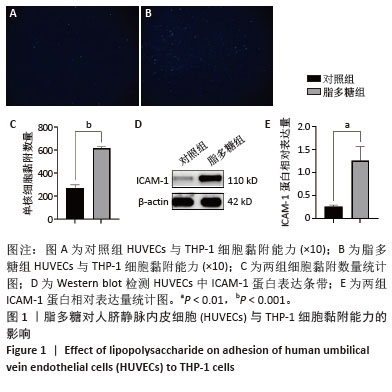
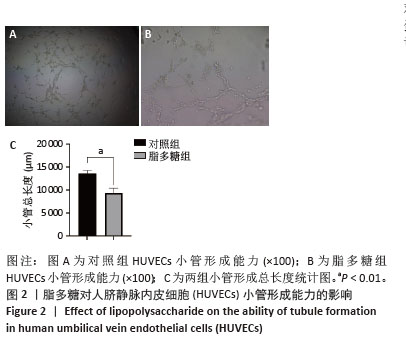
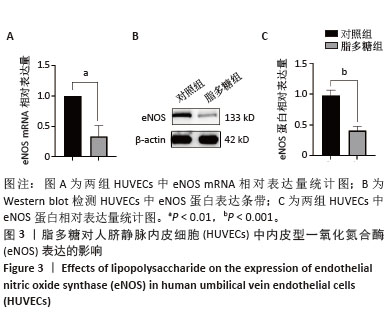
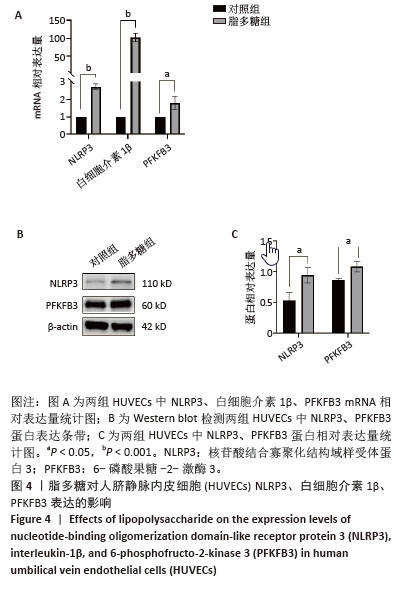
[1] 张阳,钟彦琪,邹丽,等.细胞衰老在子痫前期中的研究进展[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2023,52(6):868-872.
[2] 周玮,漆洪波.美国预防服务工作组阿司匹林预防子痫前期及相关母儿并发症的推荐[J].实用妇产科杂志,2022,38(5):346-349.
[3] PHIPPS E, PRASANNA D, BRIMA W, et al. Preeclampsia: Updates in Pathogenesis, Definitions, and Guidelines. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11(6):1102-1113.
[4] RAGUEMA N, GANNOUN MBA, ZITOUNI H, et al. Interleukin-10 rs1800871 (-819C/T) and ATA haplotype are associated with preeclampsia in a Tunisian population. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018; 11:105-110.
[5] SUBHA M, PAL P, PAL GK, et al. Decreased baroreflex sensitivity is linked to sympathovagal imbalance, low-grade inflammation, and oxidative stress in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2016; 38(8):666-672.
[6] WANG Y, LI B, ZHAO Y. Inflammation in Preeclampsia: Genetic Biomarkers, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Strategies. Front Immunol. 2022;13:883404.
[7] ZHONG Q, YAO C, ZHONG W. Causal Relationship Between Inflammation and Preeclampsia: Genetic Evidence from a Mendelian Randomization Study. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2023;26(3):231-235.
[8] LI C, TIAN Y, DOUGAREM D, et al. Systemic inflammatory regulators and preeclampsia: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Front Genet. 2024;15:1359579.
[9] SWANSON KV, DENG M, TING JP. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(8):477-489.
[10] 万玲玲,吴梦滢,张宇骄,等.炎性因子干扰素γ以焦亡途径影响人血管平滑肌细胞的迁移和凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(7):1422-1428.
[11] LIU X, LI Z, LU D. MicroRNA-223-3p downregulates the inflammatory response in preeclampsia placenta via targeting NLRP3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024;24(1):175.
[12] 杨勇,张华.TXNIP激活NLRP3炎性小体在子痫前期发病中的作用[J].重庆医科大学学报,2016,41(7):658-662.
[13] FINUCANE OM, SUGRUE J, RUBIO-ARAIZ A, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome modulates glycolysis by increasing PFKFB3 in an IL-1β-dependent manner in macrophages. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):4034.
[14] 孟炜程.NLRP3炎症小体调控红细胞中的葡萄糖酵解和释氧功能的研究[D].西安:中国人民解放军空军军医大学,2024.
[15] FULLER GG, KIM JK. Compartmentalization and metabolic regulation of glycolysis. J Cell Sci. 2021;134(20):jcs258469.
[16] VANGRIEKEN P, AL-NASIRY S, REMELS AHV, et al. Placental Methylglyoxal in Preeclampsia: Vascular and Biomarker Implications. Hypertension. 2024;81(7):1537-1549.
[17] 李琪.lncRNA MALAT1与miR-26竞争性结合调控PFKFB3介导的糖酵解在早发型子痫前期中的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学, 2021.
[18] ELLIS R, KATERELOS M, CHOY SW, et al. Increased expression and phosphorylation of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase isoforms in urinary exosomes in pre-eclampsia. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):60.
[19] TAKADA K, SUZUKAWA M, IGARASHI S, et al. Serum IgA augments adhesiveness of cultured lung microvascular endothelial cells and suppresses angiogenesis. Cell Immunol. 2023;393-394:104769.
[20] CHEN Z, WU M, HUANG H, et al. Plasma Exosomal miR-199a-5p Derived from Preeclampsia with Severe Features Impairs Endothelial Cell Function via Targeting SIRT1. Reprod Sci. 2022;29(12):3413-3424.
[21] WU Y, SUN T, MEDINA P, et al. A Novel Stem Cell Model to Study Preeclampsia Endothelial Dysfunction. Reprod Sci. 2024;31(10): 2993-3003.
[22] 陈露萍,杨轶童,赵苗苗,等.川芎嗪通过激活SIRT1信号通路减轻内皮细胞炎症损伤的机制研究[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2024, 26(9):967-973.
[23] DUNN AB, HANSON L, VANDEVUSSE L, et al. Through the Microbial Looking Glass: Premature Labor, Preeclampsia, and Gestational Diabetes: A Scoping Review. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2019;33(1):35-51.
[24] HUANG J, LIU Y, XU D, et al. Causal associations between Helicobacter pylori infection and pregnancy and neonatal outcomes: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024;14:1343499.
[25] SHEN J, HU N, WANG Z, et al. Ghrelin alleviates placental dysfunction by down-regulating NF-κB phosphorylation in LPS-induced rat model of preeclampsia. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024;972:176569.
[26] SUN J, ZHANG W. Huc-MSC-derived exosomal miR-144 alleviates inflammation in LPS-induced preeclampsia-like pregnant rats via the FosB/Flt-1 pathway. Heliyon. 2024;10(2):e24575.
[27] REN G, LIU R, MAI H, et al. GAB1 attenuates lipopolysaccharidemediated endothelial dysfunction via regulation of SOCS3. Exp Ther Med. 2024; 28(4):400.
[28] 孔稳稳,韦惠珍,徐媛颖,等.虎杖苷通过调节JAK2/STAT3信号通路改善血管内皮细胞损伤的研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2024, 59(7):1201-1205.
[29] 李淑艳,李晓峰,许星照,等.Mcc950对H2O2诱导的ARPE-19细胞炎性损伤的保护作用[J].国际眼科杂志,2018,18(9):1583-1588.
[30] EREZ O, ROMERO R, JUNG E, et al. Preeclampsia and eclampsia: the conceptual evolution of a syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022; 226(2S):S786-S803.
[31] YUNG HW, COLLEONI F, DOMMETT E, et al. Noncanonical mitochondrial unfolded protein response impairs placental oxidative phosphorylation in early-onset preeclampsia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(36):18109-18118.
[32] MENG ML, FRERE Z, FULLER M, et al. Maternal Cardiovascular Morbidity Events Following Preeclampsia: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Anesth Analg. 2023;136(4):728-737.
[33] TURBEVILLE HR, SASSER JM. Preeclampsia beyond pregnancy: long-term consequences for mother and child. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020;318(6):F1315-F1326.
[34] JUNG E, ROMERO R, YEO L, et al. The etiology of preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;226(2S):S844-S866.
[35] ATTA S, MEKKY R, IBRAHIM M, et al. Increased Expression of Neprilysin Is Associated with Inflammation in Preeclampsia. Reprod Sci. 2024; 31(5):1385-1390.
[36] GUAN X, FU Y, LIU Y, et al. The role of inflammatory biomarkers in the development and progression of pre-eclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1156039.
[37] 毛翔,蒋涵,王中群.内皮细胞在心血管疾病中的作用新进展[J].江苏大学学报(医学版),2025,35(1):86-92.
[38] ZHANG L, LI C, YANG L, et al. Estrogen Protects Vasomotor Functions in Rats During Catecholamine Stress. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8: 679240.
[39] 周彬,余舒杰,刘定辉,等.SIRT1/eNOS/NO通路在人参皂苷Rb1抗内皮细胞复制性衰老中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018, 34(10):1762-1768.
[40] 曾海龙,黄志秋,张艺能,等.p38MAPK/eNOS信号通道在胰高血糖素样肽-1抑制AGEs诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞凋亡中的作用[J].南方医科大学学报,2016,36(1):116-119.
[41] BUI TM, WIESOLEK HL, SUMAGIN R. ICAM-1: A master regulator of cellular responses in inflammation, injury resolution, and tumorigenesis. J Leukoc Biol. 2020;108(3):787-799.
[42] SHAH DA, KHALIL RA. Bioactive factors in uteroplacental and systemic circulation link placental ischemia to generalized vascular dysfunction in hypertensive pregnancy and preeclampsia. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015;95(4):211-226.
[43] 彭璇,薛立群,张居作,等.PPARγ对猪血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移及小管形成的影响[J].中国畜牧兽医,2017,44(9):2809-2815.
[44] 叶先智,姚桂芬,付守芝,等.枸杞多糖对脂多糖诱导的内皮细胞功能障碍及AKT/eNOS通路的影响[J].中国医院药学杂志,2024, 44(14):1645-1650.
[45] 王建丰,余慧林,余又新,等.METTL3介导的m6A甲基化调控脂多糖诱导的内皮细胞通透性变化[J].安徽医科大学学报,2024, 59(6):1023-1028.
[46] 卓剑,郑武平,温江华,等.血必净注射液在内皮祖细胞修复脂多糖诱导的肾内皮细胞损伤中的作用及机制[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2021,30(23):2533-2539+2595.
[47] LEE S, SHIN J, KIM JS, et al. Targeting TBK1 Attenuates LPS-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Regulating of mTORC1 Pathways in Trophoblasts. Front Immunol. 2021;12:743700.
[48] DE BOCK K, GEORGIADOU M, SCHOORS S, et al. Role of PFKFB3-driven glycolysis in vessel sprouting. Cell. 2013;154(3):651-663.
[49] 王雅萍,徐友娣,汤琳琳,等.尿酸及NLRP3炎症小体与妊娠期高血压的相关性分析[J].现代生物医学进展,2020,20(1):85-88+105. |