炎症反应、减轻骨损伤、调节细胞生命活动、提高抗氧化应激能力,发挥治疗类风湿关节炎作用,揭示出中医药治疗类风湿关节炎的内在作用机制及其所发挥出的巨大潜力。
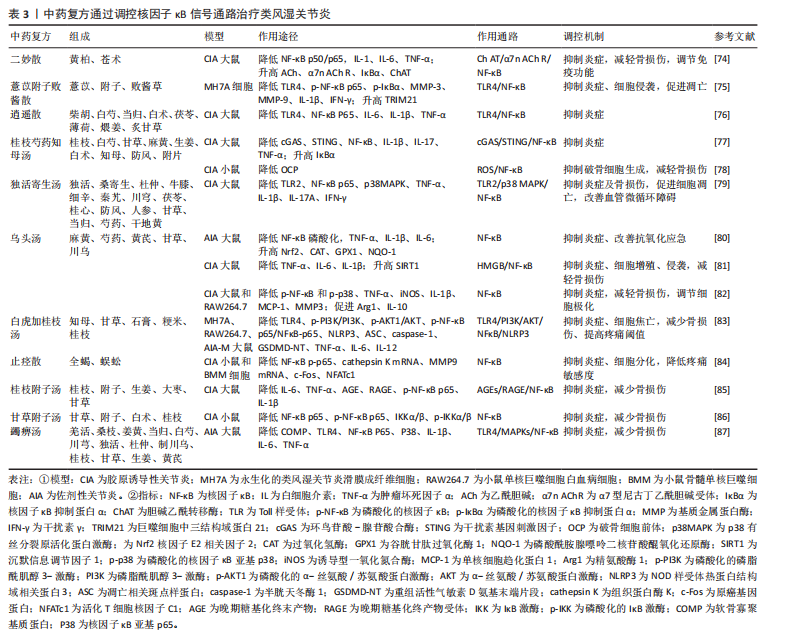
2.3.3 中药复方 二妙散出自明代医家朱丹溪所作的《丹溪心法》,由黄柏、苍术两味药组成,在治疗类风湿关节炎中发挥巨大疗效。李玉彤等[74]通过构建颈部单侧迷走神经切断的胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠,发现二妙散能够明显上调胆碱乙酰转移酶(ChAT)表达,诱导乙酰胆碱(acetylcholine,Ach)生成,促进α7n AChR活化,从而调控下游IκBα、核因子κB p50/p65的表达,降低白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α炎症水平,减轻骨损伤,而且能够减少脾脏白髓和生发中心,改善机体免疫能力。
薏苡附子败酱散具有清热解毒、活血化瘀功效,是治疗肠痈的代表方剂。最近有研究证实,薏苡附子败酱散通过提高TRIM21表达,抑制Toll样受体4/核因子κB通路,降低基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9,白细胞介素1β、干扰素γ含量,抑制细胞增殖、侵袭,诱导细胞凋亡[75]。
经典方剂逍遥散出自《太平惠民和剂局方》,是抗炎抗应激的代表方。李媛媛等[76]用逍遥散干预类风湿关节炎伴发抑郁症的胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠,发现其可以调节Toll样受体4/核因子κB信号通路,抑制海马Toll样受体4、核因子κB P65表达,降低海马白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6及血清白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α水平,改善大鼠抑郁样行为及关节和神经炎症,减轻骨损伤,发挥双重治疗作用。
桂枝芍药知母汤源于仲景《金匮要略》,有祛风除湿、温经散寒功效。丁明辉等[77]发现,桂枝芍药知母汤通过下调cGAS、核因子κB p65、STING表达,上调IκBα表达,降低白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素17、肿瘤坏死因子α水平,从而抑制炎症,减轻关节肿胀。同时通过促进破骨细胞前体线粒体自噬,抑制活性氧/核因子κB信号,从而抑制破骨细胞形成,减轻骨损伤[78]。
独活寄生汤首载于《备急千金药方》,是用于治疗“痹症”的经典方
药,该方集“补正”与“祛邪”为一体,标本兼治,共奏补益肝肾、除湿止痛之功,临床上对风寒湿痹的治疗发挥巨大疗效。梁霄等[79]发现,独活寄生汤能够呈剂量依赖性下调Toll样受体2、核因子κB p65、p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶蛋白表达,降低体内肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素17A、干扰素γ水平,抑制滑膜细胞增殖,诱导滑膜细胞凋亡,减轻骨损伤,而且能够降低胸腺、脾脏指数,改善机体免疫功能。此外,独活寄生汤可以改善血管管袢形态、血流速度及袢周状态,缓解胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠机体微循环凝滞状态,发挥治疗类风湿关节炎作用。
乌头汤出自《金匮要略》:“病历节不可屈伸,疼痛,乌头汤主之”。该方剂由麻黄、川乌、芍药、黄芪、炙甘草组成,这5种中药相辅相成,对“历节病”的治疗有重大效果。研究结果显示:乌头汤能够下调核因子κB蛋白磷酸化水平,下调肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6含量,上调核因子E2相关因子2 、过氧化氢酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶1、醌氧化还原酶1(NQO1)含量,改善佐剂性关节炎大鼠的关节炎症,提高抗氧化应激能力[80]。此外,乌头汤通过上调胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠体内沉默信息调节因子1含量,调控高迁移率族蛋白B1/核因子κB信号通路,降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1含量,抑制细胞侵袭和M1型巨噬细胞极化, 减轻骨损伤[81]。同时,乌头汤通过下调核因子κB和p38磷酸化水平,调控M1/M2型巨噬细胞极化,并降低肿瘤坏死因子α、诱导型一氧化氮合成酶、白细胞介素1β、为单核细胞趋化蛋白1、基质金属蛋白酶3含量,升高精氨酸酶1、白细胞介素10含量,抑制炎症,减轻骨损伤[82]。
白虎加桂枝汤是由白虎汤加桂枝组成,方中重用石膏除里热,桂枝通表邪,全方清里不遏表,通络不助热,共同发挥清热解毒、通络止痛之功。研究发现,白虎加桂枝汤可以抑制Toll样受体4/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B/核因子κB/NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3信号,下调凋亡相关斑点样蛋白(ASC)、GSDMD蛋白N端(GSDMD-NT)、caspase-1、NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3炎性小体的表达,抑制细胞焦亡,同时降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素12水平,抑制炎症,减轻骨损伤、提高疼痛阈值,此外,白虎加桂枝汤还能够降低脾脏和胸腺指数,提高机体免疫功能,并未对肝脏、肾脏产生毒性损伤[83]。
止痉散由全蝎、蜈蚣两位虫类药组成,药简力专,可直达经络,搜刮匿于筋骨深处之邪,在治疗风寒湿痹时能够迅速改善病情,缓解疼痛。研究结果显示,止痉散通过抑制核因子κB信号通路,下调白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α细胞因子的释放,缓解炎症水平,并降低组织蛋白酶K、基质金属蛋白酶9、骨保护素和核因子κB受体活化因子配体含量,抑制破骨细胞分化,减轻骨损伤[84]。
桂枝附子汤和甘草附子汤均是桂枝汤的加减化裁,在类风湿性关节炎的治疗中发挥显著疗效。其中,桂枝附子汤具有祛风除湿、温阳通络之功,可补益身体阳气,外散寒湿之邪。研究表明,桂枝附子汤通过抑制AGEs/RAGE/核因子κB通路激活,下调肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6水平,抑制炎症,减轻骨损伤[85]。甘草附子汤具有温阳通痹、除湿止痛之功,临床上常治疗表里阳虚、痹着筋骨的风湿骨痹。甘草附子汤通过抑制核因子κB p65、IκB激酶α/β表达,下调核因子κB信号通路,缓解胶原诱导性关节炎小鼠炎症反应,减轻骨损伤[86]。
蠲痹汤出自清代程国彭《医学心悟》,能够“通治风、寒、湿三气”,被誉为“治痹祖方”。娄飞等[87]用蠲痹汤对寒湿痹阻型类风湿关节炎大鼠进行诱导,发现蠲痹汤能够阻止Toll样受体4/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/核因子κB信号通路激活,下调COMP、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α表达,同时上调白细胞介素10,减轻骨损伤,改善体内炎症水平。
综上所述,二妙散、薏苡附子败酱散、逍遥汤、桂枝芍药知母汤、独活寄生汤、乌头汤、白虎加桂枝汤、止痉散、桂枝附子汤、甘草附子汤、蠲痹汤均可以调控核因子κB信号通路降低体内炎症水平,减轻骨损伤,从而发挥治疗效果。二妙散、独活寄生汤、白虎加桂枝汤可以改善免疫器官指数,调节免疫功能。桂枝芍药知母汤可以抑制线粒体自噬和破骨细胞生成,止痉散能够抑制破骨细胞分化。其中,乌头汤、止痉散还可以调控巨噬细胞极化,白虎加桂枝汤、止痉散能够降低疼痛敏感度。独活寄生汤可以修复类风湿关节炎引起的微循环血管障碍。中药复方调控核因子κB信号通路治疗类风湿关节炎的作用机制,见表3。
| [1] DI MATTEO A, BATHON JM, EMERY P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2023; 402(10416):2019-2033. [2] LIN YJ, ANZAGHE M, SCHÜLKE S. Update on the Pathomechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells. 2020;9(4):880. [3] GAO Y, ZHANG Y, LIU X. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenesis and therapeutic advances. MedComm (2020). 2024;5(3):e509. [4] BINDU S, MAZUMDER S, BANDYOPADHYAY U. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: A current perspective. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;180:114147. [5] LIU X, WANG Z, QIAN H, et al. Natural medicines of targeted rheumatoid arthritis and its action mechanism. Front Immunol. 2022;13:945129. [6] CAPECE D, VERZELLA D, FLATI I, et al. NF-κB: blending metabolism, immunity, and inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2022;43(9): 757-775. [7] ARAVILLI RK, VIKRAM SL, KOHILA V. Phytochemicals as potential antidotes for targeting NF-κB in rheumatoid arthritis. 3 Biotech. 2017;7(4):253. [8] ZHANG Q, LENARDO MJ, BALTIMORE D. 30 Years of NF-κB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell. 2017;168(1-2):37-57. [9] LIU X, SHAO Y, ZHOU J, et al. Nuclear Factor κB Signaling and Its Related Non-coding RNAs in Cancer Therapy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;19:208-217. [10] PENG C, OUYANG Y, LU N, et al. The NF-κB Signaling Pathway, the Microbiota, and Gastrointestinal Tumorigenesis: Recent Advances. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1387. [11] SUN SC. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(9):545-558. [12] LIU S, MA H, ZHANG H, et al. Recent advances on signaling pathways and their inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol. 2021;230:108793. [13] PAPAVASSILIOU KA, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. Transcription Factor Drug Targets. J Cell Biochem. 2016;117(12):2693-2696. [14] ROBERTI A, CHAFFEY LE, GREAVES DR. NF-κB Signaling and Inflammation-Drug Repurposing to Treat Inflammatory Disorders?. Biology (Basel). 2022;11(3):372. [15] BALENDRAN T, LIM K, HAMILTON JA, et al. Targeting transcription factors for therapeutic benefit in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1196931. [16] GAO LN, FENG QS, ZHANG XF, et al. Tetrandrine suppresses articular inflammatory response by inhibiting pro-inflammatory factors via NF-κB inactivation. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(9):1557-1568. [17] MIGLIORANZA SCAVUZZI B, HOLOSHITZ J. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Oxidative Stress, and Rheumatic Diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(7):1306. [18] LI Y, LIANG Q, ZHOU L, et al. An ROS-responsive artesunate prodrug nanosystem co-delivers dexamethasone for rheumatoid arthritis treatment through the HIF-1α/NF-κB cascade regulation of ROS scavenging and macrophage repolarization. Acta Biomater. 2022;152:406-424. [19] MENG J, YU P, JIANG H, et al. Molecular hydrogen decelerates rheumatoid arthritis progression through inhibition of oxidative stress. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(10):4472-4477. [20] LUO M, ZHAO F, CHENG H, et al. Macrophage polarization: an important role in inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1352946. [21] BASHIR S, SHARMA Y, ELAHI A, et al. Macrophage polarization: the link between inflammation and related diseases. Inflamm Res. 2016;65(1):1-11. [22] TARDITO S, MARTINELLI G, SOLDANO S, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Autoimmun Rev. 2019;18(11):102397. [23] WANG YH, PENG YJ, LIU FC, et al. Interleukin 26 Induces Macrophage IL-9 Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(8):7526. [24] LIN YH, WANG YH, PENG YJ, et al. Interleukin 26 Skews Macrophage Polarization Towards M1 Phenotype by Activating cJUN and the NF-κB Pathway. Cells. 2020;9(4):938. [25] YAO Z, GETTING SJ, LOCKE IC. Regulation of TNF-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation. Cells. 2021;11(1):132. [26] FANG Q, ZHOU C, NANDAKUMAR KS. Molecular and Cellular Pathways Contributing to Joint Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020: 3830212. [27] HUTAMI IR, IZAWA T, MINO-OKA A, et al. Fas/S1P1crosstalk via NF-κB activation in osteoclasts controls subchondral bone remodeling in murine TMJ arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490(4):1274-1281. [28] TAGHADOSI M, ADIB M, JAMSHIDI A, et al. The p53 status in rheumatoid arthritis with focus on fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Immunol Res. 2021;69(3):225-238. [29] NYGAARD G, FIRESTEIN GS. Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(6):316-333. [30] SORICE M. Crosstalk of Autophagy and Apoptosis. Cells. 2022;11(9):1479. [31] Newton K, Strasser A, Kayagaki N, et al. Cell death. Cell. 2024;187(2):235-256. [32] MENG Q, WEI K, SHAN Y. E3 ubiquitin ligase gene BIRC3 modulates TNF-induced cell death pathways and promotes aberrant proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1433898. [33] GAO C, SONG XD, CHEN FH, et al. The protective effect of natural medicines in rheumatoid arthritis via inhibit angiogenesis. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1380098. [34] RIDIANDRIES A, TAN JT, BURSILL CA. The Role of CC-Chemokines in the Regulation of Angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(11):1856. [35] XIA ZB, MENG FR, FANG YX, et al. Inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation and angiogenesis of human fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(23):e10920. [36] WU ZM, XIANG YR, ZHU XB, et al. Icariin represses the inflammatory responses and survival of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by regulating the TRIB1/TLR2/NF-kB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;110:108991. [37] 黄成硕,林娴,陈驹,等.基于STING/NF-κB信号通路探讨蓟黄素对小鼠类风湿性关节炎的影响[J].天津中医药大学学报,2024,43(11):987-991. [38] 张颖茵,严雪梅,陈凯然,等.千斤拔总黄酮通过抑制NF-κB信号通路增强自噬对抗TNF-α诱导的人风湿性关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞炎症[J].中草药,2025, 56(3):877-884. [39] 覃清霞,何莲花,魏梅,等.蔓性千斤拔素D通过TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路调控CIA大鼠炎症反应的相关机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(17):134-141. [40] PENG S, HU C, LIU X, et al. Rhoifolin regulates oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokine levels in Freund’s adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis via inhibition of NF-κB. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020;53(6):e9489. [41] 陈小鹏.土茯苓落新妇苷基于NF-κB信号通路抑制大鼠类风湿性关节炎的研究[D].合肥:安徽中医药大学,2022. [42] YANG H, LIU C, LIN X, et al. Wogonin inhibits the migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024;755:109965. [43] 范文强,郭占非,张超,等.雷公藤甲素对类风湿关节炎破骨细胞分化影响及机制[J].青岛大学学报(医学版),2023, 59(2):232-236. [44] 柏金容.基于AMPK/Sirt 1/NF-κB信号通路研究吴茱萸苷治疗类风湿关节炎的作用机制[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2022. [45] JIA N, MA H, ZHANG T, et al. Gentiopicroside attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in mice via modulating the CD147/p38/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;108:108854. [46] 沈燚,孙艺琦,李鹤鸣,等.巴戟天环烯醚萜苷下调GSK-3β抑制JAK2/STAT3和NF-κB通路减轻Ⅱ型胶原诱导的关节炎大鼠骨破坏的机制[J].药学学报,2024, 59(10):2763-2772. [47] FENG Y, MEI L, WANG M, et al. Anti-inflammatory and Pro-apoptotic Effects of 18beta-Glycyrrhetinic Acid In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:681525. [48] 冷冬月,李旭峰,方兴刚.吴茱萸碱抑制HMGB1/TLR-4/NF-κB信号通路对类风湿关节炎大鼠的改善作用[J].河北医药, 2023,45(18):2760-2764. [49] 周婷婷,杨文广,胡艳婷,等.基于Toll样受体4/核因子κB信号通路探究苦参碱对类风湿关节炎风湿热痹证的治疗作用及机制[J].中医正骨,2022,34(10): 1-9+26. [50] SHARMA A, TIRPUDE NV, BHARDWAJ N, et al. Berberis lycium fruit extract and its phytoconstituents berberine and rutin mitigate collagen-CFA-induced arthritis (CIA) via improving GSK3β/STAT/Akt/MAPKs/NF-κB signaling axis mediated oxi-inflammation and joint articular damage in murine model. Inflammopharmacology. 2022;30(2):655-666. [51] 陈迎,焦宁.钩藤碱通过上调SOCS3抑制NOD2/NF-κB信号通路调节巨噬细胞极化影响类风湿性关节炎进展[J].解剖科学进展,2024,30(4):345-348. [52] 丁子阳,于其华.姜黄素下调TLR-4/NF-κB减少类风湿关节炎炎症反应和破骨细胞生成[J].解剖科学进展,2022,28(3):257-260. [53] ZHENDONG Y, CHANGJUN C, HAOCHENG H, et al. Regulation of macrophage polarization and pyroptosis by 4-methylcatechol alleviates collagen-induced arthritis via Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025; 146:113855. [54] GE G, BAI J, WANG Q, et al. Punicalagin ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by downregulating M1 macrophage and pyroptosis via NF-κB signaling pathway. Sci China Life Sci. 2022;65(3):588-603. [55] ZHOU Y, LI P, ZHI Z, et al. Vanillic acid ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by suppressing the inflammation response via inhibition of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Inflammopharmacology. 2025;33(4):1949-1963. [56] LI L, PAN Z, NING D, et al. Rosmanol and Carnosol Synergistically Alleviate Rheumatoid Arthritis through Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK Pathway. Molecules. 2021;27(1):78. [57] LIU F, LIU Y, ZHAN S, et al. Chebulanin exerts its anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects via inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK activation in collagen-induced arthritis mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;88:106823. [58] SHEN Y, TENG L, QU Y, et al. Anti-proliferation and anti-inflammation effects of corilagin in rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;284:114791. [59] FERNÁNDEZ-RODRÍGUEZ JA, ALMONTE-BECERRIL M, RAMIL-GÓMEZ O, et al. Autophagy Activation by Resveratrol Reduces Severity of Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021;65(2):e2000377. [60] 陈燕,李世刚.中药多糖防治类风湿性关节炎的研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(1):202-204. [61] 康聪,杨光,王芳,等.牛膝多糖调控转移相关蛋白1/核因子-κB通路对类风湿关节炎大鼠踝关节破坏的影响实验研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2024,53(12):1624-1628+1639. [62] 李光淳,李高峰,张兆琦,等.枸杞多糖对类风湿关节炎大鼠炎症反应及TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2024,44(5):1119-1124. [63] 刘君,董秋梅.基于TLR4/NF-κB通路研究诃子多糖对CIA模型大鼠及其肠黏膜屏障的影响[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2023,25(5):1774-1781. [64] Meng M, Wang L, Yao Y, et al. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide peptide (GLPP) attenuates rheumatic arthritis in rats through inactivating NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine. 2023;119:155010. [65] 李梅,蒋锦梅,欧大明,等.白术多糖对类风湿性关节炎大鼠的抗炎作用及TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报,2022,57(4):552-557. [66] 杨梅.人参皂苷CK调节糖皮质激素受体抑制类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞活化的作用及机制[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2022. [67] 何晓丽,钟先锦,龚菊梅,等.桔梗总皂苷对胶原性关节炎大鼠的抗炎作用及对TLR/MyD88/NF-κB通路的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2021,37(8):931-935. [68] 孟庆良,孟婉婷,卞华,等.大黄素对TNF-α诱导的类风湿性关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞增殖的影响[J].中成药,2021, 43(2):480-484. [69] 管咏梅,万志艳,王舒慧,等.基于NF-κB、Nrf2/HO-1信号通路及Bcl-2/Caspase-3凋亡蛋白表达探讨雷公藤-川芎组分配伍对类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025,31(2):17-26. [70] 赵呈雷,何晶晶,王馨莹,等.全蝎-土鳖虫药对抑制NF-κB信号通路减轻胶原诱导关节炎小鼠骨破坏研究[J].中草药, 2023,54(17):5640-5648. [71] 葛珊,魏昀,吴晨,等.秦艽、威灵仙主要成分龙胆苦苷、木兰花碱对RA模型大鼠抗炎作用机制研究[J].中药药理与临床,2022,38(4):62-67. [72] 张蕊.铁棒锤诃子配伍对类风湿性关节炎的治疗作用及机制研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2022. [73] 李杰.苯甲酰乌头原碱配伍芍药苷对MH7A细胞MAPK-NF-κB信号通路的影响[D].成都:电子科技大学,2020. [74] 李玉彤,刘静淑,李振.经方二妙散通过ChAT/α7nAChR/NF-κB途径治疗胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠的作用机制研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2025,41(2):374-380+386. [75] 刘冬梅,刘润萍,曾芳馨.薏苡附子败酱散通过抗三结构域蛋白21-Toll样受体4-t-核因子-κB信号通路对类风湿关节炎MH7A细胞的影响[J].安徽医药,2024, 28(8):1512-1517. [76] 李媛媛,张碧涛,崔子龙,等.基于TLR4/NF-κB信号通路研究逍遥散对慢性心理应激加重胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠病情的调节作用[J].中华中医药杂志,2024, 39(5):2211-2218. [77] 丁明辉,曹茸,徐鹏刚,等.桂枝芍药知母汤抑制cGAS/STING/NF-κB通路对类风湿关节炎大鼠炎症活动的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2024,33(8):1053-1059. [78] Yao H, Xiang L, Huang Y, et al. Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu granules attenuate bone destruction in mice with collagen-induced arthritis by promoting mitophagy of osteoclast precursors to inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Phytomedicine. 2023; 118:154967. [79] 梁霄,李娅兰,张筠昊,等.基于TLR2/p38 MAPK/NF-κB信号通路探讨独活寄生汤对类风湿性关节炎大鼠的抗炎作用及机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2023, 29(11):43-52. [80] Xie Y, Mai CT, Zheng DC, et al. Wutou decoction ameliorates experimental rheumatoid arthritis via regulating NF-kB and Nrf2: Integrating efficacy-oriented compatibility of traditional Chinese medicine. Phytomedicine. 2021;85:153522. [81] Shen P, Lin W, Huang Y, et al. Wutou decoction attenuates rheumatoid arthritis in rats through SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of the HMGB1/NF-κB pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025;337(Pt 3):118921. [82] Lin W, Shen P, Huang Y, et al. Wutou decoction attenuates the synovial inflammation of collagen-induced arthritis rats via regulating macrophage M1/M2 type polarization. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023; 301:115802. [83] Li W, Wang K, Liu Y, et al. A Novel Drug Combination of Mangiferin and Cinnamic Acid Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting TLR4/NFκB/NLRP3 Activation-Induced Pyroptosis. Front Immunol. 2022; 13:912933. [84] Ling Y, Yang J, Hua D, et al. ZhiJingSan Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis via Regulating RANKL/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates Bone Erosion in Collagen-Induced Mouse Arthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:693777. [85] 尹谢添,赵诗超,向楠,等.桂枝附子汤调控AGEs/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路对类风湿关节炎大鼠的影响[J].中成药,2023, 45(6):1809-1815. [86] 钱凯,郑雪霞,李海鸿,等.甘草附子汤调控NF-κB信号通路抑制胶原诱导型关节炎小鼠骨质破坏的作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(23):1-9. [87] 娄飞,周莹,蒋翠蕾,等.基于TLR4/MAPKs/NF-κB信号通路探讨蠲痹汤对寒湿痹阻证类风湿关节炎模型大鼠的治疗作用及机制研究[J].中药材,2021,44(9): 2200-2204. |
| [1] | 陈豪杰, 王 黛, 沈 山. 种植体周围炎中的免疫炎症微环境机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2054-2062. |
| [2] | 胡雄科, 刘少华, 谭 谦, 刘 昆, 朱光辉. 紫草素干预骨髓间充质干细胞改善老年小鼠股骨的微结构[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [3] | 韩念荣, 黄异飞, 艾克热木·吾斯曼, 刘岩路, 胡 炜. 高糖微环境中程序性细胞死亡受体1抑制大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1649-1657. |
| [4] | 刘安婷, 陆江涛, 张文杰, 贺 玲, 唐宗生, 陈晓玲. 血小板裂解物调控腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶抑制镉诱导的神经细胞凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1800-1807. |
| [5] | 陈 驹, 郑锦畅, 梁 振, 黄成硕, 林 颢, 曾 莉. β-石竹烯对小鼠膝骨关节炎的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347. |
| [6] | 吕国庆, 艾孜麦提江·肉孜, 熊道海. 鸢尾素抑制人关节软骨细胞中铁死亡的作用及其机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [7] | 吴治林, 何 秦, 王枰稀, 石 现, 袁 松, 张 骏, 王 浩. DYRK2:基于东亚和欧洲人群揭示类风湿关节炎合并骨质疏松症的治疗新靶点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [8] | 彭志伟, 陈 雷, 佟 磊. 木犀草素促进糖尿病小鼠创面愈合的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [9] | 朱奎成, 杜春燕, 章金涛. 无毛基因突变促进无毛小鼠白色脂肪组织褐变的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1424-1430. |
| [10] | 李 豪, 陶红成, 曾 平, 刘金富, 丁 强, 牛驰程, 黄 凯, 康宏誉. 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路调控骨关节炎的发生发展:指导中药靶点治疗[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1476-1485. |
| [11] | 郭 英, 田 峰, 王春芳. 类风湿关节炎潜在药物靶点:来自欧洲数据库的大样本分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [12] | 刘新月, 李春年, 李一卓, 徐世芳. 口腔牙槽骨缺损的再生修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [13] | 郑 银, 吴振桦, 张 成, 阮可馨, 刚骁琳, 汲 泓. 免疫吸附治疗类风湿关节炎的安全性和有效性:网状Meta分析和系统评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [14] | 陈伊娴, 陈 晨, 卢立恒, 汤锦鹏, 于晓巍. 雷公藤甲素治疗骨关节炎的网络药理学分析与实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [15] | 包卓玛, 侯孜明, 江 露, 李玮怡, 张宗星, 刘道忠, 袁 林. 枫杨总黄酮调控类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞增殖、迁移及凋亡的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 816-823. |
核因子κB信号通路是细胞内参与炎症、代谢和免疫等重要生物学行为的信号通路[6],在类风湿关节炎的生理病理中发挥重要的作用。近年来多项研究证实,中医药可以多靶向调节核因子κB信号通路治疗类风湿关节炎[7]。此篇文章通过阅读相关文献,介绍了核因子κB信号通路调控类风湿关节炎的作用机制,并通过检索近5年中国知网(CNKI)、PubMed数据库,对中药单体、药对及复方通过调节该通路影响类风湿关节炎的研究进行系统的总结和归纳,以期为临床上中医药治疗类风湿关节炎和创新药物的研发提供参考依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索时间 在2025年3月进行检索。
1.1.2 来源文献时限 检索以2016年3月至2025年3月为主的相关文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网、PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索途径 主题词检索。
1.1.5 检索词 英文检索词为:“NF-κB,rheumatoid arthritis,Traditional Chinese Medicine,bone injury,TCM monomeric compounds,TCM herb pairs,TCM compound formulations,Research Progress”中文检索词为:“NF-κB,类风湿关节炎,中医药,骨损伤,中药单体,中药药对,中药复方,研究进展”
1.1.6 检索文献类型 研究原著、期刊、综述。
1.1.7 检索策略 中英文数据库检索策略图为例,见图1。
1.2 入选标准
纳入标准:①有关核因子κB、类风湿关节炎和核因子κB介导类风湿关节炎机制的相关研究;②有关中
药单体、药对及复方通过调控核因子κB信号通路治疗类风湿关节炎的相关研究。
排除标准:①与此次研究主题相关度低的文献;②重复、过时及质量低的文献。1.3 文章质量评估 在数据库初步共检索出1 439篇文献,其中中国知网1 128篇,PubMed数据库311篇,严格按照纳入和排除标准进行筛选,最终纳入87篇文献进行综述,其中中文文献32篇,英文文献55篇。文献筛选流程图见图2。
Summary and prospects
核因子κB信号通路作为常见的炎症信号通路,被异常激活影响细胞增殖、分化、免疫抑制、炎症反应,从而加剧类风湿关节炎中骨损伤及功能丧失,严重者可致残,发生多器官病变。尽管近年来新兴靶向药物和生物制剂治疗已取得初步进展,但存在价格昂贵、药物疗效参差不齐、不良反应多等问题。面对这一困境,中医药治疗类风湿关节炎得到国内外医学界一致关注,此文章对国内外相关研究进行综述,发现中药可以通过调控核因子κB信号通路治疗类风湿关节炎,疗效颇佳且不良反应少,具有显著的优势。通过总结近5年来中医药调控核因子κB信号通路治疗类风湿关节炎的研究,发现中药单体、药对及复方能够靶向核因子κB信号通路,有效调节细胞生命活动,参与免疫细胞极化和破骨细胞形成,诱导细胞凋亡、抑制细胞增殖;提高机体免疫力,调节机体细胞因子水平和氧化应激能力,以此为类风湿关节炎的发病机制及治疗手段提供新的参考价值和理论依据。
尽管中医药通过调控核因子κB信号通路在治疗类风湿关节炎上取得一系列进展,但仍存在一些问题亟待解决:首先,目前研究工作主要局限于分子和细胞层面的基础研究,对核因子κB不同蛋白亚型发挥的的特异性作用研究甚少,且对多器官交互网络的调控机制研究具有一定局限性,需进一步深入探讨;第二,在复方的研究中,未深入探究不同的煎煮时长和煎煮方法对该信号通路的激活可能产生的不同影响;第三,方剂中各单体存在易挥发、难溶于水、易氧化变质等特性,剂型不同,则意味着方剂中各中药单体不同的形态和性能,是否应该合理改变方剂剂型以提高药物生物利用度,有待进一步探索;第四,在核因子κB信号通路对类风湿关节炎的调控机制中,也涉及到磷脂酰肌醇 3-激酶/蛋白激酶B、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、Janus激酶/信号转导与转录激活子、Wnt/β-连环蛋白和核因子E2相关因子2等通路,例如钩藤碱通过上调SOCS3抑制NOD2/核因子κB信号通路,4-甲基儿茶酚可同时作用于核因子E2相关因子2/HO-1和核因子κB/NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3信号通路;不同通路之间产生的级联放大效应和多因子协同作用机制难以明确。鉴于此,未来研究需聚焦分子-细胞-器官-整体的多尺度交互网络,突破传统单靶点研究的局限性,深入研究煎煮方法及煎煮时长对该通路产生的不同影响;在临床转化方面,应结合现代医学最新研究技术及实验手段,量化采集数据,采用多批次、小批量的形式,开发新的药剂剂型、优化给药途径,拓展功能主治,并将“整体观念”运用于实验中,为中医药治疗类风湿关节炎提供更加完善、科学、准确的治疗方略。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||