[1] POLA E, LOGROSCINO CA, GENTIEMPO M, et al. Medical and surgical treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012;16 Suppl 2:35-49.
[2] MADELAR RTR, ITO M. The Need for Comprehensive Medical Management in Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis: A Review Article. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2023;8(3):243-252.
[3] YAW TEE LY, HUNTER S, BAKER JF. BMP use in the surgical treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis: Is it safe. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;95:94-98.
[4] SKAF GS, DOMLOJ NT, FEHLINGS MG, et al. Pyogenic spondylodiscitis: an overview. J Infect Public Health. 2010;3(1):5-16.
[5] ZARAJCZYK A, PONIEWOZIK P, FIDUT N, et al. Spondylodiscitis - a silent infection with loud consequences. Wiad Lek. 2025;78(3):651-656.
[6] ZARGHOONI K, RÖLLINGHOFF M, SOBOTTKE R, et al. Treatment of spondylodiscitis. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):405-411.
[7] KARADIMAS EJ, BUNGER C, LINDBLAD BE, et al. Spondylodiscitis. A retrospective study of 163 patients. Acta Orthop. 2008;79(5):650-659.
[8] THAVARAJASINGAM SG, VEMULAPALLI KV, VISHNU KS, et al. Conservative versus early surgical treatment in the management of pyogenic spondylodiscitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):15647.
[9] LIU Y, WU T, TAN J, et al. Minimally Invasive versus Traditional Surgery: Efficacy of PELD and PLIF in Treating Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis. Med Sci Monit. 2024;30:e943176.
[10] WEI X, CHEN F, YU C, et al. Effectiveness of lumbar braces after lumbar surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024;144(4):1523-1533.
[11] KANG TW, PARK SY, OH H, et al. Risk of reoperation and infection after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and open lumbar discectomy : a nationwide population-based study. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(8):1392-1399.
[12] WANG D, WEN J, XUE W, et al. [Channel-assisted minimally invasive interbody fusion and short segmental vertebral fixation for the treatment of non-specific lumbar intervertebral infection]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020;33(9):848-852.
[13] YAMADA K, TAKAHATA M, NAGAHAMA K, et al. Posterolateral full-endoscopic debridement and irrigation is effective in treating thoraco-lumbar pyogenic spondylodiscitis, except in cases with large abscess cavities. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(3):859-866.
[14] SCHATLO B, ROHDE V, ABBOUD T, et al. The Role of Diskectomy in Reducing Infectious Complications after Surgery for Lumbar Spondylodiscitis. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2023;84(1):3-7.
[15] 黄群,朱现玮,严飞,等.经皮椎间孔镜下病灶清除治疗腰椎间隙感染的疗效分析[J].骨科,2022,13(2):97-101.
[16] 陈志达,宋超,林斌,等.斜外侧椎间融合术治疗单节段非特异性腰椎间隙感染的临床疗效分析[J].骨科,2022,13(2):102-109.
[17] WU Z, SUN H, ZHANG Y, et al. Biomechanical Finite Element Analysis of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy via a Transforaminal Approach. World Neurosurg. 2024;185:e291-e298.
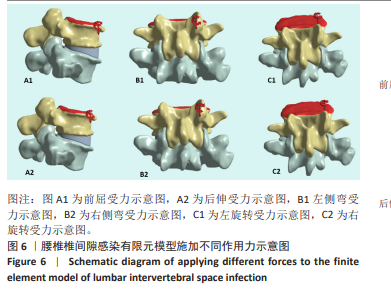
[18] 史经甫,吴东迎,袁峰,等.椎间孔镜术中行关节突成形有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2023,44(6):912-916.
[19] SUN W, LI D, ZHAO S, et al. The effect of large channel-based foraminoplasty on lumbar biomechanics in percutaneous endoscopic discectomy: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):402.
[20] CAO L, LIU Y, MEI W, et al. Biomechanical changes of degenerated adjacent segment and intact lumbar spine after lumbosacral topping-off surgery: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):104.
[21] SHI Y, XIE YZ, ZHOU Q, et al. The biomechanical effect of the relevant segments after facet-disectomy in different diameters under posterior lumbar percutaneous endoscopes: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):593.
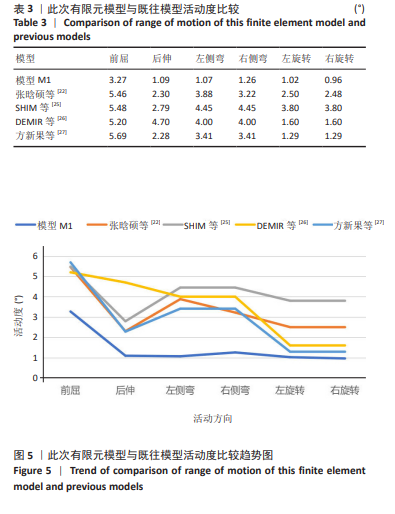
[22] 张晗硕,丁宇,蒋强,等.脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压与单侧入路双侧减压治疗腰椎管狭窄症的生物力学稳定性及有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(13):1981-1986.
[23] THEODOROU S, THEODOROU D, KAKITSUBATA Y, et al. Advanced ankylosing spondylitis: a multisite, multimodality densitometric analysis for investigation of bone loss in the axial and appendicular skeleton. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2021;67(11):1627-1632.
[24] KIM AS, TAYLOR VE, CASTRO-MARTINEZ A, et al. Early and multiple doses of zoledronate mitigates rebound bone loss following withdrawal of RANKL inhibition. J Bone Miner Res. 2025;40(3):413-427.
[25] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al.Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(22):E820-827.
[26] DEMIR E, ELTES P, CASTRO AP, et al.Finite element modelling of hybrid stabilization systems for the human lumbar spine. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2020;234(12):1409-1420.
[27] 方新果,赵改平,王晨曦,等.基于CT图像腰椎L4-L5节段有限元模型建立与分析[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2014,31(4):487-492.
[28] DING Y, ZHANG H, JIANG Q, et al. Finite element analysis of endoscopic cross-overtop decompression for single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis based on real clinical cases. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1393005.
[29] FAROOQI AS, NARAYANAN R, CANSECO JA, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Corticopedicular Spine Fixation versus Pedicle Screw Fixation in a Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Finite Element Analysis Model. World Neurosurg. 2024;190:e129-e136.
[30] LIU C, KAMARA A, YAN Y. Investigation into the biomechanics of lumbar spine micro-dynamic pedicle screw. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018; 19(1):231.
[31] RANA M, ROY S, BISWAS P, et al. Design and development of a novel expanding flexible rod device (FRD) for stability in the lumbar spine: A finite-element study. Int J Artif Organs. 2020;43(12):803-810.
[32] WEI W, WANG T, LIU J, et al. Biomechanical effect of proximal multifidus injury on adjacent segments during posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):521.
[33] 陈树东,李永津,杜炎鑫,等.经皮内镜病灶清除及灌洗引流治疗腰椎间隙感染15例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(8):59-62.
[34] LAWSON MCLEAN A, SENFT C, SCHWARZ F. Management of Lumbar Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis in Germany: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Spine Specialists. World Neurosurg. 2023;173:e663-e668.
[35] CHEN ZH, WANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Debridement and Drainage with Accurate Pathogen Detection for Infectious Spondylitis of the Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Spine. World Neurosurg. 2022;164:e1179-e1189.
[36] LI Z, HE M, CHEN X, et al. Single-stage posterior resection of the transversal process combined with an intervertebral foraminal approach for debridement, interbody fusion, internal fixation for the treatment of lumbar tuberculosis and psoas major abscess. Int Orthop. 2022;46(2):331-339.
[37] YEUNG AT. Minimally Invasive Disc Surgery with the Yeung Endoscopic Spine System (YESS). Surg Technol Int. 1999;8:267-277.
[38] ITO M, ABUMI K, KOTANI Y, et al. Clinical outcome of posterolateral endoscopic surgery for pyogenic spondylodiscitis: results of 15 patients with serious comorbid conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(2):200-206.
[39] LIM JS, KIM TH. Recurrence Rates and Its Associated Factors after Early Spinal Instrumentation for Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis: A Nationwide Cohort Study of 2148 Patients. J Clin Med. 2022;11(12):3356.
[40] FAROOQI AS, NARAYANAN R, CANSECO JA, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Corticopedicular Spine Fixation versus Pedicle Screw Fixation in a Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Finite Element Analysis Model. World Neurosurg. 2024;190:e129-e136.
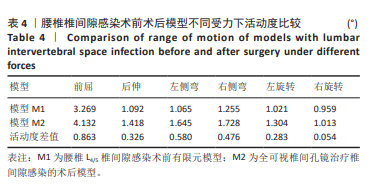
[41] MIYASAKA K, OHMORI K, SUZUKI K, et al. Radiographic analysis of lumbar motion in relation to lumbosacral stability. Investigation of moderate and maximum motion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(6): 732-737.
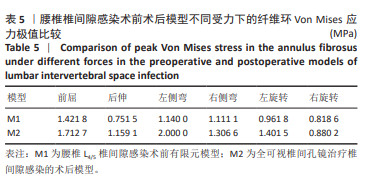
[42] LI L, SHEN T, LI YK. A Finite Element Analysis of Stress Distribution and Disk Displacement in Response to Lumbar Rotation Manipulation in the Sitting and Side-Lying Positions. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2017;40(8):580-586. |