中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (5): 917-927.doi: 10.12307/2025.236
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
瓜蒌-薤白调节肠道菌群治疗冠心病模型大鼠的作用及机制
孙广瀚1,谢珍聪1,孙 咪2,徐 洋3,郭 栋2
- 1山东中医药大学第一临床医学院,山东省济南市 250014;山东中医药大学,2教师发展中心,3药物研究院,山东省济南市 250355
Therapeutic effect and mechanism by which Trichosanthis Fructus-Allii Macrostemonis Bulbus regulates gut microbiota in a rat model of coronary heart disease #br#
#br#
Sun Guanghan1, Xie Zhencong1, Sun Mi2, Xu Yang3, Guo Dong2
- 1The First Clinical Medical College of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 2Teacher Development Center, 3Institute of Pharmacy, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
瓜蒌-薤白:通过相互依赖、相互制约,以增强治疗痰瘀互结心血管疾病效果的经典药对。在瓜蒌-薤白白酒汤、瓜蒌-薤白半夏汤、枳实薤白桂枝汤等经典方剂中处于核心地位,反映所治病证的病机特点、治疗大法和配伍原则。
心合小肠:这一理论始载于《灵枢·本输》,认为心与小肠不仅在经络上相互属络而成表里关系,而且在生理与病理上也有密切的联系。现代医学提出肠心轴学说,即肠道菌群可以通过影响脂质代谢、自主神经系统等多个机制影响心血管系统,诠释了中医“心合小肠”的科学性。
背景:基于网络药理学方法发现瓜蒌-薤白药对中主要生物活性化合物对冠心病有多功能作用;然而其治疗冠心病的机制尚未得到充分阐释。
目的:探讨瓜蒌-薤白通过调节肠道微生物的组成改善冠心病的作用及机制。
方法:40只SD大鼠按随机数字表法分为空白组、模型组、阳性药组、药对组,除空白组外,其余大鼠连续灌胃脂肪乳剂和注射垂体后叶素制备冠心病大鼠模型。造模后模型组大鼠灌胃蒸馏水(10 mL/kg)进行对照,阳性药组大鼠每日灌胃辛伐他汀4 mg/kg,药对组每日灌胃瓜蒌-薤白7.56 g/kg,各组大鼠给药均为14 d。观察大鼠心电图、心肌病理及血脂变化,并通过16S rDNA测序技术研究大鼠经干预后肠道微生物结构。
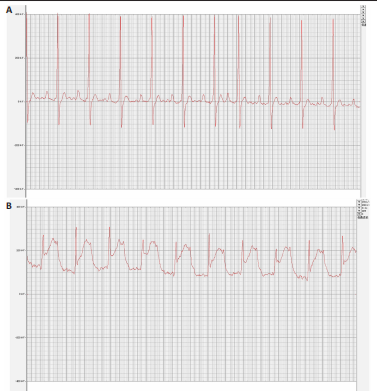
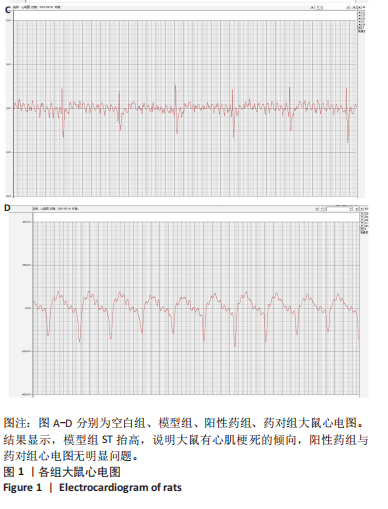
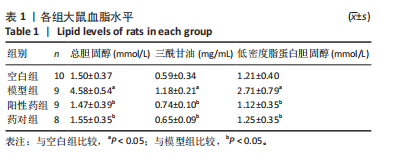
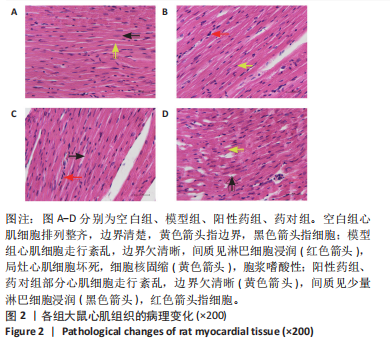
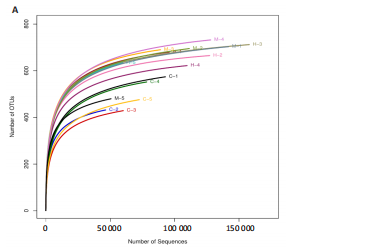
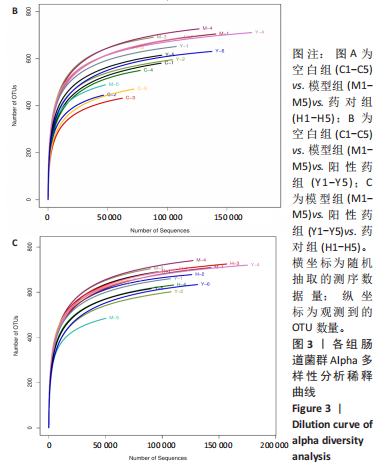
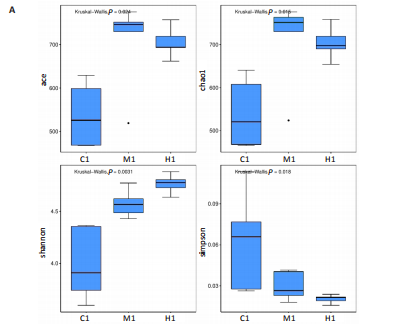
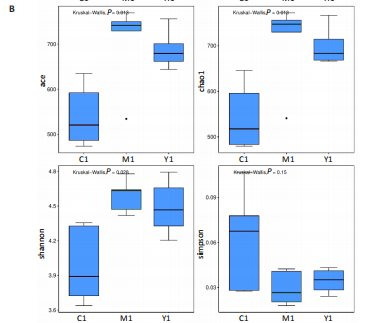
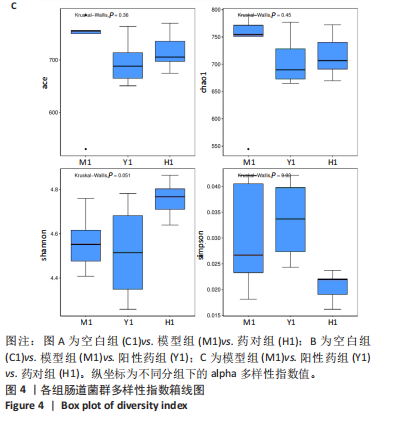
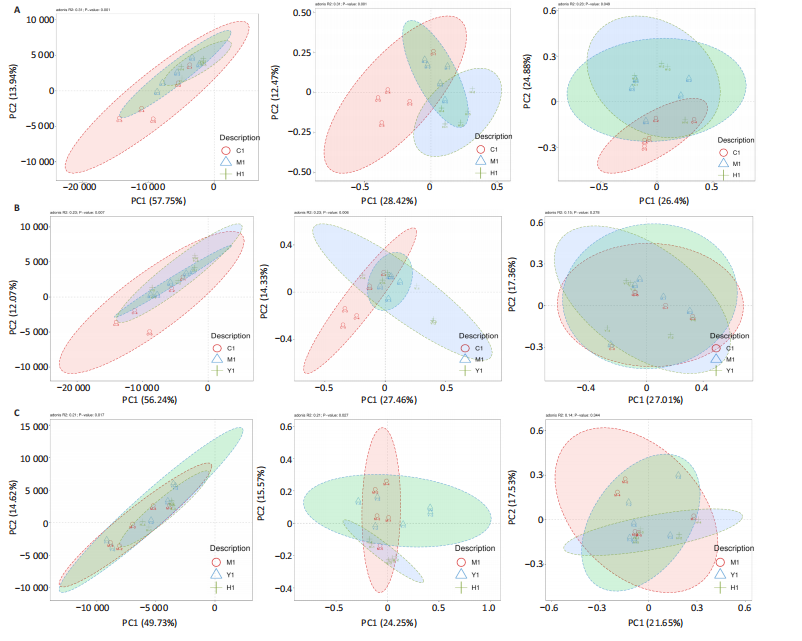
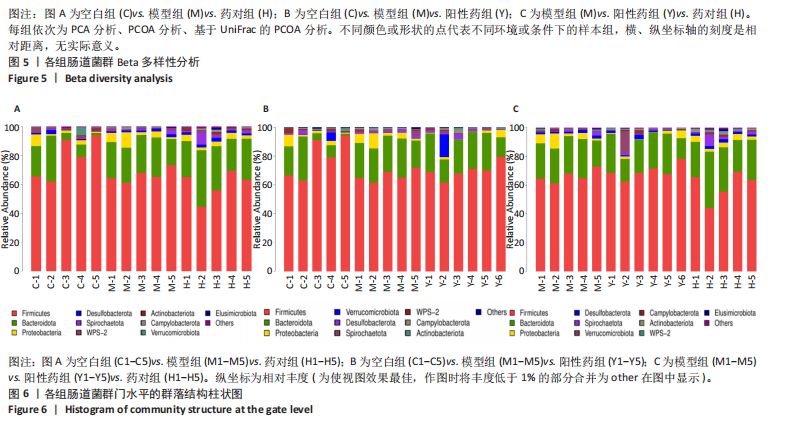
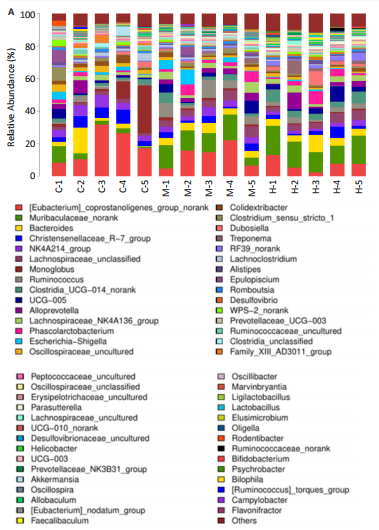
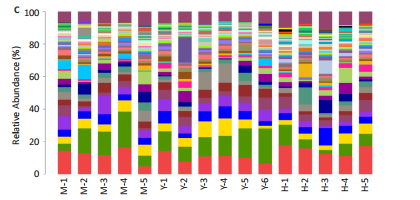
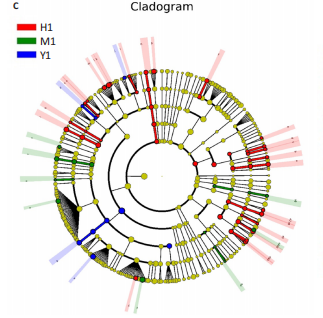
结果与结论:①心电图结果显示模型组ST抬高;阳性药组与药对组心电图无明显问题。②与空白组相比,模型组总胆固醇、三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平均显著增高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,阳性药组、药对组总胆固醇、三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平均显著下降(P < 0.05)。③与空白组相比,模型组局灶心肌细胞坏死;阳性药组、药对组部分心肌细胞走行紊乱。④与空白组比较,模型组、药对组及阳性药组的Ace、Shannon、Chao指数升高(P < 0.05),Simpson指数降低(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,阳性药组、药对组的Ace、Chao指数降低(P < 0.05),Shannon指数无差异(P > 0.05),Simpson指数降低(P < 0.05)。⑤与空白组相比,模型组Desulfovibrionia、Muribaculaceae_norank等相对丰度升高,Clostridia、[Eubacterium]_coprostanoligenes_group_norank等相对丰度降低;与模型组相比,药对组WPS-2_norank、Muribaculaceae_norank等相对丰度升高,Clostridia、[Eubacterium]_coprostanoligenes_group_norank等相对丰度降低;阳性药组Desulfobacterota、[Eubacterium]_coprostanoligenes_group_norank等相对丰度升高,Firmicutes、Muribaculaceae_norank等相对丰度降低;与阳性药相比,药对组Desulfobacterota、Bacteroides等相对丰度升高,Firmicutes、[Eubacterium]_coprostanoligenes_group_norank等相对丰度降低;LEfSe结果发现差异显著的种群富集于药对组最多,其次是空白组、阳性药组,模型组最少。⑥结论:瓜蒌-薤白可以通过调节肠道菌群改善冠心病的发生发展,为进一步研发瓜蒌-薤白提供新的启示。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0809-2291(孙广瀚)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: