[1] PYE SR, REID DM, LUNT M, et al. Lumbar disc degeneration: association between osteophytes, end-plate sclerosis and disc space narrowing. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(3):330-333.
[2] JUNGHANNS H, GEORG S. The human spine in health and disease. New York: Grune & Stratton, 1971:xi, 504-xi, 504.
[3] PRANEATPOLGRANG S, DAS S, NAVIC P, et al. Age-related changes in the vertebral osteophytes: a review. Int Med J. 2020;27(2):181-184.
[4] CHANAPA P, YOSHIYUKI T, MAHAKKANUKRAUH P. Distribution and length of osteophytes in the lumbar vertebrae and risk of rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysms: a study of dry bones from Chiang Mai, Thailand. Anat Cell Biol. 2014;47(3):157-161.
[5] KASAI Y, KAWAKITA E, SAKAKIBARA T, et al. Direction of the formation of anterior lumbar vertebral osteophytes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10(4):1-6
[6] KETTLER A, ROHLMANN F, RING C, et al. Do early stages of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration really cause instability? Evaluation of an in vitro database. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(4):578-584.
[7] FUJIWARA A, LIM TH, HOWARD S, et al. The Effect of Disc Degeneration and Facet Joint Osteoarthritis on the Segmental Flexibility of the Lumbar Spine. Spine. 2000;25(23):3036-3044.
[8] FUJIWARA A, TAMAI K, HOWARD S, et al. The Relationship Between Disc Degeneration, Facet Joint Osteoarthritis, and Stability of the Degenerative Lumbar Spine. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2000;13(5):444-450.
[9] HICKS GE, MORONE N, WEINER DK. Degenerative Lumbar Disc and Facet Disease in Older Adults. Spine. 2009;34(12): 1301-1306.
[10] JOHANSSON MS, JENSEN STOCHKENDAHL M, HARTVIGSEN J, et al. Incidence and prognosis of mid-back pain in the general population: A systematic review. Eur J Pain. 201;21(1):20-28.
[11] HOMMINGA J, LEHR AM, MEIJER GJ, et al. Posteriorly directed shear loads and disc degeneration affect the torsional stiffness of spinal motion segments: a biomechanical modeling study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(21):E1313-1319.
[12] ZHANG XY, HAN Y. Comparison of the biomechanical effects of lumbar disc degeneration on normal patients and osteoporotic patients: A finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2023;112:103952.
[13] PARK JS, GOH TS, LEE JS, et al. Analyzing isolated degeneration of lumbar facet joints: implications for degenerative instability and lumbar biomechanics using finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1294658.
[14] WANG H, LI N, HUANG H, et al. Biomechanical effect of intervertebral disc degeneration on the lower lumbar spine, Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2023;26(14):1669-1677.
[15] ROHLMANN A, ZANDER T, SCHMIDT H, et al. Analysis of the influence of disc degeneration on the mechanical behaviour of a lumbar motion segment using the finite element method. J Biomech. 2006;39(13): 2484-2490.
[16] LITTLE JP, ADAM CJ, EVANS JH, et al. Nonlinear finite element analysis of anular lesions in the L4/5 intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 2007; 40(12):2744-2751.
[17] KEAVENY TM, BUCKLEY JM. Biomechanics of Vertebral Bone. Spine Technol Handbook. 2006:63-98.
[18] GALBUSERA F, SCHMIDT H, NEIDLINGER-WILKE C, et al. The mechanical response of the lumbar spine to different combinations of disc degenerative changes investigated using randomized poroelastic finite element models. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(4):563-571.
[19] DU CF, CAI XY, GUI W, et al. Does oblique lumbar interbody fusion promote adjacent degeneration in degenerative disc disease: A finite element analysis, Comput Biol Med. 2021;128:104122.
[20] SONG C, CHANG H, ZHANG D, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Various Fixation Options: A Finite Element Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(2):517-529.
[21] CAI XY, SUN MS, HUANG YP, et al. Biomechanical effect of L4–L5 intervertebral disc degeneration on the lower lumbar spine: a finite element study. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):917-930.
[22] MENGONI M. Biomechanical modelling of the facet joints: a review of methods and validation processes in finite element analysis. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021;20(2):389-401.
[23] RENNER SM, NATARAJAN RN, PATWARDHAN AG, et al. Novel model to analyze the effect of a large compressive follower pre-load on range of motions in a lumbar spine. J Biomech. 2007;40(6):1326-1332.
[24] ZHU R, NIU WX, WANG ZP, et al. The Effect of Muscle Direction on the Predictions of Finite Element Model of Human Lumbar Spine. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:4517471.
[25] BELAID D, VENDEUVRE T, BOUCHOUCHA A, et al. Utility of cement injection to stabilize split-depression tibial plateau fracture by minimally invasive methods: A finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2018;56:27-35.
[26] DEHOUST J, MÜNCH M, SEIDE K, et al. Biomechanical aspects of the posteromedial split in bicondylar tibial plateau fractures-a finite-element investigation. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020;46(6): 1257-1266.
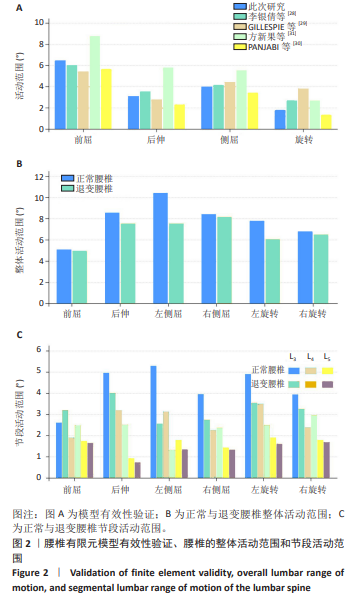
[27] 李银倩,吕杰,丁立军,等.韧带损伤影响腰椎稳定性的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(21):3286-3292.
[28] GILLESPIE KA, DICKEY JP. Biomechanical role of lumbar spine ligaments in flexion and extension: determination using a parallel linkage robot and a porcine model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(11):1208-1216.
[29] PANJABI MM, GOEL VK, TAKATA K. Physiologic strains in the lumbar spinal ligaments. An in vitro biomechanical study 1981 Volvo Award in Biomechanics. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1982;7(3):192-203.
[30] 方新果, 赵改平, 王晨曦, 等. 基于CT图像腰椎L4L5节段有限元模型建立与分析[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报,2014,33(4):487-492.
[31] PARK WM, KIM K, KIM YH. Effects of degenerated intervertebral discs on intersegmental rotations, intradiscal pressures, and facet joint forces of the whole lumbar spine. Comput Biol Med. 2013;43(9):1234-1240.
[32] RUBERTÉ LM, NATARAJAN RN, ANDERSSON GB. Influence of single-level lumbar degenerative disc disease on the behavior of the adjacent segments--a finite element model study. J Biomech. 2009; 42(3):341-348.
[33] 赵亮,闫广华,瞿东滨,等.腰椎间盘退变对软骨终板生物力学特性影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2015,33(4): 455-460.
[34] QIN DP, ZHANG XG, SON M, et al. Effect of different attributes of the mimic human lumbar spine biomechanics material structure change by finite element analysis. SN Appl Sci. 2021;3(12):880.
[35] WANG K, JIANG C, WANG L, et al. The biomechanical influence of anterior vertebral body osteophytes on the lumbar spine: A finite element study. Spine J. 2018;18(12):2288-2296.
[36] SCHMIDT H, KETTLER A, ROHLMANN A, et al. The risk of disc prolapses with complex loading in different degrees of disc degeneration - a finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2007;22(9):988-998.
[37] MIMURA M, PANJABI MM, OXLAND TR, et al. Disc degeneration affects the multidirectional flexibility of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(12):1371-1380.
[38] FELSON DT, NEOGI T. Osteoarthritis: is it a disease of cartilage or of bone? Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(2):341-344.
[39] IBARZ E, MAS Y, MATEO J, et al. Instability of the lumbar spine due to disc degeneration. A finite element simulation. Adv Biosci Biotechnol. 2013;4(4):548-556.
[40] 刘珍珍,陈建宇,钟镜联,等. 腰椎间盘退变MRI:与Modic改变相关的影像学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(52):9737-9743.
[41] 文王强,徐浩翔,张泽佩,等. 腰椎小关节退变的相关因素及生物力学特点[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(24):3883-3889.
[42] WANG YXJ, DENG M, HE LC, et al. Osteoporotic vertebral endplate and cortex fractures: A pictorial review. J Orthop Translat. 2018;15: 35-49.
[43] WILKE HJ, ROHLMANN F, NEIDLINGER-WILKE C, et al. Validity and interobserver agreement of a new radiographic grading system for intervertebral disc degeneration: Part I. Lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(6):720-730.
[44] ADAMS MA, ROUGHLEY PJ. What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2151-2161.
[45] LUOMA K, RIIHIMÄKI H, LUUKKONEN R, et al. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(4): 487-492. |