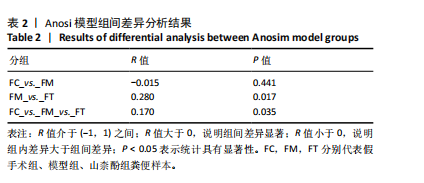
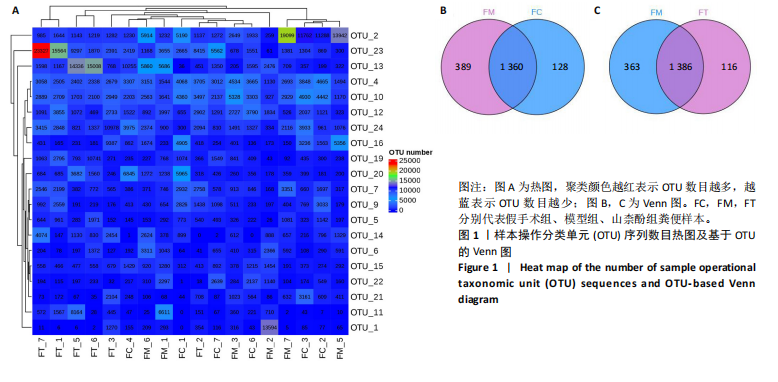
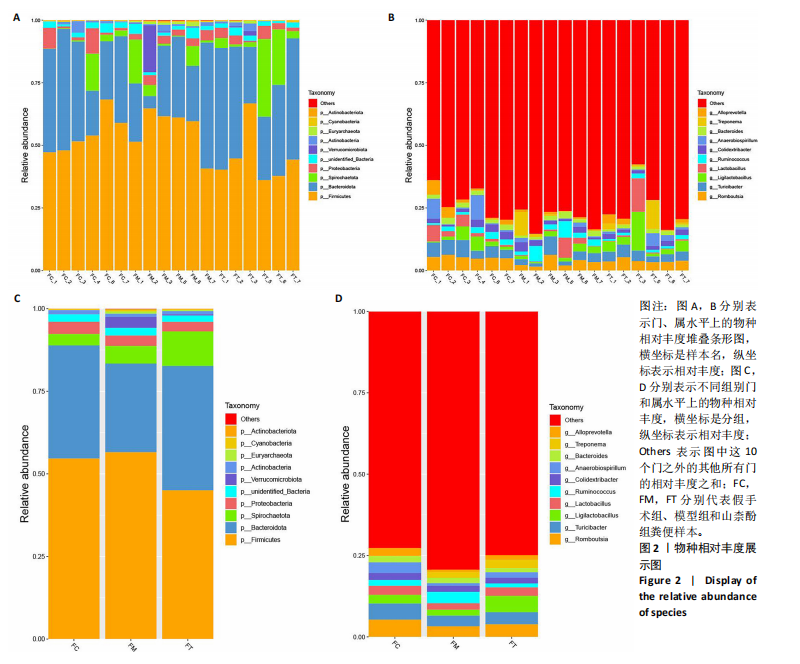
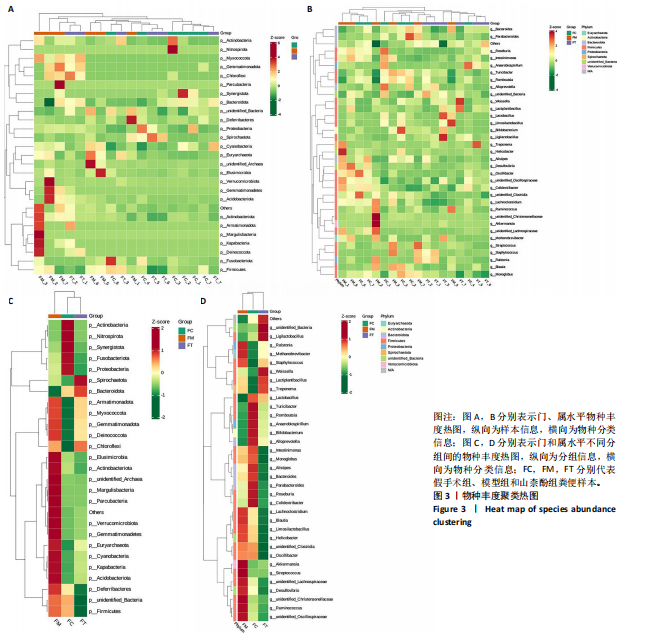
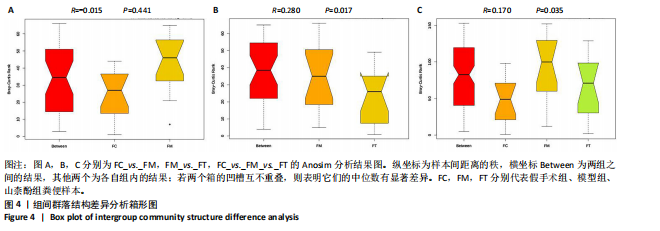
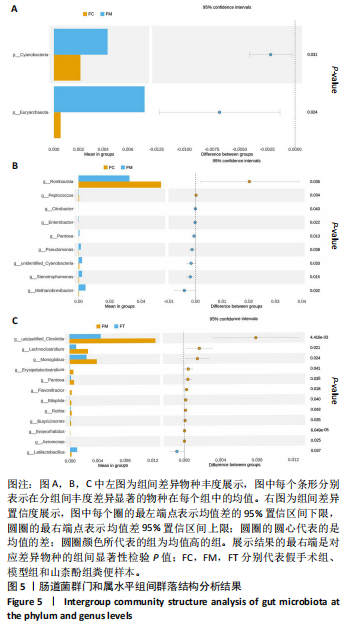
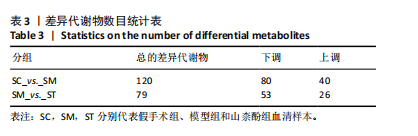
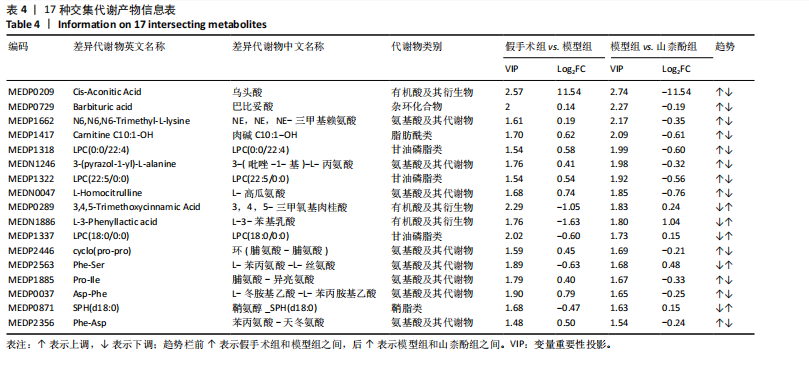
[1] IOLOASCON G, DE SIRE A, CURCI C, et al. Osteoporosis guidelines from a rehabilitation perspective: systematic analysis and quality appraisal using AGREE II. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2021;57(2):273-279.
[2] STUMPF U, SCHMIDMAIER R. Sekundäre frakturprävention/update leitlinie osteoporose 2023 des dachverbandes osteologie [Secondary fracture prevention/update osteoporosis guidelines 2023 of the umbrella organization osteology]. Unfallchirurgie (Heidelb). 2024;127(4):283-289.
[3] ZOU Z, LIU W, CAO L, et al. Advances in the occurrence and biotherapy of osteoporosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020;48(4):1623-1636.
[4] REID IR. A broader strategy for osteoporosis interventions. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(6):333-339.
[5] PICKARD JM, ZENG MY, CARUSO R, et al. Gut microbiota: Role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol Rev. 2017;279(1):70-89.
[6] 钟建春,谢兴文,李鼎鹏,等.肠道菌群与骨质疏松的关系及中药调节研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(18):237-244.
[7] 韦露,马秀梅,覃树先,等.三种党参不同炮制品对脾虚模型大鼠肠道菌群的影响[J].湖北农业科学,2021,60(18):125-128.
[8] CHEN Y, YANG C, DENG Z, et al. Gut microbially produced tryptophan metabolite melatonin ameliorates osteoporosis via modulating SCFA and TMAO metabolism. J Pineal Res. 2024;76(3):e12954.
[9] HUSSAIN MS, ALTAMIMI ASA, AFZAL M, et al. Kaempferol: paving the path for advanced treatments in aging-related diseases. Exp Gerontol. 2024;188:112389.
[10] GE J, LI G, CHEN Z, et al. Kaempferol and nicotiflorin ameliorated alcohol-induced liver injury in mice by miR-138-5p/SIRT1/FXR and gut microbiota. Heliyon. 2023;10(1):e23336.
[11] GUAN M, XU W, BAI H, et al. Potential mechanisms underlying inhibition of xenograft lung cancer models by kaempferol: modulation of gut microbiota in activating immune cell function. J Cancer. 2024; 15(5):1314-1327.
[12] PAN C, ZHANG C, LIN Z, et al. Disulfidptosis-related protein RPN1 may be a novel anti-osteoporosis targetof kaempferol. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(11):1611-1628.
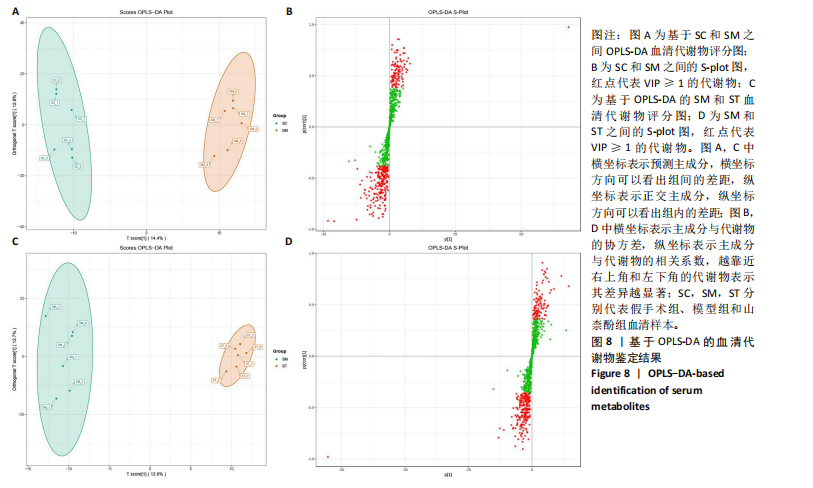
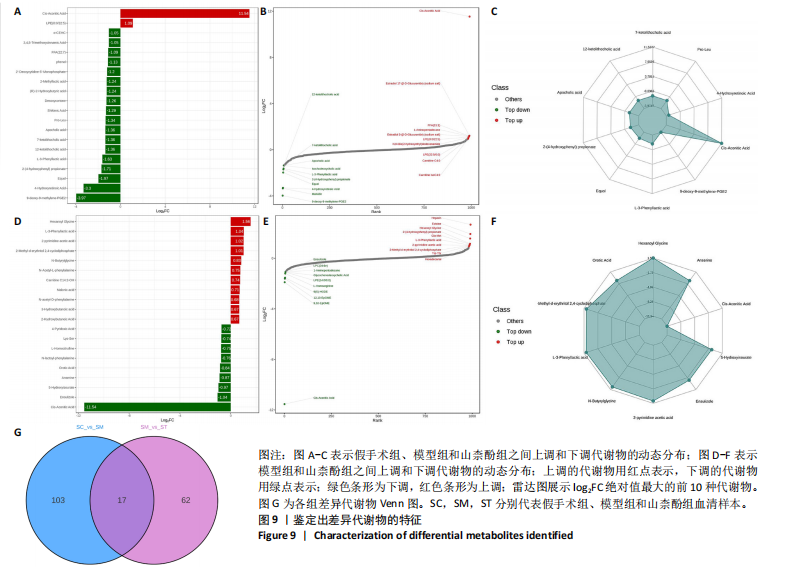
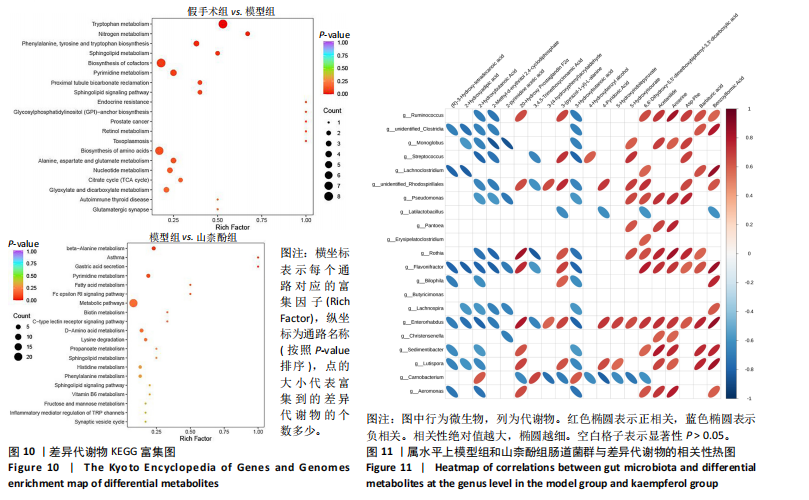
[13] 唐雪勇,刁庆春,李鑫,等.基于广泛靶向代谢组学技术的寻常型银屑病血热证、血瘀证、血燥证患者唾液代谢组学研究[J].中医杂志,2021,62(9):789-795.
[14] CAPORASO JG, LAUBER CL, WALTERS WA, et al. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):4516-4522.
[15] CHEN Z, LV M, LIANG J, et al. Neuropeptide y-mediated gut microbiota alterations aggravate postmenopausal osteoporosis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(33):e2303015.
[16] 阙敏强,石础硕,黄英杰,等.不同药物治疗原发性骨质疏松症的网状Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(35):5715-5722.
[17] MCCLOSKEY E, TAN ATH, SCHINI M. Update on fracture risk assessment in osteoporosis. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2024;31(4): 141-148.
[18] CHEN T, MENG F, WANG N, et al. The characteristics of gut microbiota and its relation with diet in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s00223-024-01260-x.
[19] BATTISTINI C, BALLAN R, HERKENHOFF ME, et al. Vitamin d modulates intestinal microbiota in inflammatory bowel diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):362.
[20] MASSY ZA, DRUEKE TB. Gut microbiota orchestrates PTH action in bone: role of butyrate and T cells. Kidney Int. 2020;98(2):269-272.
[21] ZHOU Y, ZHANG Y, QIAN Y, et al. Ziyuglycoside II attenuated OVX mice bone loss via inflammatory responses and regulation of gut microbiota and SCFAs. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;132:112027.
[22] CHANGF KY, LU CT, CHEN PC, et al. Correspondence: Association of estrogen deficiency on bone loss-impact of gut microbiota. Int J Rheum Dis. 2024;27(3):e15100.
[23] SHIN SK, KWON EY. Kaempferol ameliorates metabolic syndrome by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Nutr Res Pract. 2024;18(3):325-344.
[24] CHOI EY, HAN EJ, JEON SJ, et al. Kaempferol inhibits cervical cancer cells by inducing apoptosis and autophagy via inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Anticancer Res. 2024;44(7):2961-2972.
[25] ALMATROUDI A, ALLEMAILEM KS, ALWANIAN WM, et al. Effects and mechanisms of kaempferol in the management of cancers through modulation of inflammation and signal transduction pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(10):8630.
[26] 杨启培,陈锋,崔伟,等.山奈酚活性单体治疗骨质疏松症的相关信号通路[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(26):4242-4249.
[27] LI X, KHAN I, HUANG G, et al. Kaempferol acts on bile acid signaling and gut microbiota to attenuate the tumor burden in ApcMin/+ mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;918:174773.
[28] QU Y, LI X, XU F, et al. Kaempferol alleviates murine experimental colitis by restoring gut microbiota andinhibiting the LPS-TLR4-NF-κB axis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:679897.
[29] SUN Y, ZHANG S, NIE Q, et al. Gut firmicutes: relationship with dietary fiber and role in host homeostasis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(33): 12073-12088.
[30] HOUTMAN TA, ECKERMANN HA, SMIDT H, et al. Gut microbiota and BMI throughout childhood: the role of firmicutes, bacteroidetes, and short-chain fatty acid producers. Sci Rep.2022;12(1):3140.
[31] TIAN H, CUI J, YE C, et al. Depletion of butyrate-producing microbes of the Firmicutes predicts nonresponse to FMT therapy in patients with recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Gut Microbes. 2023;15(1): 2236362.
[32] OSAWA M, HANDA O, FUKUSHIMA S, et al. Reduced abundance of butyric acid-producing bacteria in the ileal mucosa-associated microbiota of ulcerative colitis patients. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2023; 73(1):77-83.
[33] JI C, WU M, ZOU J, et al. Protection of γ-amino butyric acid on radiation induced intestinal injury in mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2023;67(10):e2200522.
[34] LI Y, XING S, CHEN F, et al. Intracellular Fusobacterium nucleatum infection attenuates antitumor immunity inesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):5788.
[35] BOONYALEKA K, OKANO T, IIDA T, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum infection activates the noncanonical inflammasome and exacerbates inflammatory response in DSS-induced colitis. Eur J Immunol. 2023; 53(11):e2350455.
[36] CHUKKAPALLI SS, VELSKO IM, RIVERA-KWEH MF, et al. Global TLR2 and 4 deficiency in mice impacts bone resorption, inflammatory markers and atherosclerosis to polymicrobial infection. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2017;32(3):211-225.
[37] ZHANG J, ZHANG Q, LIU H, et al. Soy-whey dual-protein alleviates osteoporosis of ovariectomized rats via regulating bone fat metabolism through gut-liver-bone axis. Nutrition. 2022;103-104:111723.
[38] WANG S, WANG S, WANG X, et al. Effects of icariin on modulating gut microbiota and regulating metabolite alterations to prevent bone loss in ovariectomized rat model. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:874849.
[39] ZHANG J, ZHANG H, XIAO Y, et al. Interspecific differences and mechanisms of Lactobacillus-derived anti-inflammatory exopolysaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;263(Pt 2):130313.
[40] YAO M, LU Y, ZHANG T, et al. Improved functionality of Ligilactobacillus salivarius Li01 in alleviating colonic inflammation by layer-by-layer microencapsulation. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2021;7(1):58.
[41] PIVA F, GERVOIS P, KARROUT Y, et al. Gut-joint axis: impact of bifidobacterial cell wall lipoproteins on arthritis development. Nutrients. 2023;15(23):4861.
[42] FEICHAO S, RONGRONG C, SHICHANG J, et al. Analysis of the relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis based on mendelian randomization. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2024;20(3):284-295.
[43] KANITKAR A, CHEN C, SMOAK M, et al. In vitro characterization of polyesters of aconitic acid, glycerol, and cinnamic acid for bone tissue engineering. J Biomater Appl. 2015;29(8):1075-1078.
[44] LIANG B, SHI X, WANG X, et al. Association between amino acids and recent osteoporotic fracture: a matched incident case-control study. Front Nutr. 2024;11:1360959.
[45] LI SY, LU ZH, LEUNG JCS, et al. Association of dietary protein intake, inflammation with muscle mass, physical performance and incident sarcopenia in Chinese community-dwelling older adults. J Nutr Health Aging. 2024;28(4):100163.
[46] CONIGRAVE AD, BROWN EM, RIZZOLI R. Dietary protein and bone health: roles of amino acid-sensing receptors in the control of calcium metabolism and bone homeostasis. Annu Rev Nutr. 2008;28:131-155.
[47] GARTON M, NIM S, STONE TA, et al. Method to generate highly stable D-amino acid analogs of bioactive helical peptides using a mirror image of the entire PDB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(7):1505-1510.
[48] FITZPATRICK LA, BUZAS E, GAGNE TJ, et al. Targeted deletion of histidine decarboxylase gene in mice increases bone formation and protects against ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(10):6027-6032.
[49] XIE H, HUA Z, GUO M, et al. Gut microbiota and metabonomics used to explore the mechanism of Qing’e Pills in alleviating osteoporosis. Pharm Biol. 2022;60(1):785-800.
[50] SU Y, ELSHORBAGY A, TURNER C, et al. Circulating amino acids are associated with bone mineral density decline and ten-year major osteoporotic fracture risk in older community-dwelling adults. Bone. 2019;129:115082.
[51] DRAGOJEVIČ J, ZUPAN J, HARING G, et al. Triglyceride metabolism in bone tissue is associated with osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation: a gene expression study. J Bone Miner Metab. 2013;31(5):512-519.
[52] SEAL A, HUGHES M, WEI F, et al. Sphingolipid-induced bone regulation and its emerging role in dysfunction due to disease and infection. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(5):3024.
[53] LIN Z, JIANG T, CHEN M, et al. Gut microbiota and sleep: interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects. Open Life Sci. 2024;19(1): 20220910.
[54] SEJBUK M, SIEBIESZUK A, WITKOWSKA AM. The role of gut microbiome in sleep quality and health: dietary strategies for microbiota support. Nutrients. 2024;16(14):2259. |