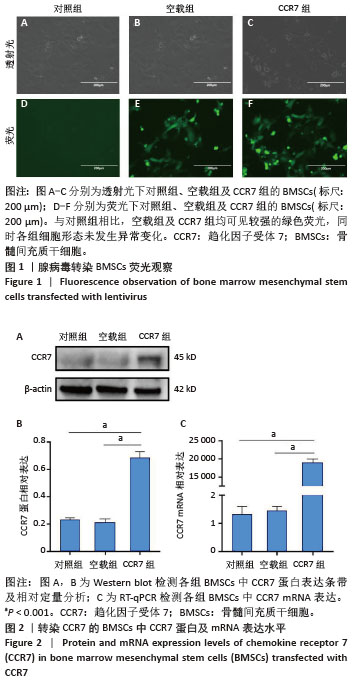
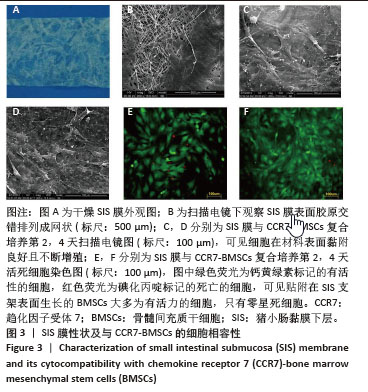
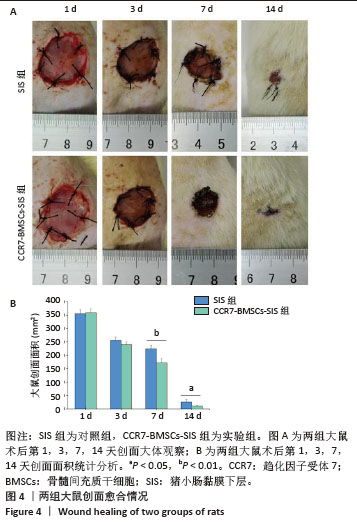
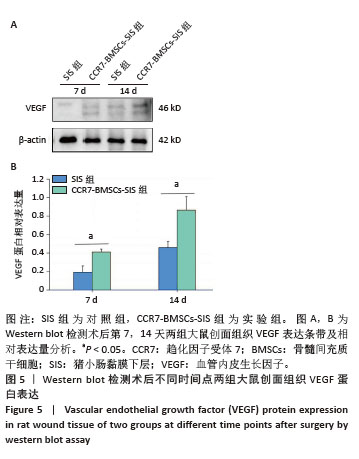
[1] HOLL J, KOWALEWSKI C, ZIMEK Z, et al. Chronic Diabetic Wounds and Their Treatment with Skin Substitutes. Cells. 2021;10(3):655.
[2] SHI CR, FERREIRA AL, KAUR M, et al. Cutaneous Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease: Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Management, and Supportive Care. Transplant Cell Ther. 2024;30(9S):S513-S533.
[3] OZHATHIL DK, TAY MW, WOLF SE, et al. A Narrative Review of the History of Skin Grafting in Burn Care. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(4):380.
[4] KHAN AA, KHAN IM, NGUYEN PP, et al. Skin Graft Techniques. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2020;37(4):821-835.
[5] COSTELLO L, DICOLANDREA T, TASSEFF R, et al. Tissue engineering strategies to bioengineer the ageing skin phenotype in vitro. Aging Cell. 2022;21(2):e13550.
[6] CHEN J, FAN Y, DONG G, et al. Designing biomimetic scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Biomater Sci. 2023;11(9):3051-3076.
[7] ZHAO Y, PENG H, SUN L, et al. The application of small intestinal submucosa in tissue regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2024;26:101032.
[8] FUJII M, TANAKA R. Porcine Small Intestinal Submucosa Alters the Biochemical Properties of Wound Healing: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines. 2022;10(9):2213.
[9] JELODARI S, SADRODDINY E. Decellularization of Small Intestinal Submucosa. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1345:71-84.
[10] SUHANDI C, MOHAMMED AFA, WILAR G, et al. Effectiveness of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome on Wound Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023;20(7):1053-1062.
[11] SUKMANA BI, MARGIANA R, ALMAJIDI YQ, et al. Supporting wound healing by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) therapy in combination with scaffold, hydrogel, and matrix; State of the art. Pathol Res Pract. 2023;248:154575.
[12] POLTAVETS V, FAULKNER JW, DHATRAK D, et al. CXCR4-CCR7 Heterodimerization Is a Driver of Breast Cancer Progression. Life (Basel). 2021;11(10):1049.
[13] VAHEDI L, SHEIDAEI S, GHASEMI M, et al. Cytoplasmic CCR7 (CCR7c) Immunoexpression Is Associated with Tumor Invasion in Gastric Cancer. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2023;17(4):267-274.
[14] RIZEQ B, MALKI MI. The Role of CCL21/CCR7 Chemokine Axis in Breast Cancer Progression. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(4):1036.
[15] HE J, ZHANG X, XIA X, et al. Organoid technology for tissue engineering. J Mol Cell Biol. 2020;12(8):569-579.
[16] SPEED OE, BAREISS A, PATEL VA, et al. Otologic use of porcine small intestinal submucosal graft (biodesign): A MAUDE database review. Am J Otolaryngol. 2023;44(5):103961.
[17] ZANG C, XIAN H, ZHANG H, et al. Clinical outcomes of a novel porcine small intestinal submucosa patch for full-thickness hand skin defects: a retrospective investigation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):50.
[18] JEFFERY S. Clinical benefits of small intestinal submucosa extracellular matrix and review of the evidence. J Wound Care. 2023;32(Sup2):S11-S19.
[19] GUO X, XIA B, LU XB, et al. Grafting of mesenchymal stem cell-seeded small intestinal submucosa to repair the deep partial-thickness burns. Connect Tissue Res. 2016;57(5):388-397.
[20] LEE C, SHIM S, JANG H, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and small intestinal submucosa hydrogel composite promotes combined radiation-wound healing of mice. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(9):1048-1059.
[21] FAN MR, GONG M, DA LC, et al. Tissue engineered esophagus scaffold constructed with porcine small intestinal submucosa and synthetic polymers. Biomed Mater. 2014;9(1):015012.
[22] ROSHANGAR L, SOLEIMANI RAD J, KHEIRJOU R, et al. Skin Burns: Review of Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Wounds. 2019; 31(12):308-315.
[23] PEÑA OA, MARTIN P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(8):599-616.
[24] LIU L, ZHENG CX, ZHAO N, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Aggregation-Released Extracellular Vesicles Induce CD31+ EMCN+ Vessels in Skin Regeneration and Improve Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(20):e2300019.
[25] WEI Q, WANG Y, MA K, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Facilitate Diabetic Wound Healing Through MiR-17-5p-mediated Enhancement of Angiogenesis. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(3):1025-1040.
[26] HONG W, YANG B, HE Q, et al. New Insights of CCR7 Signaling in Dendritic Cell Migration and Inflammatory Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 841687.
[27] GERALDO LH, GARCIA C, XU Y, et al. CCL21-CCR7 signaling promotes microglia/macrophage recruitment and chemotherapy resistance in glioblastoma. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023;80(7):179.
[28] CAI QY, LIANG GY, ZHENG YF, et al. CCR7 enhances the angiogenic capacity of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells in vitro via activation of the NF-κB/VEGF signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(7):3282-3292.
[29] YUAN LH, CHEN XL, DI Y, et al. CCR7/p-ERK1/2/VEGF signaling promotes retinal neovascularization in a mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Int J Ophthalmol. 2017;10(6):862-869.
[30] NAITO H, IBA T, TAKAKURA N. Mechanisms of new blood-vessel formation and proliferative heterogeneity of endothelial cells. Int Immunol. 2020; 32(5):295-305.
[31] AHMAD A, NAWAZ MI. Molecular mechanism of VEGF and its role in pathological angiogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2022;123(12):1938-1965.
[32] QUEISSER A, SERONT E, BOON LM, et al. Genetic Basis and Therapies for Vascular Anomalies. Circ Res. 2021;129(1):155-173.
[33] DI BENEDETTO P, RUSCITTI P, BERARDICURTI O, et al. Blocking Jak/STAT signalling using tofacitinib inhibits angiogenesis in experimental arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):213.
[34] VIMALRAJ S. A concise review of VEGF, PDGF, FGF, Notch, angiopoietin, and HGF signalling in tumor angiogenesis with a focus on alternative approaches and future directions. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;221:1428-1438.
[35] FU T, SULLIVAN DP, GONZALEZ AM, et al. Mechanotransduction via endothelial adhesion molecule CD31 initiates transmigration and reveals a role for VEGFR2 in diapedesis. Immunity. 2023;56(10):2311-2324.e6.
[36] ZENG Z, CHEN H, CAI J, et al. IL-10 regulates the malignancy of hemangioma-derived endothelial cells via regulation of PCNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;688:108404. |