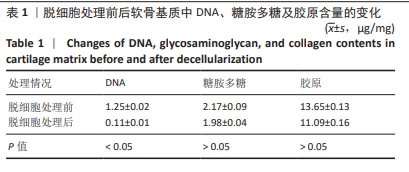
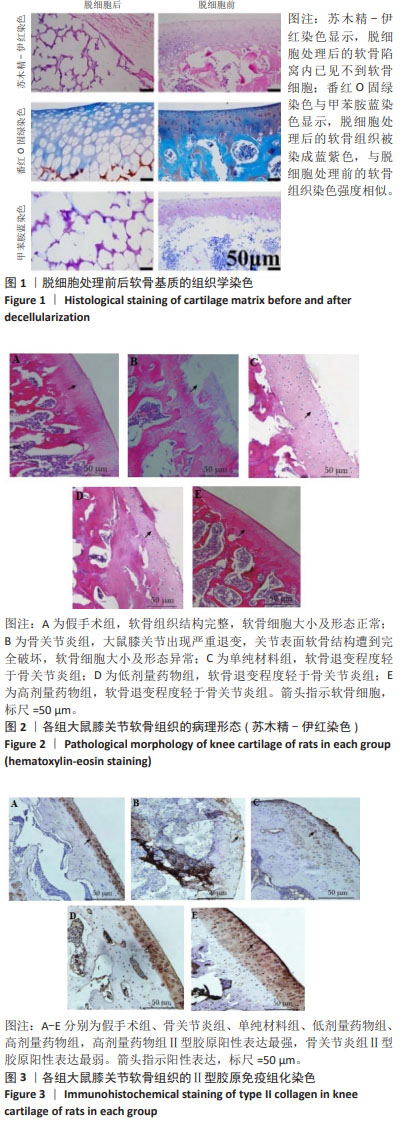
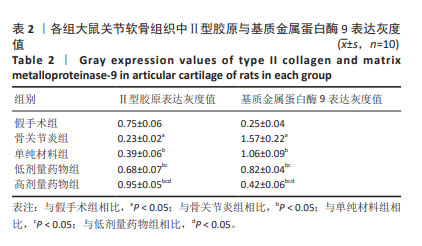
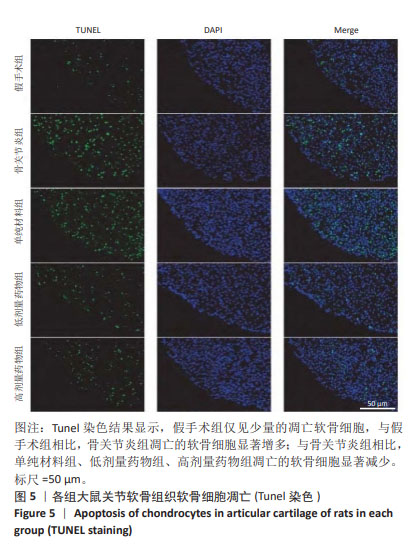
[1] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311.
[2] HALL M, VAN DER ESCH M, HINMAN RS, et al. How does hip osteoarthritis differ from knee osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(1):32-41.
[3] KUMAR A, PALIT P, THOMAS S, et al. Osteoarthritis: Prognosis and emerging therapeutic approach for disease management. Drug Dev Res. 2021;82(1): 49-58.
[4] BHATTACHARJEE M, ESCOBAR IVIRICO JL, KAN HM, et al. Injectable amnion hydrogel-mediated delivery of adipose-derived stem cells for osteoarthritis treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(4):e2120968119.
[5] LI G, LIU S, CHEN Y, et al. An injectable liposome-anchored teriparatide incorporated gallic acid-grafted gelatin hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):3159.
[6] ZHU W, CAO L, SONG C, et al. Cell-derived decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds for articular cartilage repair. Int J Artif Organs. 2021;44(4):269-281.
[7] CHEN D, ZHANG Y, LIN Q, et al. The effect of cartilage decellularized extracellular matrix-chitosan compound on treating knee osteoarthritis in rats. PeerJ. 2021;9:e12188.
[8] TIAN G, JIANG S, LI J, et al. Cell-free decellularized cartilage extracellular matrix scaffolds combined with interleukin 4 promote osteochondral repair through immunomodulatory macrophages: In vitro and in vivo preclinical study. Acta Biomater. 2021;127:131-145.
[9] KIM M, AHN J, LEE J, et al. Combined Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Cartilage Acellular Matrix Injection Therapy for Osteoarthritis in Goats. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;19(1):177-187.
[10] JEON HJ, YOON KA, AN ES, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combined with Cartilage Acellular Matrix Mediated Via Bone Morphogenic Protein 6 in a Rabbit Model of Articular Cruciate Ligament Transection. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020; 16(3):596-611.
[11] JIN X, FU W, ZHOU J, et al. Oxymatrine attenuates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced HUVEC injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via the activation of the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(4):187.
[12] WANG XL, CHEN F, SHI H, et al. Oxymatrine inhibits neuroinflammation byRegulating M1/M2 polarization in N9 microglia through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108139.
[13] 高歌,方官琴,付凌云,等.氧化苦参碱通过抑制心肌细胞焦亡改善脂多糖诱导的心肌损伤[J].中药材,2022,45(12):2962-2968
[14] MOHETAER D, CAO L, WANG Y. Oxymatrine Protects Chondrocytes against IL-1β-triggered Apoptosis in Vitro and Inhibits Osteoarthritis in Mice Model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:2745946.
[15] 刘茜,李雪健,王忠山.猪软骨脱细胞基质对人脂肪干细胞增殖及分化的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2020,38(2):122-127
[16] ZHANG Y, DAI J, YAN L, et al. Intra-articular injection of decellularized extracellular matrices in the treatment of osteoarthritis in rabbits. PeerJ. 2020;8:e8972.
[17] 李明静,张健强,郭靖,等.艾灸不同腧穴对KOA大鼠不同组织TNF-α、MMP-13表达的影响[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2023, 25(4):1390-1397.
[18] JIN Z, CHANG B, WEI Y, et al. Curcumin exerts chondroprotective effects against osteoarthritis by promoting AMPK/PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;151:113092.
[19] KARAMANOS NK, THEOCHARIS AD, PIPERIGKOU Z, et al. A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrix. FEBS J. 2021;288(24): 6850-6912.
[20] LIU C, PEI M, LI Q, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix mediates tissue construction and regeneration. Front Med. 2022;16(1):56-82.
[21] KARAMANOS NK, THEOCHARIS AD, PIPERIGKOU Z, et al. A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrix. FEBS J. 2021;288(24): 6850-6912.
[22] GUVATOVA ZG, BORISOV PV, ALEKSEEV AA, et al. Age-Related Changes in Extracellular Matrix.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2022;87(12):1535-1551.
[23] LI SH, WU QF. MicroRNAs target on cartilage extracellular matrix degradation of knee osteoarthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(3):1185-1197.
[24] ZOU ZL, SUN MH, YIN WF, et al. Avicularin suppresses cartilage extracellular matrix degradation and inflammation via TRAF6/MAPK activation. Phytomedicine. 2021;91:153657.
[25] YANG Y, LIN H, SHEN H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular matrix enhances chondrogenic phenotype of and cartilage formation by encapsulated chondrocytes in vitro and in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2018;69: 71-82.
[26] LU L, SHANG X, LIU B, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defect using adipose-derived stem cell-loaded scaffold derived from native cartilage extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(6):4244-4257.
[27] LIU J, LU Y, XING F, et al. Cell-free scaffolds functionalized with bionic cartilage acellular matrix microspheres to enhance the microfracture treatment of articular cartilage defects. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(6):1686-1697.
[28] MA P, YUE L, YANG H, et al. Chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of amurensin H by regulating TLR4/Syk/NF-κB signals. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(2):1958-1968.
[29] YAO M, ZHANG J, LI Z, et al. Marein protects human nucleus pulposus cells against high glucose-induced injury and extracellular matrix degradation at least partly by inhibition of ROS/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106126.
[30] JIN Q, LI Z, XU Q, et al. Matrine From Sophora Flavescens Attenuates on Collagen-Induced Osteoarthritis by Modulating the Activity of miR-29B-3P/PGRN Axis. Physiol Res. 2023;72(4):475-483.
[31] WEI K, DAI J, WANG Z, et al. Oxymatrine suppresses IL-1β-induced degradation of the nucleus pulposus cell and extracellular matrix through the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020;245(6): 532-541.
[32] WU J, LI H, HU F, et al. Stevioside attenuates osteoarthritis via regulating Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB pathway. J Orthop Translat. 2022;38:190-202.
[33] CHEN Z, ZHONG H, WEI J, et al. Inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling leads to increased activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):300.
[34] ZHANG Q, LIU J, DUAN H, et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress.J Adv Res. 2021;34:43-63.
[35] LIU X, ZHU Q, ZHANG M, et al. Isoliquiritigenin Ameliorates Acute Pancreatitis in Mice via Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:7161592.
[36] FENG Y, CUI R, LI Z, et al. Methane Alleviates Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury by Inhibiting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Apoptosis through the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:7067619. |