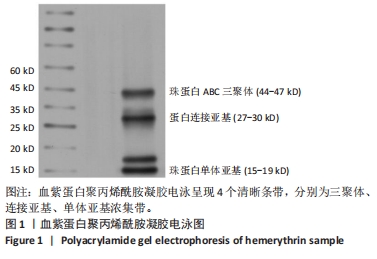
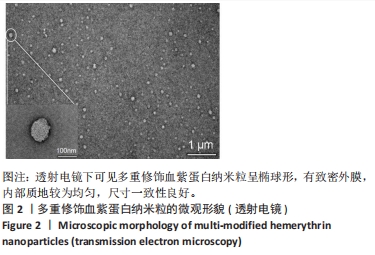
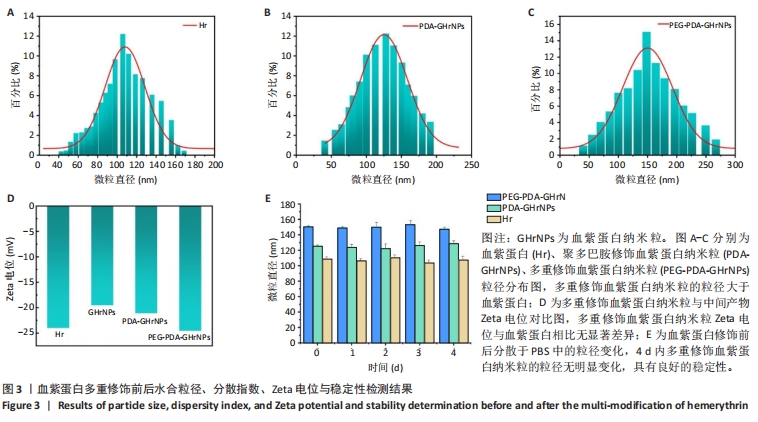
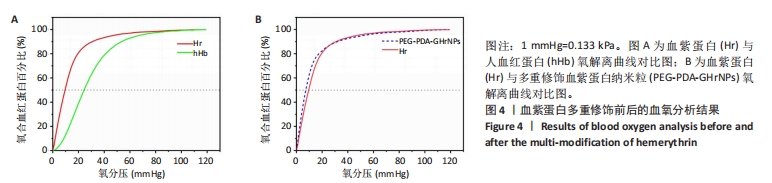
[1] 杜鹏飞,樊毫军,赵会民,等.我国紧急输血的可及性与便利性调查[J].中国输血杂志,2021,34(7):738-742.
[2] 赵冬雁,马宏伟,汤丁洁,等. 2018-2021年COVID-19疫情前后国内18家血液中心红细胞成分血供应情况分析[J].中国输血杂志, 2023,36(10):892-898.
[3] 刘嘉馨,杨成民.红细胞代用品研究进展与现状[J].中国输血杂志, 2022,35(8):785-790.
[4] CAP AP, CANNON JW, READE MC. Synthetic blood and blood products for combat casualty care and beyond. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021; 91(2S Suppl 2):S26-s32.
[5] FAGGIANO S, RONDA L, BRUNO S, et al. From hemoglobin allostery to hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers. Mol Aspects Med. 2022;84: 101050.
[6] MA Y, ZHANG Q, DAI Z, et al. Structural optimization and prospect of constructing hemoglobin oxygen carriers based on hemoglobin. Heliyon. 2023;9(9):e19430.
[7] JANSMAN MMT, HOSTA-RIGAU L. Recent and prominent examples of nano- and microarchitectures as hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;260:65-84.
[8] DUBÉ GP, PITMAN AN, MACKENZIE CF. Relative Efficacies of HBOC-201 and Polyheme to Increase Oxygen Transport Compared to Blood and Crystalloids. Shock. 2019;52(1S Suppl 1):100-107.
[9] CAO M, ZHAO Y, HE H, et al. New Applications of HBOC-201: A 25-Year Review of the Literature. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:794561.
[10] BHATTACHARJEE RN, PATEL SVB, SUN Q, et al. Renal Protection Against Ischemia Reperfusion Injury: Hemoglobin-based Oxygen Carrier-201 Versus Blood as an Oxygen Carrier in Ex Vivo Subnormothermic Machine Perfusion. Transplantation. 2020; 104(3):482-489.
[11] SIMONS M, GRETTON S, SILKSTONE GGA, et al. Comparison of the oxidative reactivity of recombinant fetal and adult human hemoglobin: implications for the design of hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(4):BSR20180370.
[12] TATEZAWA R, ABUMIYA T, ITO Y, et al. Neuroprotective effects of a hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier (stroma-free hemoglobin nanoparticle) on ischemia reperfusion injury. Brain Res. 2023;1821: 148592.
[13] WANG Q, GONG J, BAI Q, et al. Hemoglobin coated oxygen storage metal-organic framework as a promising artificial oxygen carrier. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(19):4002-4005.
[14] HUI W, MU W, ZHAO C, et al. Solid-Phase Polymerization Using Anion-Exchange Resin Can Almost Completely Crosslink Hemoglobin to Prepare Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carriers. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:1777-1791.
[15] ROAMCHARERN N, PAYOUNGKIATTIKUN W, ANWISED P, et al. Physicochemical properties and oxygen affinity of glutaraldehyde polymerized crocodile hemoglobin: the new alternative hemoglobin source for hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):852-861.
[16] LIANG S, CHEN Y, ZHANG S, et al. RhB-encapsulating silica nanoparticles modified with PEG impact the vascular endothelial function in endothelial cells and zebrafish model. Sci Total Environ. 2020;711:134493.
[17] FARCAS AD, TOMA VA, ROMAN I, et al. Glutaraldehyde-Polymerized Hemoglobin: In Search of Improved Performance as Oxygen Carrier in Hemorrhage Models. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2020; 2020:1096573.
[18] TAGUCHI K, YAMASAKI K, MARUYAMA T, et al. Comparison of the Pharmacokinetic Properties of Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carriers. J Funct Biomater. 2017;8(1):11.
[19] HAFEEZ S, ZAIDI N. Red Blood Cell Substitutes: Liposome Encapsulated Hemoglobin and Magnetite Nanoparticle Conjugates as Oxygen Carriers. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1618.
[20] BAIDUKOVA O, WANG Q, CHAIWAREE S, et al. Antioxidative protection of haemoglobin microparticles (HbMPs) by PolyDopamine. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup3):S693-s701.
[21] GU X, ALLYN M, SWINDLE-REILLY K, et al. ZIF-8 metal organic framework nanoparticle loaded with tense quaternary state polymerized bovine hemoglobin: potential red blood cell substitute with antioxidant properties. Nanoscale. 2023;15(19):8832-8844.
[22] PENG S, LIU J, QIN Y, et al. Metal-Organic Framework Encapsulating Hemoglobin as a High-Stable and Long-Circulating Oxygen Carriers to Treat Hemorrhagic Shock. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(39): 35604-35612.
[23] MUZZELO C, NEELY C, SHAH P, et al. Prolonging the shelf life of Lumbricus terrestris erythrocruorin for use as a novel blood substitute. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(1):39-46.
[24] ZIMMERMAN D, DIIUSTO M, DIENES J, et al. Direct comparison of oligochaete erythrocruorins as potential blood substitutes. Bioeng Transl Med. 2017;2(2):212-221.
[25] POZY E, SAVLA C, PALMER AF. Photocatalytic Synthesis of a Polydopamine-Coated Acellular Mega-Hemoglobin as a Potential Oxygen Therapeutic with Antioxidant Properties. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(5):2022-2029.
[26] JANI VP, JELVANI A, MOGES S, et al. Polyethylene Glycol Camouflaged Earthworm Hemoglobin. PLoS One. 2017;12(1):e0170041.
[27] 荣龙,余春红,任烽,等.一种蚯蚓血红蛋白冻干制剂的制备方法[P].CN116239676A,2021-06-25
[28] 荣龙,余春红,任烽,等.一种PEG修饰蚯蚓血红蛋白的方法[P].CN116199771A,2023-06-02
[29] 杨康,赵会民,樊毫军,等.聚多巴胺修饰蚯蚓血红蛋白纳米氧载体的构建及性能检测[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(21):3369-3374.
[30] 杨康,赵会民.血红蛋白氧载体的研究目标及新进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(20):3263-3268.
[31] KRUCZKOWSKA W, KCIUK M, PASIEKA Z, et al. The artificial oxygen carrier erythrocruorin-characteristics and potential significance in medicine. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023;101(8):961-972.
[32] TIMM B, ABDULMALIK O, CHAKRABARTI A, et al. Purification of Lumbricus terrestris erythrocruorin (LtEc) with anion exchange chromatography. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2020; 1150:122162.
[33] SAVLA C, MUNOZ C, HICKEY R, et al. Purification of Lumbricus terrestris Mega-Hemoglobin for Diverse Oxygen Therapeutic Applications. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(9):4957-4968.
[34] SAVLA C, PALMER AF. Structural Stability and Biophysical Properties of the Mega-Protein Erythrocruorin Are Regulated by Polyethylene Glycol Surface Coverage. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22(5):2081-2093.
[35] SHI D, BEASOCK D, FESSLER A, et al. To PEGylate or not to PEGylate: Immunological properties of nanomedicine’s most popular component, polyethylene glycol and its alternatives. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;180: 114079.
[36] RAJESH A, ZIMMERMAN D, SPIVACK K, et al. Glutaraldehyde cross-linking increases the stability of Lumbricus terrestris erythrocruorin. Biotechnol Prog. 2018;34(2):521-528.
[37] SHI J, LIAN H, HUANG Y, et al. In vitro genotoxicity evaluation and metabolic study of residual glutaraldehyde in animal-derived biomaterials. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(6):619-625.
[38] AHMED R, UL AIN HIRA N, WANG M, et al. Genipin, a natural blue colorant precursor: Source, extraction, properties, and applications. Food Chem. 2023;434:137498.
[39] YU Y, XU S, LI S, et al. Genipin-cross-linked hydrogels based on biomaterials for drug delivery: a review. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(5):1583-1597.
[40] WANG Q, ZHANG R, LU M, et al. Bioinspired Polydopamine-Coated Hemoglobin as Potential Oxygen Carrier with Antioxidant Properties. Biomacromolecules. 2017;18(4):1333-1341.
[41] HU J, WANG Q, MA N, et al. Characterization and Biosafety Evaluation of Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carriers Coated with Polydopamine. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2020;16(8):1314-1323.
[42] EL YAKHLIFI S, BALL V. Polydopamine as a stable and functional nanomaterial. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;186:110719.
[43] AIT BACHIR Z, HUANG Y, HE M, et al. Effects of PEG surface density and chain length on the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of methotrexate-loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:5657-5671.
[44] CHEN BM, CHENG TL, ROFFLER SR. Polyethylene Glycol Immunogenicity: Theoretical, Clinical, and Practical Aspects of Anti-Polyethylene Glycol Antibodies. ACS Nano. 2021;15(9):14022-14048.
[45] SAMAJA M, MALAVALLI A, VANDEGRIFF KD. How Nitric Oxide Hindered the Search for Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carriers as Human Blood Substitutes. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(19):14902.
|