[1] MISHRA VK, SHIH HH, PARVEEN F, et al. Identifying the Therapeutic Significance of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells. 2020;9(5):1145.
[2] LIAU LL, LOOI QH, CHIA WC, et al. Treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:112.
[3] RHODE SC, BEIER JP, RUHL T. Adipose tissue stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration-In vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci Res. 2021;99(2): 545-560.
[4] ZHOU LN, WANG JC, ZILUNDU PLM, et al. A comparison of the use of adipose-derived and bone marrow-derived stem cells for peripheral nerve regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):153.
[5] AL-GHADBAN S, BUNNELL BA. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Immunomodulatory Effects and Therapeutic Potential. Physiology (Bethesda). 2020;35(2):125-133.
[6] WANG Y, FANG J, LIU B, et al. Reciprocal regulation of mesenchymal stem cells and immune responses. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29(11): 1515-1530.
[7] WANG LT, LIU KJ, SYTWU HK, et al. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell therapy for immune and inflammatory diseases: Use of cell-free products and human pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(9):1288-1303.
[8] WILLMS E, JOHANSSON HJ, MÄGER I, et al. Cells release subpopulations of exosomes with distinct molecular and biological properties. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22519.
[9] SAILLIET N, ULLAH M, DUPUY A, et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Transplantation. Front Immunol. 2022;13:800018.
[10] HADE MD, SUIRE CN, MOSSELL J, et al. Extracellular vesicles: Emerging frontiers in wound healing. Med Res Rev. 2022;42(6):2102-2125.
[11] AN Y, LIN S, TAN X, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells and application to skin wound healing. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(3):e12993.
[12] RECORD M, SILVENTE-POIROT S, POIROT M, et al. Extracellular vesicles: lipids as key components of their biogenesis and functions. J Lipid Res. 2018;59(8):1316-1324.
[13] HE C, ZHENG S, LUO Y, et al. Exosome Theranostics: Biology and Translational Medicine. Theranostics. 2018;8(1):237-255.
[14] HADE MD, SUIRE CN, SUO Z. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Applications in Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2021;10(8): 1959.
[15] BU H, HE D, HE X, et al. Exosomes: Isolation, Analysis, and Applications in Cancer Detection and Therapy. Chembiochem. 2019;20(4):451-461.
[16] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
[17] WORTZEL I, DROR S, KENIFIC CM, et al. Exosome-Mediated Metastasis: Communication from a Distance. Dev Cell. 2019;49(3):347-360.
[18] WANG C, LI Z, LIU Y, et al. Exosomes in atherosclerosis: performers, bystanders, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets. Theranostics. 2021; 11(8):3996-4010.
[19] WATANABE Y, TSUCHIYA A, TERAI S. The development of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the present, and the perspective of cell-free therapy in the future. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021;27(1):70-80.
[20] FAMILTSEVA A, JEREMIC N, TYAGI SC. Exosomes: cell-created drug delivery systems. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;459(1-2):1-6.
[21] ZHANG Y, BI J, HUANG J, et al. Exosome: A Review of Its Classification, Isolation Techniques, Storage, Diagnostic and Targeted Therapy Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6917-6934.
[22] MONDAL J, PILLARISETTI S, JUNNUTHULA V, et al. Hybrid exosomes, exosome-like nanovesicles and engineered exosomes for therapeutic applications. J Control Release. 2023;353:1127-1149.
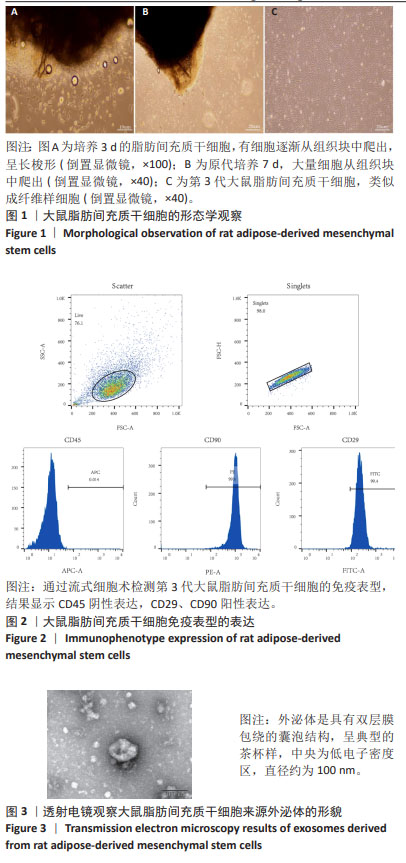
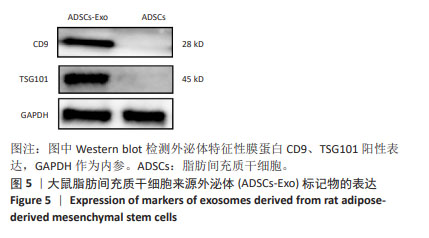
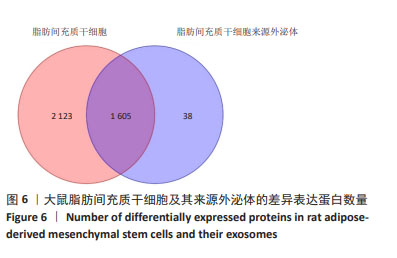
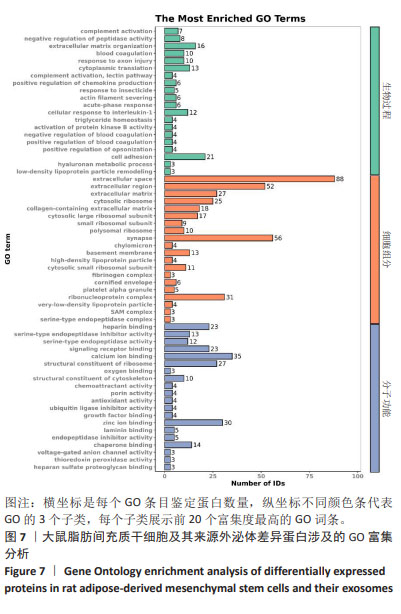
[23] 刘海琴,马华根,唐元瑜.原代大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞的体外培养扩增及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(19):2953-2957.
[24] DOYLE LM, WANG MZ. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells. 2019;8(7):727.
[25] ZHAO R, ZHAO T, HE Z, et al. Composition, isolation, identification and function of adipose tissue-derived exosomes. Adipocyte. 2021;10(1): 587-604.
[26] HAN Y, LI X, ZHANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2019;8(8):886.
[27] PIXLEY JS. Mesenchymal stem cells to treat type 1 diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(4):165315.
[28] SONG Y, DU H, DAI C, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis: a pilot study with long-term follow-up and repeated injections. Regen Med. 2018;13(3):295-307.
[29] SHERMAN LS, ROMAGANO MP, WILLIAMS SF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapies in brain disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019;95:111-119.
[30] CHEN SY, YANG RL, WU XC, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation: Neuroprotection and Nerve Regeneration After Spinal Cord Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:4763-4776.
[31] FATHOLLAHI A, GABALOU NB, ASLANI S. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in systemic lupus erythematous, a mesenchymal stem cell disorder. Lupus. 2018;27(7):1053-1064.
[32] REGMI S, PATHAK S, KIM JO, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for the treatment of inflammatory diseases: Challenges, opportunities, and future perspectives. Eur J Cell Biol. 2019;98(5-8):151041.
[33] MAZINI L, ROCHETTE L, ADMOU B, et al. Hopes and Limits of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1306.
[34] XUNIAN Z, KALLURI R. Biology and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(9): 3100-3110.
[35] MELDOLESI J. Exosomes and Ectosomes in Intercellular Communication. Curr Biol. 2018;28(8):R435-R444.
[36] TANG Y, ZHOU Y, LI HJ. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: a review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):71.
[37] AGUIAR KOGA BA, FERNANDES LA, FRATINI P, et al. Role of MSC-derived small extracellular vesicles in tissue repair and regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;10:1047094.
[38] SUN Y, LIU G, ZHANG K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):561.
[39] HARRELL CR, VOLAREVIC V, DJONOV V, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes Derived from Adipose Tissue-Sourced Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Neural and Retinal Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(9):4487.
[40] FANG Y, ZHANG Y, ZHOU J, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: a novel pathway for tissues repair. Cell Tissue Bank. 2019;20(2):153-161.
[41] GOODARZI P, ALAVI-MOGHADAM S, PAYAB M, et al. Metabolomics Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2019; 8(Suppl1):30-40.
[42] TOH WS, LAI RC, ZHANG B, et al. MSC exosome works through a protein-based mechanism of action. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018;46(4): 843-853.
[43] KIMIZ-GEBOLOGLU I, ONCEL SS. Exosomes: Large-scale production, isolation, drug loading efficiency, and biodistribution and uptake. J Control Release. 2022;347:533-543.
[44] PEGTEL DM, GOULD SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88: 487-514.
[45] SALUNKHE S, DHEERAJ, BASAK M, et al. Surface functionalization of exosomes for target-specific delivery and in vivo imaging & tracking: Strategies and significance. J Control Release. 2020;326:599-614.
[46] YAMASHITA T, TAKAHASHI Y, TAKAKURA Y. Possibility of Exosome-Based Therapeutics and Challenges in Production of Exosomes Eligible for Therapeutic Application. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(6):835-842.
[47] ALONSO-ALONSO ML, GARCÍA-POSADAS L, DIEBOLD Y. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Review of Common Cargos. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(3):854-901.
[48] ZHU A, LIU N, SHANG Y, et al. Signaling pathways of adipose stem cell-derived exosomes promoting muscle regeneration. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(21):2525-2534.
[49] LEE M, BAN JJ, YANG S, et al. The exosome of adipose-derived stem cells reduces β-amyloid pathology and apoptosis of neuronal cells derived from the transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2018;1691:87-93. |