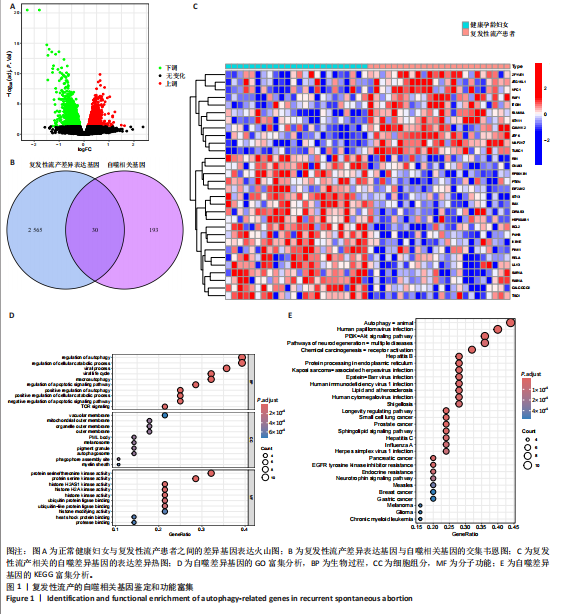
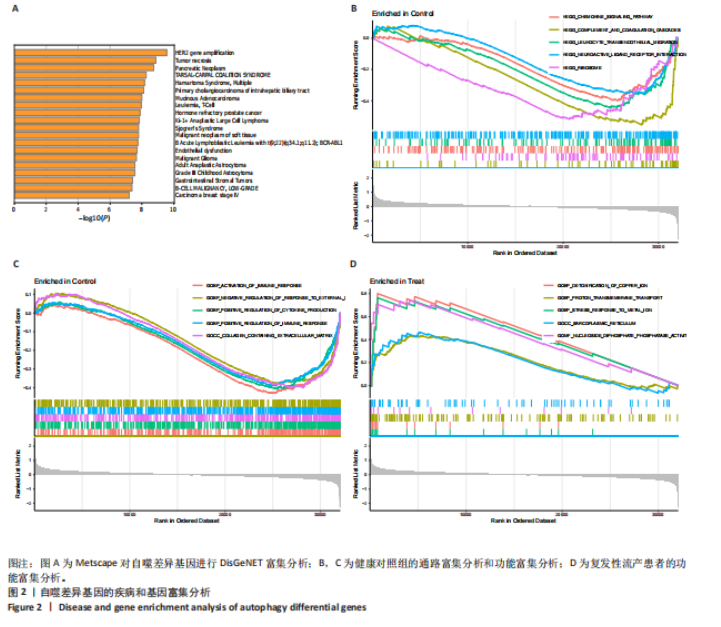
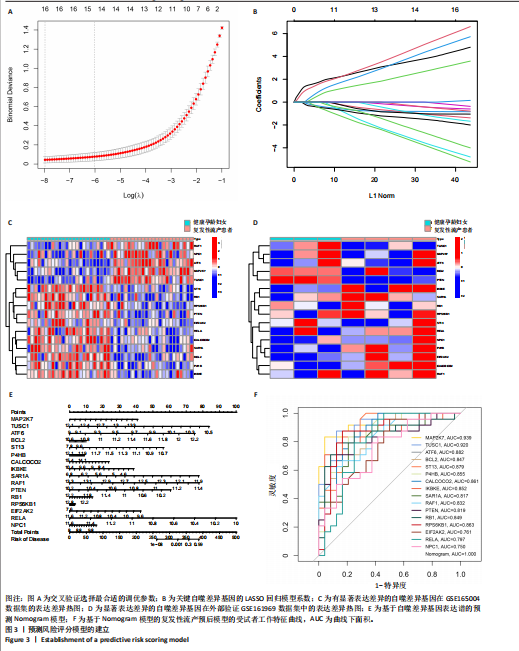
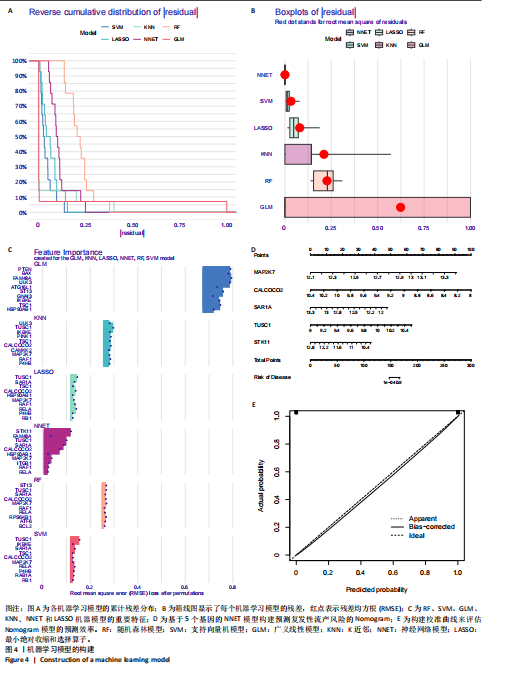
[1] WANG J, HAN T, ZHU X. Role of maternal-fetal immune tolerance in the establishment and maintenance of pregnancy. Chin Med J (Engl). 2024;137(12):1399-1406.
[2] LIN M, XU H, QIU J. Inflammation in recurrent miscarriage-a comprehensive perspective from uterine microenvironment and immune cell imbalance to therapeutic strategies. Ginekol Pol. 2023; 95(4):266-275.
[3] VAN WELY M. Series of overviews on miscarriage and recurrent miscarriage. Fertil Steril. 2023;120(5):932-933.
[4] BILIBIO JP, GAMA TB, NASCIMENTO ICM, et al. Causes of recurrent miscarriage after spontaneous pregnancy and after in vitro fertilization. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2020;83(5):e13226.
[5] YAMAGUCHI N, TAKAKURA Y, AKIYAMA T. Autophagy and proteasomes in thymic epithelial cells: essential bulk protein degradation systems for immune homeostasis maintenance. Front Immunol. 2023;15:1488020.
[6] PARZYCH KR, KLIONSKY DJ. An overview of autophagy: morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox Sign. 2014;20(3):460-473.
[7] SHAN D, DONG R, HU Y. Current understanding of autophagy in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Placenta. 2021;115:53-59.
[8] ZHANG L, DONG Y, XU X, et al. The role of autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(2):141-145.
[9] QIN Q, GU Z, LI F, et al. A Diagnostic Model for Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Blood Levels of Autophagy-Related Genes. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:881890.
[10] GHARTEY-KWANSAH G, ADU-NTI F, ABOAGYE B, et al. Autophagy in the control and pathogenesis of parasitic infections. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:101.
[11] YANG S, WANG H, LI D, et al. Role of Endometrial Autophagy in Physiological and Pathophysiological Processes. J Cancer. 2019;10(15):3459-3471.
[12] ZHAO J, XU Z, XIE J, et al. The novel lnc-HZ12 suppresses autophagy degradation of BBC3 by preventing its interactions with HSPA8 to induce trophoblast cell apoptosis. Autophagy. 2024;20(10):2255-2274.
[13] YE Z, MENG Q, ZHANG W, et al. Exploration of the Shared Gene and Molecular Mechanisms Between Endometriosis and Recurrent Pregnancy Loss. Front Vet Sci. 2022;9:867405.
[14] XING ZY, LIU W, XING RJ, et al. Integrated analysis ceRNA network of autophagy-related gene RNF144B in steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):28737.
[15] BUSNELLI A, GAROLLA A, TERSIGNI C, et al. Sperm human papillomavirus infection and risk of idiopathic recurrent pregnancy loss: insights from a multicenter case-control study. Fertil Steril. 2023; 119(3):410-418.
[16] WANG R, DAI F, DENG Z, et al. ITGA3 participates in the pathogenesis of recurrent spontaneous abortion by downregulating ULK1-mediated autophagy to inhibiting trophoblast function. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00563.2024.
[17] YANG Y, LIU B, TIAN J, et al. Vital role of autophagy flux inhibition of placental trophoblast cells in pregnancy disorders induced by HEV infection. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2023;12(2):2276336.
[18] ZHAO X, JIANG Y, JIANG T, et al. Physiological and pathological regulation of autophagy in pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020; 302(2):293-303.
[19] SU Y, ZHANG JJ, HE JL, et al. Endometrial autophagy is essential for embryo implantation during early pregnancy. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020; 98(4):555-567.
[20] DENG T, WU X, WANG Y, et al. Toe1 promotes proliferation and differentiation of neural progenitor cells. Heliyon. 2024;10(20):e39535.
[21] TIAN W, LIAO H, LI N, et al. Monomethyl Phthalate Causes Early Embryo Development Delay, Apoptosis, and Energy Metabolism Disruptions Through Inducing Redox Imbalance. Reprod Sci. 2024;31(1):139-149.
[22] TIAN M, ZHANG Y, LIU Z, et al. The PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathway is altered in pre-eclampsia and regulates T cell responses in pre-eclamptic rats. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27683.
[23] HEYDARIFARD Z, ZADHEIDAR S, YAVARIAN J, et al. Potential role of viral infections in miscarriage and insights into the underlying molecular mechanisms. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2022;62(2):54-67.
[24] ALNAES-KATJAVIVI P, ROALD B, STAFF AC. Uteroplacental acute atherosis in preeclamptic pregnancies: Rates and clinical outcomes differ by tissue collection methods. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020;19:11-17.
[25] MATSUZAKI S, GREMEAU AS, POULY JL. Impaired pathogen-induced autophagy and increased IL-1β and TNFα release in response to pathogenic triggers in secretory phase endometrial stromal cells of endometriosis patients. Reprod Biomed Online. 2020;41(5):767-781.
[26] LIU J, CHAKRABORTY C, GRAHAM CH, et al. Noncatalytic domain of uPA stimulates human extravillous trophoblast migration by using phospholipase C, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase. Exp Cell Res. 2003;286(1):138-151.
[27] LIU J, PUSCHECK EE, WANG F, et al. Serine-threonine kinases and transcription factors active in signal transduction are detected at high levels of phosphorylation during mitosis in preimplantation embryos and trophoblast stem cells. Reproduction. 2004;128(5):643-654.
[28] BRUNO MT, CARUSO S, SCALIA G, et al. Papillomavirus Infection as Potential Cause of Miscarriage in the Early Gestational Age: A Prospective Study. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023;13(9):1659.
[29] MA N, LIU B, JIN Y, et al. Aquaporin 9 causes recurrent spontaneous abortion by inhibiting trophoblast cell epithelial-mesenchymal transformation and invasion through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Biol Reprod. 2023;109(5):736-748.
[30] SUN C, ROSENSTOCK TR, COHEN MA, et al. Autophagy Dysfunction as a Phenotypic Readout in hiPSC-Derived Neuronal Cell Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2549:103-136.
[31] RANA T, BEHL T, SEHGAL A, et al. Exploring the Role of Autophagy Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol Neurobiol. 2021; 58(10):4886-4905.
[32] BOUDY AS, FERRIER C, SELLERET L, et al. Prognosis of HER2-positive pregnancy-associated breast cancer: Analysis from the French CALG (Cancer Associé à La Grossesse) network. Breast. 2020;54:311-318.
[33] RAY D, YUN YC, IDRIS M, et al. A tumor-associated splice-isoform of MAP2K7 drives dedifferentiation in MBNL1-low cancers via JNK activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(28):16391-16400.
[34] HE S, NING Y, MA F, et al. IL-23 Inhibits Trophoblast Proliferation, Migration, and EMT via Activating p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Promote Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022;32(6):792-799.
[35] HAM J, SONG J, SONG G, et al. Oryzalin impairs maternal-fetal interaction during early pregnancy via ROS-mediated P38 MAPK/AKT and OXPHOS downregulation. Food Chem Toxicol. 2023;174:113665.
[36] SANG W, YAN X, WANG L, et al. CALCOCO2 prevents AngII-induced atrial remodeling by regulating the interaction between mitophagy and mitochondrial stress. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;140:112841.
[37] YAMANO K, YOULE RJ. Two different axes CALCOCO2-RB1CC1 and OPTN-ATG9A initiate PRKN-mediated mitophagy. Autophagy. 2020; 16(11):2105-2107.
[38] YAN C, GONG L, CHEN L, et al. PHB2 (prohibitin 2) promotes PINK1-PRKN/Parkin-dependent mitophagy by the PARL-PGAM5-PINK1 axis. Autophagy. 2020;16(3):419-434.
[39] ZHAO Y, LIANG Y, CAI L, et al. Comprehensive Proteomic Analysis Reveals Distinct Features and a Diagnostic Biomarker Panel for Early Pregnancy Loss in Histological Subtypes. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2024;23(11):100848.
[40] XIAO J, LI W, LI G, et al. STK11 overexpression prevents glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis via activating the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α axis. Hum Cell. 2022;35(4):1045-1059.
[41] HUANG Y, ZHANG H, FENG J, et al. STK11 mutation affects the killing effect of NK cells to promote the progression of lung adenocarcinoma. APMIS. 2022;130(11):647-656.
[42] ALHARBI KK, KHAN IA, ELDESOUKY MH, et al. The genetic polymorphism in the STK11 does not affect gestational diabetes. Acta Biochim Pol. 2015;62(3):569-572.
|