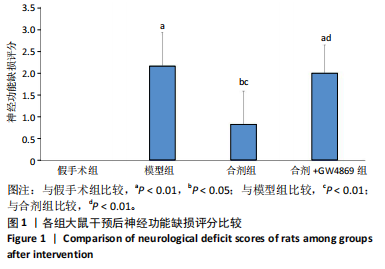
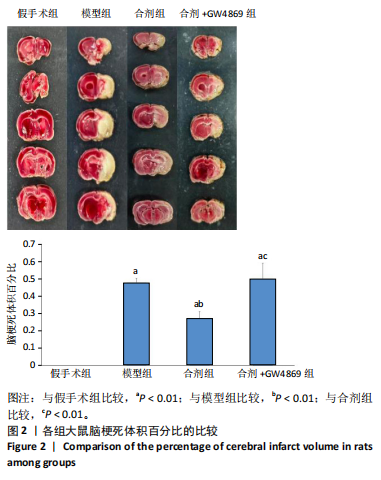
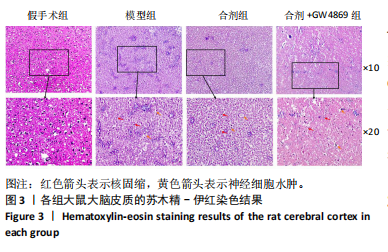
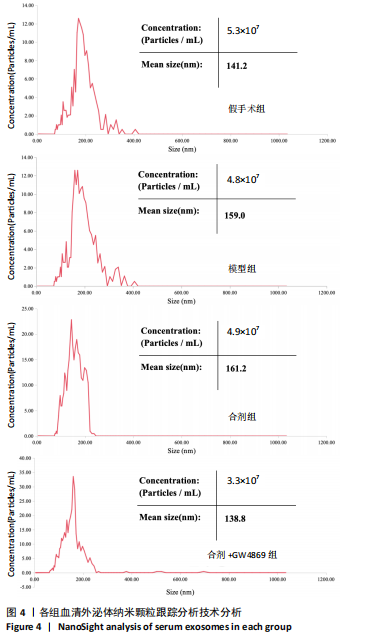
[1] DORŇÁK T, JUSTANOVÁ M, KONVALINKOVÁ R, et al. Prevalence and evolution of spasticity in patients suffering from first-ever stroke with carotid origin: a prospective, longitudinal study. Eur J Neurol. 2019;26(6):880-886.
[2] PUNDIK S, MCCABE J, SKELLY M, et al. Association of spasticity and motor dysfunction in chronic stroke. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2019; 62(6):397-402.
[3] 薛瑞文.益气健脾化瘀方结合躯干训练对缺血性脑卒中偏瘫患者炎性因子及NGF、BDNF水平的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2019,28(2):188-192.
[4] 徐辉,邹艳丽,周辉,等.补阳还五汤对缺血性脑卒中患者恢复期的疗效评价[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2017,12(8):1155-1157+1176.
[5] 刘悦,卢阳佳,邝伟川,等.中风复元口服液治疗气虚痰浊内阻型中风60例临床疗效观察[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2012,14(12):18-20.
[6] 陈玉宁,蒋颖,廖翔宇,等.补气活血合剂干预脑缺血再灌注模型大鼠相关因子及自噬蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(6):1152-1158.
[7] WANG Y, YU Z, CHENG M, et al. Buyang huanwu decoction promotes remyelination via miR-760-3p/GPR17 axis after intracerebral hemorrhage. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;328:118126.
[8] LI P, TANG T, LIU T, et al. Systematic Analysis of tRNA-Derived Small RNAs Reveals Novel Potential Therapeutic Targets of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Buyang-Huanwu-Decoction) on Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(4):895-908.
[9] CHEN B, XU Y, TIAN F, et al. Buyang Huanwu decoction promotes angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia through modulating caveolin-1-mediated exosome MALAT1/YAP1/HIF-1α axis. Phytomedicine. 2024;129:155609.
[10] YANG J, GAO F, ZHANG Y, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction (BYHWD) Enhances Angiogenic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell by Upregulating VEGF Expression After Focal Cerebral Ischemia. J Mol Neurosci. 2015;56(4):898-906.
[11] ZHAO M, YANG B, LI L, et al. Efficacy of Modified Huangqi Chifeng decoction in alleviating renal fibrosis in rats with IgA nephropathy by inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway through exosome regulation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022; 285:114795.
[12] ZHAO L, DING LD, XIA ZH, et al. A Network-Based Approach to Investigate the Neuroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Action of Huangqi-Chuanxiong and Sanleng-Ezhu Herb Pairs in the Treatment of Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:844186.
[13] DU X, AMIN N, XU L, et al. Pharmacological intervention of curcumin via the NLRP3 inflammasome in ischemic stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1249644.
[14] LONG J, GU C, ZHANG Q, et al. Extracellular vesicles from medicated plasma of Buyang Huanwu decoction-preconditioned neural stem cells accelerate neurological recovery following ischemic stroke. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1096329.
[15] HU D, MO X, LUO J, et al. 17-DMAG ameliorates neuroinflammation and BBB disruption via SOX5 mediated PI3K/Akt pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;123:110698.
[16] WANG SW, DENG LX, CHEN HY, et al. MiR-124 affects the apoptosis of brain vascular endothelial cells and ROS production through regulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(14):4647.
[17] LONGA EZ, WEINSTEIN PR, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[18] CHEN Y, WRIGHT N, GUO Y, et al. Mortality and recurrent vascular events after first incident stroke: a 9-year community-based study of 0.5 million Chinese adults. Lancet Glob Health. 2020;8(4):e580-e590.
[19] VAN KRANENDONK KR, TREURNIET KM, BOERS AMM, et al. Hemorrhagic transformation is associated with poor functional outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke due to a large vessel occlusion. J Neurointerv Surg. 2019;11(5):464-468.
[20] WONG GJ, YOO B, LIEBESKIND D, et al. Frequency, Determinants, and Outcomes of Emboli to Distal and New Territories Related to Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke. 2021; 52(7):2241-2249.
[21] 龚贵香,汤健.缺血性脑卒中二级预防中阿司匹林与氯吡格雷的不良反应[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2016,19(4):118-119.
[22] 樊欢欢,曹克刚.从“玄府-脑络-毒邪”探讨中风病的中医病机[J].北京中医药,2024,43(1):85-87.
[23] 李文颢.基于数据挖掘的7707例脑卒中后遗症中药应用规律研究[D].广州: 广州中医药大学,2019.
[24] 刘佩.基于外泌体miR-21介导的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路探讨三七总皂苷对脑缺血后神经血管单元的保护机制[D].百色:右江民族医学院,2022.
[25] 陈翠兰.麝香酮处理干细胞来源外泌体对缺血性脑卒中大鼠的神经保护作用研究[D].南宁:广西中医药大学,2023.
[26] LIU S, FAN M, XU JX, et al. Exosomes derived from bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate cognitive decline in AD-like mice by improving BDNF-related neuropathology. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):35.
[27] HE R, JIANG Y, SHI Y, et al. Curcumin-laden exosomes target ischemic brain tissue and alleviate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ROS-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;117:111314.
[28] Wang J, Liu H, Chen S, et al. Moderate exercise has beneficial effects on mouse ischemic stroke by enhancing the functions of circulating endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes. Exp Neurol. 2020;330:113325.
[29] Zhong Y, Luo L. Exosomes from Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Ameliorate Ischemic Injuries by Suppressing the RNA Component of Mitochondrial RNA-processing Endoribonuclease via the Induction of miR-206/miR-1-3p Levels. Neuroscience. 2021;476:34-44.
[30] Yang C, Yuan F, Shao W, et al. Protective role of exosomes derived from regulatory T cells against inflammation and apoptosis of BV-2 microglia under oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion challenge. Genet Mol Biol. 2022;45(4):e20220119.
[31] Liu W, Yu M, Xie D, et al. Melatonin-stimulated MSC-derived exosomes improve diabetic wound healing through regulating macrophage M1 and M2 polarization by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):259.
[32] Zhu Q, Zhang Y, Li M, et al. MiR-124-3p impedes the metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer via extracellular exosome transport and intracellular PI3K/AKT signaling. Biomark Res. 2023;11(1):1.
[33] Lin S, Que Y, Que C, et al. Exosome miR-3184-5p inhibits gastric cancer growth by targeting XBP1 to regulate the AKT, STAT3, and IRE1 signalling pathways. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2023;19(2):e27-e38.
[34] Wang P, Xue Y, Zuo Y, et al. Exosome-Encapsulated microRNA-140-5p Alleviates Neuronal Injury Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage by Regulating IGFBP5-Mediated PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(12):7212-7228.
[35] 程馨缘, 杜根发, 韩鹏勋, 等. 黄芪治疗局灶节段性肾小球硬化的分子作用机制及miRNA-mRNA 调控网络构建[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2023, 25(1):107-119.
[36] 靳晓飞,张彐宁,周晓红,等.黄芪甲苷对脑缺血再灌注大鼠炎症因子及超微结构的影响[J].中国比较医学杂志,2020,30(4):1-6.
[37] 张怡,侯仙明,张拴成,等.黄芪甲苷通过调控Caspase-1介导的经典焦亡途径抑制细胞焦亡缓解脑缺血/再灌注损伤的研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2024, 40(2):325-329.
[38] 康洁.黄芪甲苷依赖于PPARγ在脑缺血再灌注中发挥神经保护作用[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2022.
[39] 张修红,傅开龙,林侃,等.补阳还五汤通过miR-26a-5p激活PTEN/PI3K/Akt信号通路减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J].中国中药杂志,2024,49(15):4197-4206.
[40] 邓敏贞,黄丽平,马阮昕,等.石菖蒲挥发油联合人参总皂苷通过调节PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路对痴呆模型APP/PS1双转基因小鼠的Aβ_(40)和GFAP的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2018,34(4):92-95. |