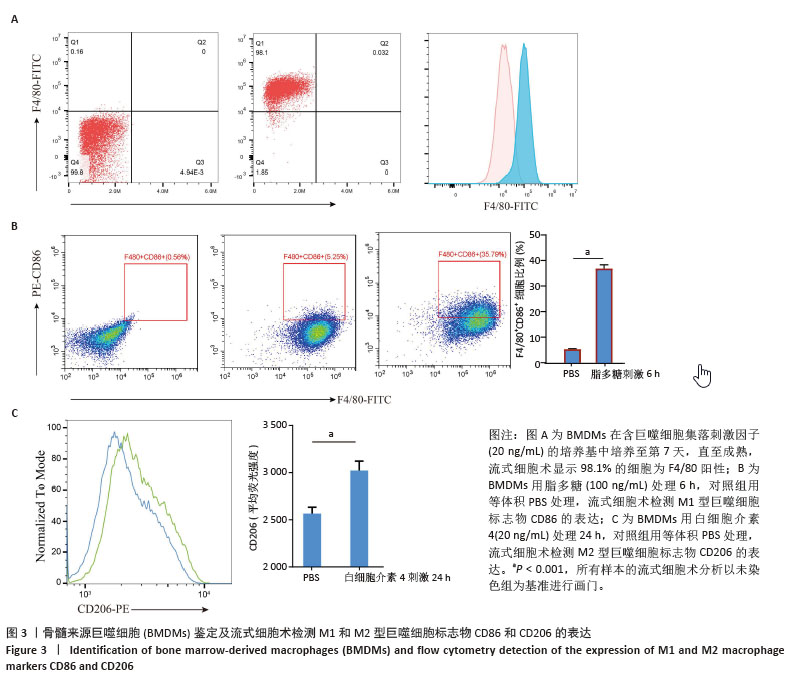
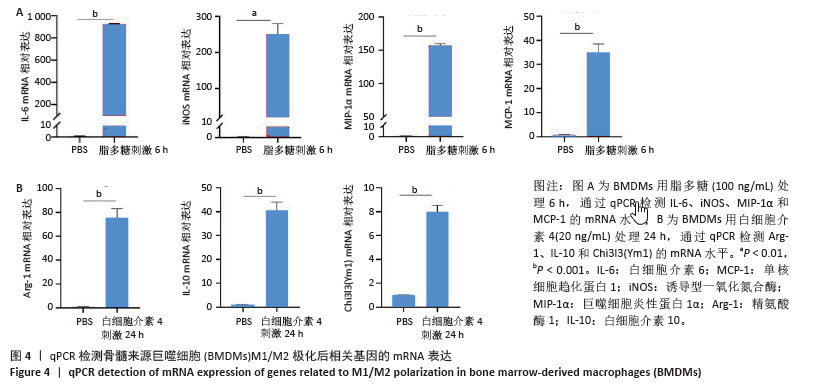
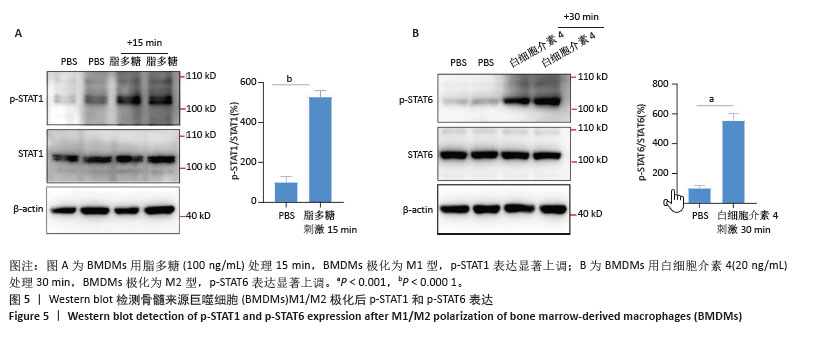
[1] GORDON S, MARTINEZ FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. 2010;32(5):593-604.
[2] ABDOLLAHI E, SAGHAFI N, HASANZADE M. Are M1 and M2 macrophages effectual players in pathological conditions. Proc Anticancer Res. 2022;6(3):34-41.
[3] MURRAY PJ, ALLEN JE, BISWAS SK, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41(1):14-20.
[4] KADOMOTO S, IZUMI K, MIZOKAMI A. Macrophage Polarity and Disease Control. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):144.
[5] RUYTINX P, PROOST P, VAN DAMME J, et al. Chemokine-Induced Macrophage Polarization in Inflammatory Conditions. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1930.
[6] SICA A, MANTOVANI A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(3):787-795.
[7] BIDAULT G, VIRTUE S, PETKEVICIUS K, et al. SREBP1-induced fatty acid synthesis depletes macrophages antioxidant defences to promote their alternative activation. Nat Metab. 2021;3(9):1150-1162.
[8] 高煜茹,王涛.肺泡巨噬细胞极化及凋亡在脓毒症急性肺损伤中作用机制的研究进展[J].中国现代医药杂志,2022,24(11):99-104.
[9] CHEN R, ZHENG S, ZHAO X, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of macrophages by a nano-sized opsonization strategy to restore M1/M2 balance for osteoarthritis therapy. J Control Release. 2025; 380:469-489.
[10] YU T, GAN S, ZHU Q, et al. Modulation of M2 macrophage polarization by the crosstalk between Stat6 and Trim24. Nat Commun. 2019; 10(1):4353.
[11] SO Y, YIM D, KIM HK, et al. Functional Nanosheet Immunoswitches Reprogramming Innate Macrophages for Immunotherapy of Colorectal Cancer and Sepsis. ACS Nano. 2025;19(5):5165-5177.
[12] 薛翔,刘红梅,邵旦兵,等.JAK/STAT信号通路调节机制的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(11):2161-2165.
[13] YU J, LI P, LI Z, et al. Topical Administration of 0.3% Tofacitinib Suppresses M1 Macrophage Polarization and Allograft Corneal Rejection by Blocking STAT1 Activation in the Rat Cornea. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022;11(3):34.
[14] 汤祥瑞,张勇,祝领,等.晚期糖基化产物通过RAGE/TLR4/STAT1信号通路诱导巨噬细胞M1型极化[J].安徽医科大学学报,2021, 56(5):751-756.
[15] OH H, PARK SH, KANG MK, et al. Asaronic Acid Attenuates Macrophage Activation toward M1 Phenotype through Inhibition of NF-κB Pathway and JAK-STAT Signaling in Glucose-Loaded Murine Macrophages. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(36):10069-10078.
[16] CHAO H, ZHENG L, HSU P, et al. IL-13RA2 downregulation in fibroblasts promotes keloid fibrosis via JAK/STAT6 activation. JCI Insight. 2023; 8(6):e157091.
[17] BONELLI M, KERSCHBAUMER A, KASTRATI K, et al. Selectivity, efficacy and safety of JAKinibs: new evidence for a still evolving story. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83(2):139-160.
[18] SEDANO R, MA C, JAIRATH V, et al. Janus Kinase Inhibitors for the Management of Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2022;18(1):14-27.
[19] SCHLUNDT C, EL KHASSAWNA T, SERRA A, et al. Macrophages in bone fracture healing: Their essential role in endochondral ossification. Bone. 2018;106:78-89.
[20] CHEN S, SAEED AFUH, LIU Q, et al. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):207.
[21] CASSETTA L, POLLARD JW. Targeting macrophages: therapeutic approaches in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17(12):887-904.
[22] SU P, LI O, KE K, et al. Targeting tumor‑associated macrophages: Critical players in tumor progression and therapeutic strategies (Review). Int J Oncol. 2024;64(6):60.
[23] SINDER BP, PETTIT AR, MCCAULEY LK. Macrophages: Their Emerging Roles in Bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(12):2140-2149.
[24] BATOON L, MILLARD SM, RAGGATT LJ, et al. Osteal macrophages support osteoclast-mediated resorption and contribute to bone pathology in a postmenopausal osteoporosis mouse model. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(11):2214-2228.
[25] KAUR S, RAGGATT LJ, BATOON L, et al. Role of bone marrow macrophages in controlling homeostasis and repair in bone and bone marrow niches. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;61:12-21.
[26] XU Y, YAN H, ZHANG X, et al. Roles of Altered Macrophages and Cytokines: Implications for Pathological Mechanisms of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:876269.
[27] WEIVODA MM, BRADLEY EW. Macrophages and Bone Remodeling. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(3):359-369.
[28] NASONOV EL, AVDEEVA AS, KOROTAEVA TV, et al.The role of interleukin 17 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Are there any prospects for the use of IL-17 inhibitors. Nauchno-Prakticheskaya Revmatologiya. 2023;61(2):165-180.
[29] 曹文琪,冯秀芝,赵奕,等.巨噬细胞极化对2型糖尿病性骨质疏松症成骨-成血管偶联的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2026,30(4): 917-925.
[30] 李平顺,王佳,田杰祥,等.由“伏毒-巨噬细胞极化-微炎症状态”路径探讨OP研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2025,31(2):222-228+312.
[31] 张洁,肖天骄,李丽,等.白细胞介素4调控巨噬细胞极化及骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(25): 3960-3966.
[32] 姚兰宣,王雪菲,刘洋,等.间充质干细胞及其衍生细胞外囊泡靶向巨噬细胞干预自身免疫性疾病[J].中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(31):6772-6781.
[33] 王文涛,侯振扬,王熠军,等.Apelin-13抑制巨噬细胞M1极化缓解全身炎症性骨丢失[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(8):1548-1555.
[34] MA PF, GAO CC, YI J, et al. Cytotherapy with M1-polarized macrophages ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating immune microenvironment in mice. J Hepatol. 2017;67(4):770-779.
[35] UNUVAR PURCU D, KORKMAZ A, GUNALP S, et al. Effect of stimulation time on the expression of human macrophage polarization markers. PLoS One. 2022;17(3):e0265196.
[36] MARTINEZ FO, GORDON S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:13.
[37] SPRENKLE NT, SEREZANI CH, PUA HH. MicroRNAs in Macrophages: Regulators of Activation and Function. J Immunol. 2023;210(4): 359-368.
[38] ZHANG X, YANG X, ZHANG S, et al. Wei-Tong-Xin exerts anti-inflammatory effects through TLR4-mediated macrophages M1/M2 polarization and affects GLP-1 secretion. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2023;75(4):574-584.
[39] ALOBAID SM, ALSHAHRANI RM, ALONAZI AS, et al. Liraglutide Attenuates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy via the ILK/PI3K/AKT/PTEN Signaling Pathway in Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024;17(3):374.
[40] CHATERJEE O, SUR D. Artificially induced in situ macrophage polarization: An emerging cellular therapy for immuno-inflammatory diseases. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;957:176006.
[41] SZULC-KIELBIK I, KIELBIK M. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Reasons to Be Cheerful, Reasons to Be Fearful. Exp Suppl. 2022;113:107-140.
[42] LIU M, LIU L, SONG Y, et al. Targeting macrophages: a novel treatment strategy in solid tumors. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):586.
[43] YING W, CHERUKU PS, BAZER FW, et al. Investigation of macrophage polarization using bone marrow derived macrophages. J Vis Exp. 2013;(76):50323.
[44] SAADE M, ARAUJO DE SOUZA G, SCAVONE C, et al. The Role of GPNMB in Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:674739.
[45] OH H, PARK SH, KANG MK, et al. Asaronic Acid Inhibited Glucose-Triggered M2-Phenotype Shift Through Disrupting the Formation of Coordinated Signaling of IL-4Rα-Tyk2-STAT6 and GLUT1-Akt-mTOR-AMPK. Nutrients. 2020;12(7):2006.
[46] PECKERT-MAIER K, LANGGUTH P, STRACK A, et al. CD83 expressed by macrophages is an important immune checkpoint molecule for the resolution of inflammation. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1085742.
[47] LUO M, ZHAO F, CHENG H, et al. Macrophage polarization: an important role in inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 2024;15: 1352946.
[48] YAO Y, XU XH, JIN L. Macrophage Polarization in Physiological and Pathological Pregnancy. Front Immunol. 2019;10:792.
[49] HALIMANI N, NESTERCHUK M, ANDREICHENKO IN, et al. Phenotypic Alteration of BMDM In Vitro Using Small Interfering RNA. Cells. 2022; 11(16):2498.
[50] TODA G, YAMAUCHI T, KADOWAKI T, et al. Preparation and culture of bone marrow-derived macrophages from mice for functional analysis. STAR Protoc. 2020;2(1):100246.
[51] ZAJD CM, ZIEMBA AM, MIRALLES GM, et al. Bone Marrow-Derived and Elicited Peritoneal Macrophages Are Not Created Equal: The Questions Asked Dictate the Cell Type Used. Front Immunol. 2020;11:269.
[52] FANG X, WU Y, QIN H, et al. Protocol for building an in vitro model of M2-like tumor-associated macrophages with lactic acid or conditioned medium from Lewis cells. STAR Protoc. 2024;5(2):103120.
[53] YIN W, WANG JH, LIANG YM, et al. Neferine Targeted the NLRC5/NLRP3 Pathway to Inhibit M1-type Polarization and Pyroptosis of Macrophages to Improve Hyperuricemic Nephropathy. Curr Mol Med. 2025;25(1):90-111. |