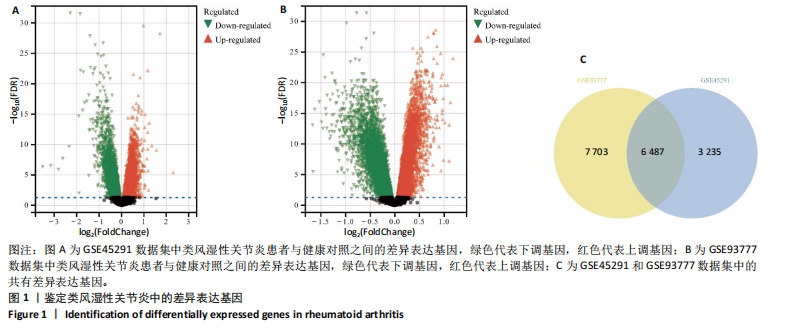
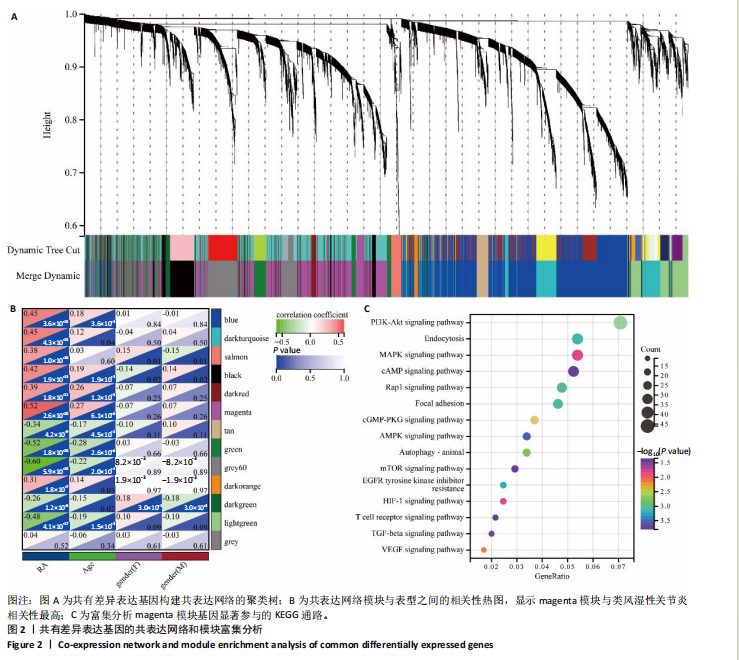
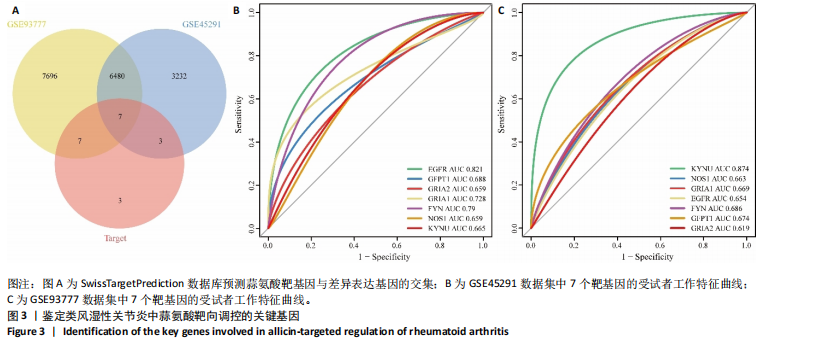
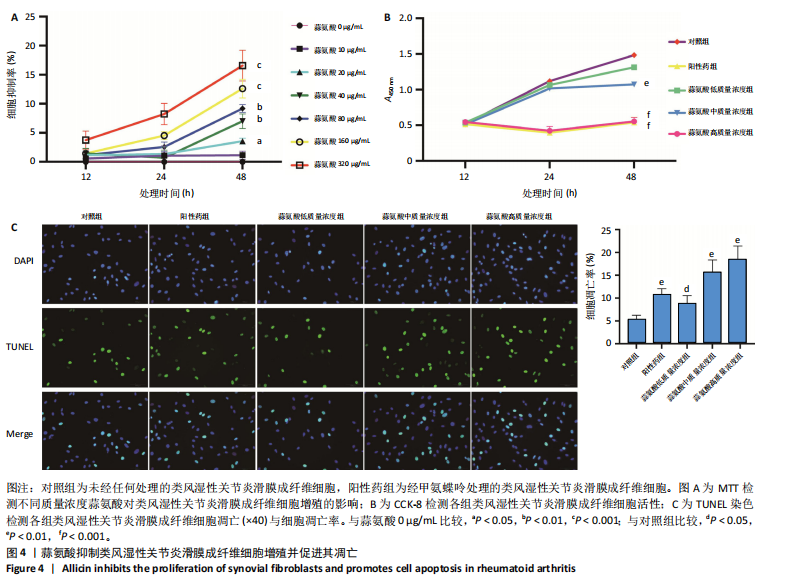
[1] LA R, ZHOU L, YIN Y, et al. Association between oxidative balance score and rheumatoid arthritis in female: a cross-sectional study. BMC Womens Health. 2024;24(1):225.
[2] Collaborators GBDRA. Global, regional, and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis, 1990-2020, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(10):e594-e610.
[3] DING Q, HU W, WANG R, et al. Signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):68.
[4] MAISHA JA, EL-GABALAWY HS, O’NEIL LJ. Modifiable risk factors linked to the development of rheumatoid arthritis: evidence, immunological mechanisms and prevention. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1221125.
[5] GUSKI LS, JURGENS G, PEDDER H, et al. Monotreatment With Conventional Antirheumatic Drugs or Glucocorticoids in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Network Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(10): e2335950.
[6] SHARMA SD, BLUETT J. Towards Personalized Medicine in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Open Access Rheumatol. 2024;16:89-114.
[7] LONG Z, XIANG W, HE Q, et al. Efficacy and safety of dietary polyphenols in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 47 randomized controlled trials. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1024120.
[8] MOOSAVIAN SP, PAKNAHAD Z, HABIBAGAHI Z, et al. The effects of garlic (Allium sativum) supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers, fatigue, and clinical symptoms in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phytother Res. 2020;34(11):2953-2962.
[9] ARELLANO BUENDIA AS, JUAREZ ROJAS JG, GARCIA-ARROYO F, et al. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of allicin in the kidney of an experimental model of metabolic syndrome. PeerJ. 2023;11:e16132.
[10] GONG Q, WANG X, LIU Y, et al. Potential Hepatoprotective Effects of Allicin on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Toxics. 2024;12(5):328.
[11] XIANG Q, CHENG Z, WANG J, et al. Allicin Attenuated Advanced Oxidation Protein Product-Induced Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Apoptosis in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:6685043.
[12] 姜玥,刘宵达,吴素琴. anti-IL-33对类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞增殖与凋亡的影响[J].医学信息,2021,34(13):81-83.
[13] LI M, TIAN F, GUO J, et al. Therapeutic potential of Coptis chinensis for arthritis with underlying mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14: 1243820.
[14] ZHU M, DING Q, LIN Z, et al. New Targets and Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Signal Transduction to Epigenetic Aspect. Biomolecules. 2023;13(5):766.
[15] HU S, LIN Y, TANG Y, et al. Targeting dysregulated intracellular immunometabolism within synovial microenvironment in rheumatoid arthritis with natural products. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1403823.
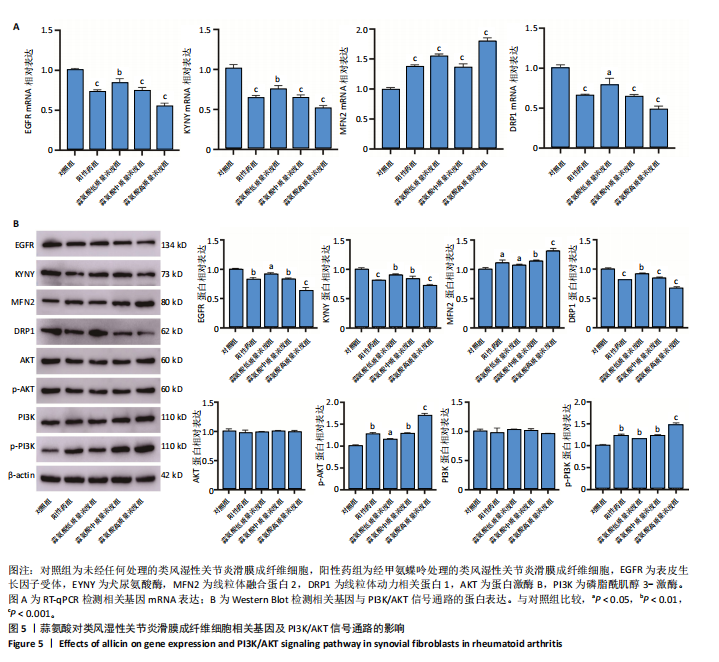
[16] SWANSON CD, AKAMA-GARREN EH, STEIN EA, et al. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 2012;188(7):3513-3521.
[17] NERVIANI A, BOUTET MA, GHIRARDI GM, et al. Axl and MerTK regulate synovial inflammation and are modulated by IL-6 inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):2398.
[18] ZHAO L, LIU M, ZHENG K, et al. Fufang Duzheng tablet attenuates adjuvant rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting arthritis inflammation and gut microbiota disturbance in rats. Heliyon. 2024;10(12):e32705.
[19] KEHRIBAR DY, EMMUNGIL H, TURKMEN NB, et al. EGFR blocker lapatinib inhibits the synthesis of matrix metalloproteinases from synovial fibroblasts. Turk J Med Sci. 2022;52(4):1355-1361.
[20] LIANG C, YU Y, TANG Q, et al. Discovering KYNU as a feature gene in hidradenitis suppurativa. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2023;37: 3946320231216317.
[21] MU KL, RAN F, PENG LQ, et al. Identification of diagnostic biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis based on machine learning-assisted comprehensive bioinformatics and its correlation with immune cells. Heliyon. 2024;10(15):e35511.
[22] RYCHKOV D, NEELY J, OSKOTSKY T, et al. Cross-Tissue Transcriptomic Analysis Leveraging Machine Learning Approaches Identifies New Biomarkers for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:638066.
[23] TONG Y, LI X, DENG Q, et al. Advances of the small molecule drugs regulating fibroblast-like synovial proliferation for rheumatoid arthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1230293.
[24] SHI H, ZHANG Y, YIN J, et al. Lysine succinylation analysis reveals the effect of Sirt5 on synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2024; 13(2):110-116.
[25] JIN L, CHEN Q, HU K, et al. The FTO-CMPK2 Pathway in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes Modulates Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Inflammation and Cartilage Homeostasis via mtDNA Regulation. Int J Biol Sci. 2024; 20(5):1617-1633.
[26] QIAN H, DENG C, CHEN S, et al. Targeting pathogenic fibroblast-like synoviocyte subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024;16(6):316-333.
[27] NYGAARD G, FIRESTEIN GS. Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(6):316-333.
[28] MOOSAVIAN SP, PAKNAHAD Z, HABIBAGAHI Z. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, evaluating the garlic supplement effects on some serum biomarkers of oxidative stress, and quality of life in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Clin Pract. 2020; 74(7):e13498.
[29] ZHANG Y, GONG Y. Allicin regulates Treg/Th17 balance in mice with collagen-induced arthritis by increasing the expression of MEKK2 protein. Food Sci Nutr. 2021;9(5):2364-2371.
[30] RASLAN MA, RASLAN SA, SHEHATA EM, et al. Different modalities to manage rheumatoid arthritis: an A to Z story. Future Sci OA. 2024; 10:FSO968.
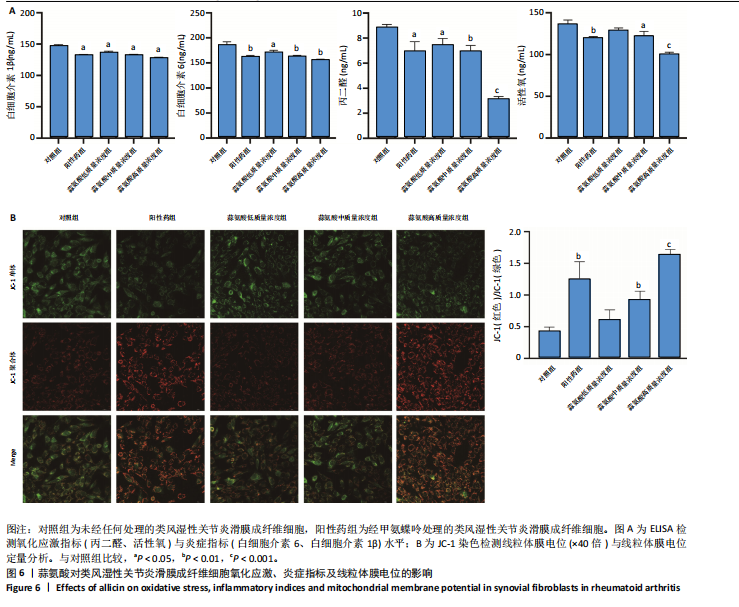
[31] LOPEZ-ARMADA MJ, FERNANDEZ-RODRIGUEZ JA, BLANCO FJ. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(6):1151.
[32] LI S, HUO C, LIU A, et al. Mitochondria: a breakthrough in combating rheumatoid arthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1439182.
[33] CLAYTON SA, MACDONALD L, KUROWSKA-STOLARSKA M, et al. Mitochondria as Key Players in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:673916.
[34] CUI L, WEIYAO J, CHENGHONG S, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and mitochondrial homeostasis: The crossroads of metabolism and immunity. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:1017650.
[35] WANG G, CHEN X, SHAO Y, et al. PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitochondrial Autophagy Participates in H2O2-Induced Abnormal Proliferation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:1271-1282.
[36] DING C, NI L, LIU Q, et al. Cold air plasma improving rheumatoid arthritis via mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023;8(1):e10366. |