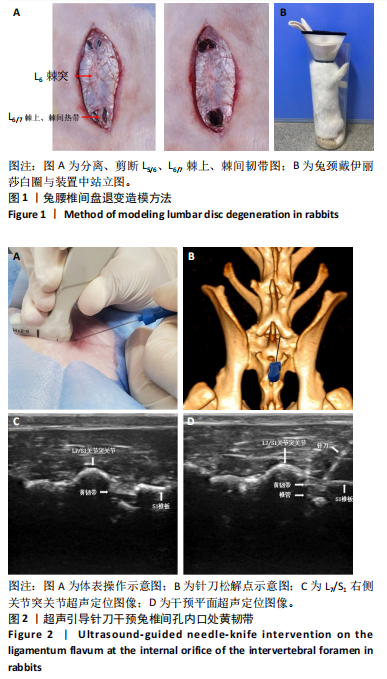
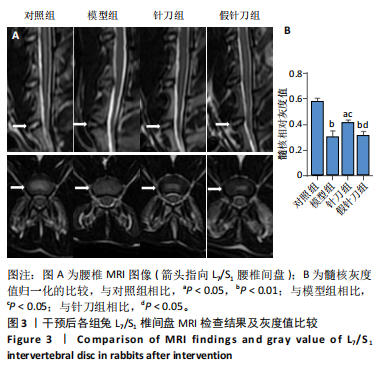
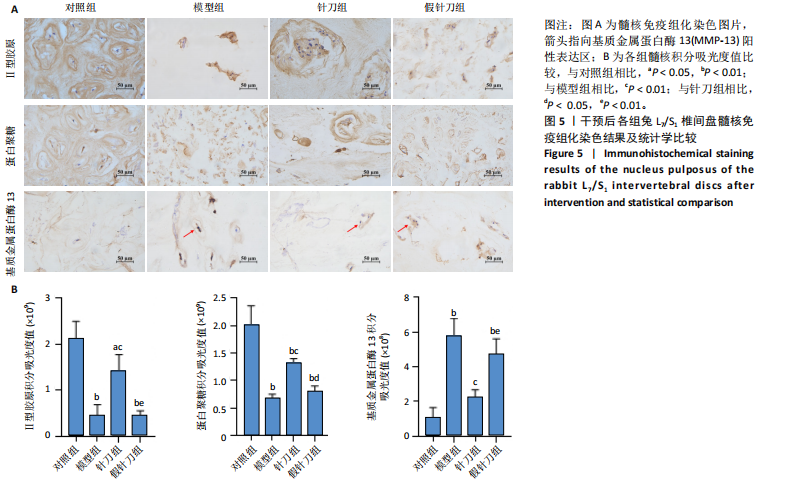
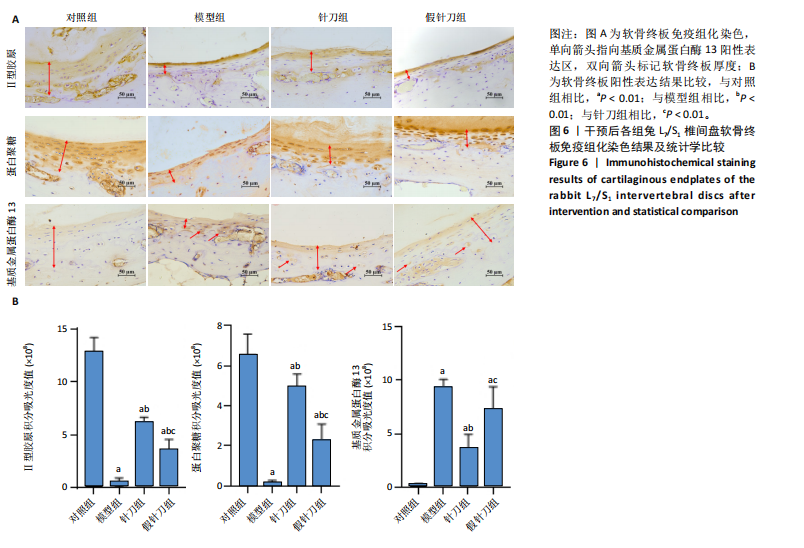
[1] SENCK S, TRIEB K, KASTNER J, et al. Visualization of intervertebral disc degeneration in a cadaveric human lumbar spine using microcomputed tomography. J Anat. 2020;236(2):243-251.
[2] MOHD II, TEOH SL, MOHD NN, et al. Discogenic Low Back Pain: Anatomy, Pathophysiology and Treatments of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):208.
[3] 石翀,王海龙,邱祖云,等. 超声引导下针刀经皮松解黄韧带治疗腰椎间盘突出症的初步疗效观察[J]. 中日友好医院学报,2022, 36(3):178-179.
[4] 顾晞,甘宁.水针刀椎管内靶点治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效观察[J].云南中医学院学报,2022,45(3):31-34.
[5] VAN DER GRAAF JW, KROEZE RJ, BUCKENS C, et al. MRI image features with an evident relation to low back pain: a narrative review. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(5):1830-1841.
[6] BONNHEIM NB, WANG L, LAZAR AA, et al. The contributions of cartilage endplate composition and vertebral bone marrow fat to intervertebral disc degeneration in patients with chronic low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(7):1866-1872.
[7] BOOS N, WEISSBACH S, ROHRBACH H, et al.Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs:2002 Volvo Award in basic science. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(23):2631-2644.
[8] LAKSTINS K, ARNOLD L, GUNSCH G, et al. Characterization of the human intervertebral disc cartilage endplate at the molecular, cell, and tissue levels. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(9):1898-1907.
[9] LAO YJ, XU TT, JIN HT, et al. Accumulated Spinal Axial Biomechanical Loading Induces Degeneration in Intervertebral Disc of Mice Lumbar Spine. Orthop Surg. 2018;10(1):56-63.
[10] ZHOU N, SHEN B, BAI C, et al. Nutritional deficiency induces nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis via the ATF4-PKM2-AKT signal axis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):946.
[11] 赵宇. 超声引导下针刀松解兔腰椎肥厚黄韧带的作用及其对TGF-β1/Smad2通路的影响[D]. 福州:福建中医药大学,2023.
[12] 陈灿, 赵宇, 胡斌涵, 等. 超声引导下针刀松解黄韧带对兔退变腰椎间盘整合素α5、β1表达的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(2):331-338.
[13] 赵兵营. 椎体终板生物力学特性研究[D]. 太原:太原理工大学, 2022.
[14] WONG J, SAMPSON S L, BELL-BRIONES H, et al. Nutrient supply and nucleus pulposus cell function: effects of the transport properties of the cartilage endplate and potential implications for intradiscal biologic therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(6):956-964.
[15] 赵宇, 郭双, 陈灿, 等. 超声引导下针刀松解兔腰椎黄韧带的解剖学研究[J].中国医药导报,2023,20(13):4-8.
[16] RUAN D, HE Q, DING Y, et al. Intervertebral disc transplantation in the treatment of degenerative spine disease: a preliminary study. Lancet. 2007;369(9566):993-999.
[17] PFIRRMANN CW, METZDORF A, ZANETTI M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(17):1873-1878.
[18] GULLBRAND SE, ASHINSKY BG, LAI A, et al. Development of a standardized histopathology scoring system for intervertebral disc degeneration and regeneration in rabbit models-An initiative of the ORSspine section. JOR Spine. 2021;4(2):e1147.
[19] 刘爽, 施杞, 杜文岚, 等. 基于筋骨平衡理论探讨椎旁肌病变与腰椎退变的关系[J].中医正骨,2024,36(2):60-64.
[20] 朱汉章. 针刀医学体系概论[J]. 中国工程科学,2006(7):1-15.
[21] 刘福水, 方婷, 周凡媛. 针刀“调筋治骨”法治疗颈椎病力学机制探讨[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2018,36(12):2862-2865.
[22] 林秀华, 刘存斌, 耿凯, 等. 超声引导下针刀松解黄韧带治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床效果[J]. 中国医药导报,2022,19(9):157-160.
[23] 陈小峰, 曹晔, 浦建枫, 等. CT引导下水针刀靶向微创松解技术在腰椎间盘突出症治疗中的应用研究[J].介入放射学杂志,2019, 28(8):754-758.
[24] 欧林宏, 乔英杰, 张万里, 等. 李华东从椎间孔内外口靶点治疗腰椎间盘突出症经验[J].山东中医杂志,2022,41(8):891-894.
[25] 周俏吟,申毅锋,孙小洁,等.可视化针刀发展的机遇和挑战[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(10):4801-4804.
[26] BURT KG, VIOLA DC, LISIEWSKI LE, et al. An in vivo model of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy from early-stage inflammation to fibrosis. JOR Spine. 2023;6(3):e1260.
[27] ZHANG Y, LENART BA, LEE JK, et al. Histological features of endplates of the mammalian spine: from mice to men. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(5):E312-E317.
[28] BRENDLER J, WINTER K, LOCHHEAD P, et al. Histological differences between lumbar and tail intervertebral discs in mice. J Anat. 2022; 240(1):84-93.
[29] LI J, MA Y, JIAO Y, et al. Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Low Back Pain Depends on Duration and Magnitude of Axial Compression. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:1045999.
[30] XU H, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. A novel rat model of annulus fibrosus injury for intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 2024;24(2): 373-386.
[31] QUAN H, ZUO X, HUAN Y, et al. A systematic morphology study on the effect of high glucose on intervertebral disc endplate degeneration in mice. Heliyon. 2023;9(2):e13295.
[32] FINE N, LIVELY S, SEGUIN CA, et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration and osteoarthritis: a common molecular disease spectrum. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023;19(3):136-152.
[33] VERES SP, ROBERTSON PA, BROOM ND. ISSLS prize winner: how loading rate influences disc failure mechanics: a microstructural assessment of internal disruption.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(21):1897-1908.
[34] 韩涛, 尹逊路, 展嘉文, 等. 补肾活血中药介导Wnt/β-catenin信号通路延缓椎间盘终板压力退变的机制研究[J].中国全科医学, 2021,24(35):4427-4436.
[35] ZHENG Q, WANG CD, SHAO S, et al. Intermittent cyclic mechanical compression promotes endplate chondrocytes degeneration by disturbing Nrf2/PINK1 signaling pathway-dependent mitophagy. Hum Cell. 2023;36(6):1978-1990.
[36] 范凯健, 吴菁, 李钦, 等.基质金属蛋白酶13在软骨重塑和关节炎中的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2018,34(5):607-611.
[37] HUANG YZ, ZHAO L, ZHU Y, et al. Interrupting TGF-β1/CCN2/integrin-α5β1 signaling alleviates high mechanical-stress caused chondrocyte fibrosis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(3):1233-1241. |