中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 426-432.doi: 10.12307/2023.982
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
软组织和硬组织再生过程中的电纺纳米纤维支架
王欣怡1,谢宪瑞2,陈玉杰1,王晓宇1,徐小青1,沈怿弘1,莫秀梅1
- 1上海纳米生物材料与再生医学研究中心,东华大学,生物与医学工程学院,上海市 201600;2滨州医学院,药学院,“方剂效应与临床评价”国家中医药管理局重点研究室,山东省滨州市 256600
-
收稿日期:2022-10-09接受日期:2023-02-17出版日期:2024-01-28发布日期:2023-07-10 -
通讯作者:莫秀梅,博士,教授,硕士生导师,博士生导师,上海纳米生物材料与再生医学研究中心,东华大学,生物与医学工程学院,上海市 201600 -
作者简介:王欣怡,女,2000年生,江苏省淮安市人,汉族,东华大学在读硕士,主要从事静电纺丝应用于组织再生的研究。 谢宪瑞,滨州医学院,药学院,“方剂效应与临床评价”国家中医药管理局重点研究室,山东省滨州市 256600
Electrospun nanofiber scaffolds for soft and hard tissue regeneration
Wang Xinyi1, Xie Xianrui2, Chen Yujie1, Wang Xiaoyu1, Xu Xiaoqing1, Shen Yihong1, Mo Xiumei1
- 1School of Biological and Medical Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai Nanobiomaterials and Regenerative Medicine Research Center, Shanghai 201600, China; 2Key Laboratory of “Prescription Effect and Clinical Evaluation” State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, School of Pharmacy, Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-09Accepted:2023-02-17Online:2024-01-28Published:2023-07-10 -
Contact:Mo Xiumei, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Biological and Medical Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai Nanobiomaterials and Regenerative Medicine Research Center, Shanghai 201600, China -
About author:Wang Xinyi, Master candidate, School of Biological and Medical Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai Nanobiomaterials and Regenerative Medicine Research Center, Shanghai 201600, China Xie Xianrui, Key Laboratory of “Prescription Effect and Clinical Evaluation” State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, School of Pharmacy, Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
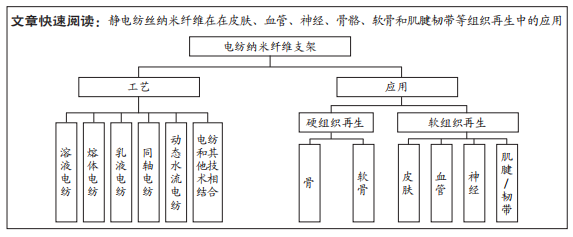
电纺纳米纤维支架:是用静电纺丝法制备的由纳米纤维丝交织而成的组织再生用支架材料,为膜状、管状及块状等,用于皮肤、血管、神经、肌腱、骨和软骨等的组织再生。组织再生:是机体对由某种原因引起死亡的细胞进行补偿与恢复的过程。组织不断地进行更新,称为生理性再生。
背景:目前,静电纺丝纳米纤维是天然细胞外基质的仿生材料,其包含互连孔隙的三维网络,已成功用作各种组织再生的支架,但目前仍面临着如何将生物材料扩展成三维结构以再现组织微环境的生理、化学以及机械性能的挑战。
目的:总结归纳静电纺丝的工艺、原理,探讨由此生产的静电纺丝纳米纤维在皮肤、血管、神经、骨骼、软骨和肌腱/韧带等组织再生中的应用。方法:以“静电纺丝、电纺纳米纤维、电纺纳米纤维支架、组织再生”为中文检索词,“Electrospinning,electrospun nanofibers,electrospun nanofiber scaffolds,tissue regeneration”为英文检索词,检索Google学术、PubMed和中国知网数据库,最终纳入88篇文献进行综述分析。
结果与结论:①静电纺丝纳米纤维是天然纤维状细胞外基质的仿生材料,并包含互连孔隙的三维网络,在各种组织再生的支架领域中应用较多。②多篇文献阐述了电纺纳米支架应用于皮肤、血管、神经、骨骼、软骨和肌腱/韧带组织再生的巨大潜力,为其最终应用于临床疾病治疗,或转化为实际产品进入市场提供了坚实的理论基础。③但目前的研究成果多是基于体外的细胞实验研究成果,能否最终应用于人体尚需临床验证。④目前国内外已有多种用于各种临床需求的电纺产品商业化,表明用于软组织和硬组织再生的电纺纳米纤维支架研究领域具有重大的研究价值和应用潜力。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9238-6171(莫秀梅)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
王欣怡, 谢宪瑞, 陈玉杰, 王晓宇, 徐小青, 沈怿弘, 莫秀梅. 软组织和硬组织再生过程中的电纺纳米纤维支架[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 426-432.
Wang Xinyi, Xie Xianrui, Chen Yujie, Wang Xiaoyu, Xu Xiaoqing, Shen Yihong, Mo Xiumei. Electrospun nanofiber scaffolds for soft and hard tissue regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 426-432.
2.1.1 电纺纳米纤维的发展历史 电纺纳米纤维自20世纪始就已有学者进行研究。有研究者最初发表了一系列关于溶液静电纺丝的专利,该专利使用溶解在溶液中的聚合物来获得纳米至微米直径范围内的超细纤维[5]。1980 年,美国专利局公开了另一种静电纺丝方法,即聚合物熔体静电纺丝,其中将聚合物熔化以产生静电纺丝溶液[16]。该过程产生的纤维比溶液静电纺丝获得的纤维大一两个数量级,这表明它可能不适用于静电纺丝纤维的所有应用[17]。尽管如此,溶液和熔融静电纺丝的发明为新技术的进一步发展和进步奠定了基础。
自从来到21世纪,传统的电纺技术在世界范围内的科研和工业界迅速发展,部分原因是人们对组织工程领域的兴趣日益浓厚。2003年,SUN等[18]报道了一种新的静电纺丝技术,即具有核壳结构的同轴静电纺丝纳米纤维,其中两种不同的溶液通过同轴喷嘴同时喷射,从而实现材料的封装,得到皮芯结构的纳米纤维。在这项技术的基础上,XU 等[19]通过乳液静电纺丝报道了含有抗癌药物的核壳结构纳米纤维,该纳米纤维不需要同轴喷嘴,而是用单轴喷嘴将乳液纺成核壳结构的纳米纤维。为了增加电纺膜的三维度,TEO 等[20]创建了一个静电纺丝系统,该系统结合了水涡流来收集纳米纤维,产生了高孔隙率的可用于组织工程的支架。类似地,2012年ALI等[21]创建了一种用于连续静电纺丝的纳米纱线系统,纳米纱可以针织或编织成组织工程支架。最近,SI等[22]将静电纺丝与冷冻干燥相结合,生成了一种纳米纤维嵌入3D多孔气凝胶中的复合材料。自2000年以来,由于人们对静电纺丝膜的兴趣日益增长,已发表的与静电纺丝相关的文章数量呈指数级增长。在按国家发表的文章总数排名中,中国排名第一,占全球发表论文总数的近50%,其次是美国和韩国。因此,中国成为静电纺丝领域研究最活跃的国家。
2.1.2 不同的电纺技术 传统的静电纺丝方法中,通常对聚合物溶液施加高压以在喷嘴尖端产生泰勒锥。使用注射泵控制聚合物溶液的流速,当带电溶液和收集器之间的电位差克服溶液的表面张力时,泰勒锥中就会喷出射流。喷出的液体射流产生的纤维继续向收集器行进,致使溶剂蒸发并产生干燥的纳米纤维。根据接收器的形状,可以制造膜状或管状纳米纤维结构,并且可以根据接收器的旋转速度调节纤维排列(取向或随机)。
与传统的静电纺丝类似,同轴静电纺丝包含一个同轴喷嘴,其中包含2个不同尺寸的喷嘴,一个围绕另一个形成一个套筒。内径较小的喷嘴输送核溶液,内径较大的喷嘴输送壳溶液。通过这种方式,包含在不同容器中的壳溶液和芯溶液通过同轴喷嘴同时喷射,并且通过与使用电位差的传统静电纺丝相同的机制产生核壳纳米纤维。同轴静电纺丝的一个优点是只有壳溶液必须是可纺的,因此可以将一些不可纺的药物、生长因子和其他功能性添加剂掺入核心溶液中,从而形成静电纺生物材料。
与同轴静电纺丝一样,乳液静电纺丝产生皮芯结构的纳米纤维,但使用聚合物乳液进行制备。该工艺是有利的,因为可以通过单个纺丝喷嘴将乳液电纺以获得具有多芯结构或皮芯结构的纳米纤维,但是无需使用同轴喷嘴。在此过程中,乳液液滴可以在纳米纤维中被拉伸以形成皮芯结构,也可以保持为液滴以形成多芯结构。同样,不可纺的药物、生长因子和其他活性物质可以分散在聚合物溶液中,并通过乳液静电纺丝进行静电纺丝。
另一种类型的静电纺丝是动态水流电纺,纳米纤维首先收集在水面上,被水旋涡捻成纱线,然后收集在旋转收集器上。在这种方法中,利用了上水池和下水池,上水池底部有一个小孔,水可以通过重力从该小孔中流出,从而在水面上形成一个漩涡;然后,当纳米纤维在水面上进行静电纺丝时,它们会经过涡流并捻成纱线。水和纱线从上水池流到下水池,水通过泵循环到上水池。随着纱线流向下水池,它被收集在旋转接收器上,从而产生多孔纳米纱线支架。与传统的电纺膜相比,这种支架具有更粗糙的表面、更大的孔径和更高的孔隙率,这表明它们在用作组织工程支架时可能更有利于细胞的三维生长 [23-24]。
另一种制备连续纳米纱线的制造方法为利用双喷头共轭静电纺,见图3。一个纺丝喷嘴通过施加正高压产生带正电荷的纳米纤维,而另一个纺丝喷嘴通过施加带负电压的高压产生带负电荷的纳米纤维。这种设置导致带相反电荷的纤维包绕在一起,被收集在旋转的漏斗上并捻成纱线[21]。

2.1.3 用于组织工程的理想支架 组织工程支架旨在作为组织缺陷的临时替代品,能够诱导细胞向内生长和新组织形成,同时随着组织成熟而在体内降解。静电纺丝是一种在制造组织工程支架方面具有巨大潜力的技术,因为它制造的仿生结构类似于天然细胞外基质的纳米丝状结构和形态。事实上,人体的细胞外基质是由多种结构蛋白(如胶原蛋白和弹性蛋白)与非结构蛋白(如糖胺聚糖)交织而成的纳米纤维凝胶网络。细胞外基质结构纤维的直径通常为 50-300 nm,纤维为细胞附着提供锚定点并保持整体组织/器官的形状和形态 [24]。如冷冻干燥后的结缔组织的超微结构所示,成纤维细胞镶嵌在胶原纤维的网络中[25]。当细胞受体与细胞外基质上的配体结合时,由外而内的信号传导可以诱导细胞行为的变化,从而在细胞和细胞外基质之间产生动态信号交流。因此,组织工程支架不仅应当对细胞外基质的结构进行生物模拟,而且应当模拟细胞外基质包含的生物信号。研究显示,纤维的尺寸对于通过纳米纤维结构诱导适当的由外向内信号传导,对改善组织工程支架在骨骼、软骨、心血管、神经和膀胱再生方面的功能至关重要 [26-27]。
几项研究说明了纳米材料对于细胞行为的调节作用。例如,PATTISON等[28]使用纳米级聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物支架以及平滑肌细胞在体外创造了一个纳米级组织工程膀胱,并且证明了更好的细胞黏附、更好的增殖以及能够分泌更多的胶原和弹性蛋白,相比于微米级而言。同样,碳纳米纤维已被证明可以增加成骨细胞的增殖能力及其碱性磷酸酶和钙的分泌[29]。这些细胞行为的变化被认为和细胞形态的改变有关[30]。当细胞黏附在微孔和微纤维支架上呈现扁平形态时,细胞表现出拉伸行为,但当它们黏附在纳米纤维支架的较大表面积上时,形态与在天然组织中观察到的形态相似。纳米纤维支架的高表面积促进了更显著的蛋白质吸附,并为细胞膜上的受体提供了更多的黏附位点。因此,与细胞外基质具有相似结构的纳米纤维支架可能通过在附着和迁移过程中改变细胞形态来诱导更合适的细胞行为,提供一个更有利于引导组织再生的微环境。
2.2 电纺纳米纤维技术的应用
2.2.1 用于皮肤组织再生的电纺纤维 皮肤是人体最大的器官,提供外部屏障以防止病原体入侵[31]。因此,经常感染的慢性、不愈合伤口或大规模外伤,例如由烧伤或车祸造成的伤口,由于存在全身感染的风险,对健康构成重大威胁。自体皮肤移植通常用于加速伤口愈合和恢复受损皮肤的功能;然而,它们会导致供区损伤,并且可能无法使用,具体取决于组织损伤的程度[32]。作为替代方案,组织工程支架可用于伤口的修复和保护。支架的其他基本功能是保持伤口和周围区域湿润、吸附分泌物、具有良好的透气性和抑制细菌生长。因此,静电纺丝支架在皮肤组织再生中具有应用潜力。
大量的天然以及合成复合物已经被电纺用于皮肤组织工程。有研究表明,和纱布对照组相比,壳聚糖和胶原或者丝素蛋白混合电纺纳米纤维能促进细胞增殖,并促进伤口愈合[33]。另外,LI等[34]使用静电纺丝法制备了由罗非鱼皮制成的纳米纤维,该纤维主要由Ⅰ型胶原蛋白组成,证明了该纳米纤维膜具有良好的生物相容性和低免疫原性,这表明罗非鱼皮可能是用于皮肤组织胶原蛋白的良好来源。而MA 等[35]聚焦于创造一种止血生物材料,将藁本嗪掺入丝素蛋白静电纺丝支架中,发现它能够促进伤口止血、具有抗炎作用且能诱导伤口愈合。同时,为了提高电纺生物材料的机械性能,生物活性玻璃已被掺入到鱼胶原电纺纳米纤维中[36],与仅含有鱼胶原的纳米纤维对照组相比,该复合材料具有更大的拉伸强度、更强的抗金黄色葡萄球菌能力,并能促进人体皮肤成纤维细胞的黏附和增殖。最近,YU 等[37]开发了一种四步工艺以制造三维支架,包括静电纺丝、机械切割/切碎、冷冻干燥和热处理。 由聚己内酯-聚乙二醇聚己内酯制成的支架表现出独特的分层多孔结构,具有较大的孔和高孔隙率,与二维膜相比,吸水率增加 3.3 倍,该三维支架也改善了小鼠成纤维细胞的黏附、增殖和迁移,使得炎症反应最小化、并促进早期再上皮化和体内肉芽组织形成。
未来在用于皮肤组织工程支架的材料中,生物活性复合物应当予以重视,例如可以添加温度或pH敏感的材料到敷料中,像这样的添加物可以通过颜色变化提供生物反馈,用于实时监测伤口愈合和感染。因此这种反馈可以为伤口护理计划提供更多的参考并改善患者的治疗效果。
2.2.2 用于血管组织再生的电纺纳米纤维 在美国每年有超过1 400万的患者接受血管移植,花费约为250亿美元[38]。人们对可用于组织工程的小直径(即内径小于 5 mm)血管移植物的需求很大程度上未得到满足。目前可用的不可吸收的小直径血管移植物由于血流速度降低和缺乏内皮化而在吻合处形成血栓和内膜增长,最终导致管腔狭窄和闭塞[39]。因此,许多组织工程师正在开发电纺的、可吸收的小直径血管移植物,以引导血管再生并规避与当前合成移植物相关的问题[40-47],典型研究成果见表 1。

2.2.3 用于神经组织再生的电纺纳米纤维 周围神经损伤可能导致患者出现感觉、运动或自主神经问题。与中枢神经系统相比,周围神经的再生能力更为强大。如果损伤小于5 mm,神经能够自我修复,表明存在内源性机制神经来再生神经和恢复功能。不幸的是,当神经缺损的长度达到5 mm以上时,自我修复就会受限,并且需要一种生物材料固定在受损神经的两端以引导再生。近些年来,电纺主要用于构建神经支架,由此产生的材料已经从简单的空心管演变为更复杂的结构,称为神经引导导管或神经导管[48]。神经导管可以包含内部细丝、海绵填充物以及物理和化学信号,以模仿神经束的结构和生物活性[49]。下文将讨论通过电纺开发的几种类型的神经导管。
简单中空管腔结构神经导管:简单中空神经导管为再生神经提供了生长的管腔,但却会限制周围组织的向内生长,并且材料的选择也会影响再生的潜能。与聚乳酸-己内酯对照相比,丝素蛋白和聚乳酸-己内酯的混合物已被证明具有生物相容性并能促进细胞增殖[50]。基于这些发现,WANG 等[51]制备了丝素蛋白和聚乳酸-己内酯取向纳米纤维支架和取向,并通过将静电纺丝支架缠绕在不锈钢棒上来制备神经导管。结果表明,与聚乳酸-己内酯对照相比,丝素蛋白-聚乳酸-己内酯神经导管包含更高密度的、更粗的神经纤维,从而使得神经结构更加成熟。这些发现强调材料对神经再生潜力的影响,并表明丝素蛋白是促进神经再生的优良选择。
掺入生长因子的神经导管:神经生长因子促进中枢和外周神经元的发育、生长、分化以及成熟,在维持正常神经的功能中起关键作用,并且能够加速神经系统损伤修复。因此,ZHANG等[52]研究了通过同轴电纺将神经生长因子掺入取向的电纺纤维以增强神经再生。在这个研究中,神经生长因子能够缓慢释放并且保持活性超过60 d,这对于长期再生的结果很重要。实验结果表明神经生长因子的生物活性和取向支架结构引导协同作用,有效地促进了神经再生。
掺入导电材料的神经导管和电刺激:导电材料(例如聚苯胺和石墨烯)可以被掺入电纺纳米纤维以产生导电的神经导管,能够将电信号从纤维传输到神经元来促进神经元的迁移、增殖以及分化。例如,ZHANG等[53]通过同轴电纺制备了可以导电的聚苯胺和神经生长因子的复合纤维支架,并且评估了电刺激和神经生长因子对再生潜能的协同效应,作者发现电刺激和神经生长因子联合可促进施万细胞的增殖和嗜铬细胞瘤细胞长轴突的延伸,这表明协同作用有利于神经再生,在另一项研究中,SUN等[54]通过原位氧化聚合将导电的聚吡咯涂覆电纺支架。聚吡咯涂层不仅赋予了导电性,而且增加了支架的亲水性,与对照组支架相比,具有累加效应且能提高施万细胞的增殖率。同样,聚吡咯涂层与电刺激相结合也证明了可诱导嗜铬细胞瘤细胞分化并增强轴突生长。这些结果表明,导电聚吡咯涂层的纳米纤维膜在周围神经修复和再生方面有广阔的应用前景。
内腔含有引导丝的神经导管:为了引导神经细胞的迁移和增殖,已经制造出含有充当细胞增殖高速公路功能的细丝的神经导管。在一个案例中,LI等[55]通过双喷丝头系统制备了聚乳酸纳米纱线并且使用它们填充了聚乳酸-己内酯电纺神经导管的内腔,在一系列体外实验中,与聚乳酸膜相比,施万细胞表现出增强的细胞增殖率,并且能够进一步通过纱线结构迁移使得轴突沿着纱线的轴延伸。同样,WU等[56]用电纺聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物制备了一种纳米纱线填充的神经导管,并包括层粘连蛋白涂层以增强细胞黏附力,体外实验表明相比于无涂层的对照组,层粘连蛋白涂层增强了细胞增殖和迁移,表明生物信号对调节和加强周围神经再生的重要性。
内腔包含多孔海绵的神经导管:和充满细丝的支架一样,填充三维海绵的神经导管更有利于细胞迁移和轴突再生。SUN等[57]已经证明了这一点,通过制备具有大孔和高孔隙充满纳米纤维海绵的电纺神经导管,见图4。当移植进10 mm坐骨神经缺损的大鼠模型中时,组织学分析显示神经导管的海绵被施万细胞浸润,这看起来类似于神经束的内部结构。和中空神经导管相比,正如步态分析和肌肉质量所表明的那样,海绵填充的支架显著促进了神经的功能性修复,这项研究表明,含有海绵的神经导管在应用于周围神经修复方面有很大的治疗潜力。

2.2.4 用于骨组织再生的电纺纳米纤维 由于骨感染、骨癌以及外伤所致的骨丢失引起的骨缺损发生率很高,因此临床对于骨移植物有大量需求[58]。自体骨移植由于其显著的骨诱导性、骨导电性且无不良免疫反应被认为是严重骨缺损的临床“金标准”[59]。然而,无论是自体骨还是异体骨的使用,在临床上都受到其可用性的限制。因此,利用组织工程再生骨是一种很有前途的方法,可以克服供体不足的缺点[60-61]。
用于骨组织工程的支架应当具有生物相容性、可生物降解性、生物活性以及具有适合骨环境的机械性能。为了满足这些需求,基于复合材料如有机和无机杂化纳米纤维,并且负载功能因子,例如骨形态发生蛋白、转化生长因子β3、血管内皮生长因子和银纳米粒子的纳米纤维支架,已经成为当前研究的重点[62]。使用静电纺来创造这些支架是有利的,由于纳米纤维是骨骼中由分层的矿化胶原纤维组成的细胞外基质的天然仿生材料[63-64]。YE等[65]创造了一种复合支架,含有纳米羟基磷灰石,它是骨的主要矿物成分。首先,电纺纳米纤维膜被切割成短纤维,冷冻干燥后进行热交联,最终创建了一个三维骨状支架;然后将合成的骨形态发生蛋白2衍生肽固定在表面,并在大鼠颅骨缺陷模型中对该支架进行了体外和体内评估。实验结果表明,纳米羟基磷灰石和骨形态发生蛋白2的存在增加了与干细胞成骨分化有关的基因表达,并且骨形态发生蛋白2肽的释放维持了21 d;与对照组相比,支架有更好的骨诱导性,能够促进Ⅰ型胶原以及成骨标志物的表达(如Runt相关的转录因子2和骨钙素),且提高了碱性磷酸酶活性,使得缺陷中心处的新骨生长。
为了调控骨重塑过程,WANG等[66]设计了一种用于介孔二氧化硅颗粒和阿仑膦酸盐双重递送的电纺支架,实验结果显示了骨的加速生长,CD31染色显示该支架将骨愈合时间从12周减少到近4周;当愈合持续到12周时,该支架的骨成熟度评分几乎是没有介孔二氧化硅颗粒和阿仑膦酸盐的对照组支架的2倍,而且该支架的血管化程度明显更高。这些结果表明,负载硅酸盐和阿仑膦酸盐的电纺纳米纤维可以调节骨重塑过程,并促进强大的血管形成,这对骨再生过程中的充分营养供应至关重要。
为了促进细胞黏附,有研究使用静电纺丝制备聚乳酸纳米纤维,其中含有淀粉和吸附在表面的精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸肽[67],结果发现与对照组相比,用精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸修饰的支架具有更好的细胞黏附性,这显示了引导骨再生的潜力。
为了模拟骨骼的矿物质组成,羟基磷灰石通过一个两阶段的过程被加入到静电纺丝丝素蛋白支架中[68]。首先,羟基磷灰石混合入静电纺丝溶液中以将颗粒定位在纤维内,然后,用受贻贝粘合剂启发的聚多巴胺化学物质对纤维表面进行改性,并用羟基磷灰石沉积,形成第二层颗粒。这种两阶段的功能化被证明可以在体外和体内改善具有 PDZ 结合基序的转录共激活因子转染的人脂肪来源的间充质干细胞的成骨,证明了这些支架与干细胞一起用于增强骨形成的潜在用途。同样,有研究制备了一种含有羟基磷灰石和五氧化二铌 (N) 颗粒的复合支架,该支架已被用作金属植入物的生物活性成分[69]。这些支架被发现是非细胞质的并能促进细胞增殖和细胞黏附,表明这种新型矿物添加剂应用于骨组织工程中的潜力。近年来,静电纺丝生物材料在骨组织工程中引起了越来越多的关注,设计这种材料以支持骨诱导和血管化可以提高它们在组织工程中的性能。
2.2.5 用于软骨组织工程的电纺纤维 运动相关的损伤、创伤和老化对关节软骨的损害可导致骨关节炎和关节衰弱性疼痛,最终可能需要进行全关节置换[70]。虽然自体移植可用于治疗轻微的损伤,但移植物的供应是有限的,并且其植入可导致不良免疫反应。此外,自体移植不能有效治疗严重的软骨缺损。因此,使用电纺支架的组织工程方法是治疗轻度和严重软骨损伤以减少骨关节炎和全部关节置换发生率的潜在策略[71]。由于电纺纳米纤维支架包括具有小孔的密集纤维,因此目前软骨组织工程的一个重点是开发将二维电纺支架加工成模仿天然细胞外基质和适合软骨修复的三维结构的更多方法。
最近,CHEN等[72]开发了一种热交联的支架,它是由来自纳米纤维膜的短纤维组成的冷冻干燥结构,所获得的支架被透明质酸功能化,透明质酸是赋予关节软骨润滑和吸震特性的蛋白质,并在体外和体内评估其刺激软骨再生的能力,由此产生的支架具有高吸水性和良好的机械强度和抗压强度。在体外实验中,软骨细胞被发现黏附在支架的表面并沿着纳米纤维增殖;此外,当植入体内的关节软骨缺陷处12周后,发现该支架相对于未处理的缺损以及未用透明质酸功能化的支架能够促进修复。这些数据表明,由电纺膜产生并进化透明质酸功能化的3D支架可能具有治疗潜力。
除了短纤维组装,气体发泡法作为一种高效的三维静电纺支架成型法近年来也得到了广泛的开发。CHEN等[73]利用气体发泡和冷冻干燥相结合的方法制备了一种三维多层的静电纺纳米纤维支架,并用于软骨组织再生。支架的制备流程为,首先通过动态水流静电纺装置制备了二维聚(L-乳酸-ε-己内酯)/丝素(PLCL/SF)纳米纤维支架(2DS),然后与透明质酸(HA)交联以进一步提高支架的生物活性,随后,通过气体发泡和冷冻干燥,成功制造了三维PLCL/SF支架(3DS)和HA交联的三维支架(3DHAS)。相比于2DS致密的结构,3DS具有疏松的多层形貌,且3DHAS表面形成了透明质酸冷冻干燥后的纳米纤维包围网络;三维发泡支架都表现出高孔隙率(> 90%),低密度(< 0.1 g/cm3),高吸水率
(≈1 500%);3DHAS表现出比3DS更好的机械性能;所有的支架在体外都表现出良好的生物相容性。值得注意的是,与其他支架相比,3DHAS显示出更好的促进软骨细胞的增殖能力和表型维持能力。裸鼠皮下植入8周后的细胞-支架构建物的组织学分析表明,3DS和3DHAS支架都形成了软骨样组织,并且3DHAS支架中形成了更成熟的软骨。此外,兔子的全层关节软骨损伤模型修复实验中,宏观评分和组织学结果都显示了3DHAS能促进更完整的软骨边界形成,更多的软骨特异性基质分泌。
类似地,CHEN等[74]进一步改进了三维发泡支架,并在炎症诱导的微环境中探究支架的成软骨能力,将纳米纤维膜与硫酸软骨素交联并经由气体发泡和冷冻干燥处理得到三维硫酸软骨素交联的纳米纤维支架(3DCSS)。3DCSS不仅具有多层疏松结构,能促进细胞渗透,并在白细胞介素1β诱导的炎症微环境中降低了软骨细胞炎症基因如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,相较于未交联硫酸软骨素组。此外,体内软骨缺损修复结果显示,3DCSS组可再生更成熟的软骨组织,且关节滑膜液中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α等炎症因子表达水平更低。
除了关节软骨,目前正在研究用于治疗先天性缺陷、创伤或疾病的透明软骨的再生。由于透明软骨具有独特的形态,例如在耳朵和鼻子,将电纺与3D打印相结合,可以构建可能有利于透明软骨再生的详细形状。例如,CHEN等[75]开发了一种用于3D打印的墨水,由透明质酸和聚环氧乙烷(PEO)溶液中的碎膜制成的电纺聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物/明胶纳米短纤维组成。该亲水支架被发现在纤维之间有大而规则的孔隙,孔隙率高,吸收大量的水,并拥有水诱导的形状记忆,30 s内形状得而快速恢复,表明这种可打印的三维支架可以用来指导体内复杂软骨结构的再生。
与人耳朵和鼻子一样,气管的软骨具有独特的形状,并且与其他组织(如肌肉、黏膜和其他结缔组织)非常接近。当形成管状结构时,电纺组织工程支架可用于引导气管软骨再生。例如,一组通过同轴静电纺丝以P(LLA-CL)和胶原蛋白作为壳层,Kartogenin 溶液作为核层创建了一种支架[76]。在间充质干细胞中诱导软骨形成的 Kartogenin 在2个月内从纳米纤维中释放出来,并通过形态分析和 PCR 显示可诱导兔骨髓来源的间充质干细胞的增殖和成软骨分化。这些结果说明核壳纳米纤维支架是运输kartogenin的有效系统并且可以用作气管软骨再生的组织工程支架。
2.2.6 用于肌腱/韧带再生的电纺纳米纤维
用于肌腱组织再生的电纺纳米纤维:肌腱和韧带损伤包括导致剧烈疼痛的炎症、撕裂和断裂,每年在全世界造成大约 5 000 万例相关手术[77-78]。目前,标准手术治疗使用自体移植物、同种异体移植物或人工假体。尽管由于其良好的重塑和缺乏免疫反应被认为是“黄金标准”,但自体移植物受到供体部位可用性的限制,并导致手术时间延长和供体部位高发病率[79]。或者,可以使用同种异体移植物,但由于供者和受者之间的性别、年龄和体质量不匹配,同种异体材料与疾病传播、免疫排斥和高再破裂率有关。为了解决这些缺点,基于静电纺丝纤维的组织工程支架为受损肌腱和韧带的治疗和再生提供了一种可能的替代方案。
肌腱组织工程的主要挑战是与分层组织的致密胶原细胞外基质相关的低自我再生能力。单轴排列的纳米纤维可用于模拟肌腱中胶原纤维的组织,并可与生化特征结合以刺激组织再生。例如,YANG等[80]开发了一种新型多层复合支架,由纤维化聚乳酸和甲基丙烯酸化明胶组成,通过双静电纺丝散布,并掺入人体脂肪干细胞。该支架由五片交联在一起并用携带干细胞的甲基丙烯酸化明胶层加固;干细胞用转化生长因子β3 处理 7 d以促进分化为肌腱细胞,实时 PCR 显示肌腱标志物 scleraxis 和tenascin-C 显著上调,表明被包裹的细胞仍然对可溶性肌腱因子有反应,并且这些结构足够多孔,可以扩散外源生化信号。这种新颖的细胞支架结构结合了聚乳酸纳米纤维支架和明胶的机械优势,以模拟肌腱的机械特征和结构,同时促进表现天然肌腱细胞表型。同样,RINOLDI 等[81]制造了一种用于肌腱组织工程的电纺纳米复合材料系统。作者创造了一种串珠纤维结构并掺入二氧化硅颗粒以提高结构的生物活性并改变它们的形貌、润湿性、刚度和降解率;他们的研究结果还表明,珠串纤维非织造复合支架是一种可能适用于引导肌腱再生有吸引力的候选物。
几个研究组一直在努力通过创造新的加工方法来提高用于肌腱和韧带的电纺支架的三维度来提高孔隙率。LARANJEIRA等[82]提出从聚乳酸、壳聚糖和纤维素的混合物中生产连续排列的纳米纤维纱线,并探索使用不同的编织技术将它们组装成 3D 支架。作者阐明了可以通过改变编织技术来调整支架的尺寸,并对其进行操作以产生与肌腱或韧带缺损的特定尺寸相匹配的结构; 此外,发现支架具有模拟肌腱和韧带的特征性非线性变形行为的应力-应变曲线,而没有在肌腱和韧带中观察到的高应变下典型塑性变形;此外,支架被证明可以在体外上调人体脂肪干细胞中细胞外基质的沉积,并促进向腱样表型的分化。鉴于形态相似性、优异的机械性能和促进分化的能力,3D 编织支架具有用于肌腱和韧带组织工程的潜力。
在另一项研究中,ZHANG等[83]用对齐的聚乳酸纤维和曲古抑菌素 A(一种组蛋白脱乙酰酶抑制剂)创建了一种静电纺丝支架,并评估了该抑制剂在肌腱细胞分化中的作用。与没有信号分子或由随机纤维组成的支架的对照组相比,曲古抑菌素 A 显著上调肌腱标志物的表达,这表明取向纤维和曲古抑菌素 A 组合可用于促进细胞分化和肌腱缺损修复。
在最近的一项研究中,研究人员使用静电纺丝来构建分层、多尺度的组件,以模拟肌腱和韧带的分层结构[84]。为了制造支架,由纳米纤维组成的几个受束状启发的聚乳酸束通过电纺聚乳酸鞘组合在一起,以模仿外膜韧带膜。分层支架具有与天然肌腱相似的刚度,并表现出与肌腱和韧带相似的变形。这些数据表明,静电纺丝支架的多尺度特征有利于创造肌腱或韧带支架所需的机械性能。
用于肌腱-骨交界处组织再生的电纺纳米纤维:设计肌腱-骨界面极具挑战性,因为它是具有独特成分和细胞的多个组织的复杂梯度,进一步需要机械强度以避免修复部位伸长或破裂。目前用于肌腱-骨修复的锚定缝合线会产生应力集中,从而限制附着强度,这表明需要组织工程解决方案[84-85]。有研究为肌腱-骨界面创建了一个静电纺丝支架,并将血小板衍生生长因子BB(PDGF-BB)以梯度固定在其取向纤维上,以促进脂肪源性干细胞的肌腱分化[86],结果表明,取向的纳米纤维上的 PDGF-BB 梯度与形态信号协同作用以在空间上控制细胞分化,导致细胞骨架的高生长率和类似于肌腱-骨插入位点的各向异性组织;此外,支架在 14 d内肌腱标记物的表达增加,例如Ⅰ,Ⅲ型胶原蛋白、tenascin-C和scleraxis。这些数据表明,PDGF-BB梯度取向纳米纤维可能有助于设计骨-肌腱界面。
为了解决肌腱/韧带组织工程支架在骨隧道段缺乏骨传导性的问题,XIE等[87]利用静电纺丝技术制备4种负载不同含量的羟基磷灰石纳米纤维纱线,然后将纱线按照梯度顺序编织成羟基磷灰石梯度支架,模拟肌腱-骨界面4个不同区域的过渡结构。体外生物学结果表明羟基磷灰石梯度支架对骨髓间充质干细胞和小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞(MC3T3-E1)均表现出良好的细胞相容性;支架的矿化区段促进MC3T3-E1的增殖,并且诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,而非矿化区段促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和成肌腱细胞分化。羟基磷灰石梯度支架可以在空间上调控骨髓间充质干细胞的分化表型,对促进肌腱-骨界面组织的再生和修复有潜在作用。
在另一种方法中,LI等[88]开发了一种双层支架,具有聚乳酸层和装载有纳米羟基磷灰石的聚乳酸层,模拟了未矿化的纤维软骨和连接处的矿化纤维软骨;与单层电纺聚乳酸对照组相比,发现该支架显著增加了肌腱-骨界面处的糖胺聚糖。这些数据表明,双层支架为肌腱-骨界面处矿化和非矿化组织的修复提供了空间控制,这可能对组织工程有益。
2.3 静电纺丝纳米纤维的商业化用途 用于生物医学应用的静电纺丝纳米纤维不仅仅只是研究和出版物,它具有真正的当前和潜在的商业化价值。例如,广州迈普再生医学科技有限公司开发了一种聚乳酸纳米纤维硬脑膜产品,用于再生人体硬脑膜。硬脑膜产品多年前已获得欧盟 CE 认证和中国食品药品监督管理局(CFDA)证书。上海松力生物技术有限公司开发用于疝气治疗的纤维蛋白原/PLC纳米纤维疝气补片产品,并于2018年获得CFDA证书。山东汉方制药有限公司开发用于伤口敷料的丝素蛋白/PLCL纳米纤维膜,并于2019年获得CFDA证书。
土耳其的Inovenso公司开发了一种由电纺纳米纤维膜制成的口罩,细菌过滤率可高达99.9%。德国的Biotronik公司基于静电纺丝技术开发了一种PU包覆的管状动脉支架,并在2018年获得了FDA认证。美国St Teresa Medical公司通过静电纺葡聚糖生产了SurgiClot?,一种已应用于临床的伤口止血敷料。英国Electrospinning公司利用聚乳酸电纺纤维开发了Mimetix?产品,一种用于3D细胞培养的细胞板。开普敦的Stellenbosch Nanofiber Company已成为电纺纳米纤维商业化平台之一,专门用于细胞培养、伤口敷料以及组织工程支架的生产等。虽然已经取得了一些商业上的成功,但仍有许多生物医学公司正在开发用于其他生物医学应用的纳米纤维支架,因此将在不久的将来看到更多商业化的纳米纤维医疗产品。

| [1] XUE J, WU T, DAI Y, et al. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications. Chem Rev. 2019;119(8):5298-5415. [2] YANG F, MURUGAN R, RAMAKRISHNA S, et al. Fabrication of nano-structured porous PLA scaffold intended for nerve tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2004;25(10):1891-1900. [3] NIECE KL, HARTGERINK JD, DONNERS JM, et al. Self-assembly combining two bioactive peptide-amphiphile molecules into nanofibers by electrostatic attraction. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125(24):7146-7147. [4] CARIM AI, HAMANN KR, BATARA NA, et al. Template-free synthesis of periodic three-dimensional PbSe nanostructures via photoelectrodeposition. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(21): 6536-6539. [5] MACCALLAN AF. Threading of needles. Br J Ophthalmol. 1934;18(1):54. [6] BHARDWAJ N, KUNDU S C. Electrospinning: a fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol Adv. 2010;28(3):325-347. [7] LI D, XIA Y. Electrospinning of nanofibers: reinventing the wheel. Adv Mater. 2004;16(14): 1151-1170. [8] LIAO Y, LOH CH, TIAN M, et al. Progress in electrospun polymeric nanofibrous membranes for water treatment:Fabrication, modification and applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2018;77:69-94. [9] LIU G, GU Z, HONG Y, et al. Electrospun starch nanofibers: recent advances, challenges, and strategies for potential pharmaceutical applications. J Control Release. 2017;252: 95-107. [10] JIANG L, JIANG Y, STIADLE J, et al. Electrospun nanofibrous thermoplastic polyurethane/poly (glycerol sebacate) hybrid scaffolds for vocal fold tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2019;94:740-749. [11] ZHANG YS, XIA Y. Multiple facets for extracellular matrix mimicking in regenerative medicine. Nanomedicine. 2015;10(5):689-692. [12] HUSSEY GS, DZIKI JL, BADYLAK SF. Extracellular matrix-based materials for regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Mater. 2018;3(7):159-173. [13] LIM CT. Nanofiber technology: current status and emerging developments. Prog Polym Sci. 2017;70:1-17. [14] CHEN FM, LIU X. Advancing biomaterials of human origin for tissue engineering. Prog Polym Sci. 2016;53:86-168. [15] TANG D, TARE RS, YANG LY, et al. Biofabrication of bone tissue: approaches, challenges and translation for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;83:363-382. [16] GUIGNARD C . Process for the manufacture of a plurality of filaments. US Patent, No. 4230650. 1980. [17] LARRONDO L, ST JOHN MANLEY R. Electrostatic fiber spinning from polymer melts. I. Experimental observations on fiber formation and properties. J Polym Sci Polym Phys Ed. 1981;19(6):909-920. [18] SUN Z, ZUSSMAN E, YARIN AL, et al. Compound core-shell polymer nanofibers by co-electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2003;15(22):7992-8001. [19] XU X, ZHUANG X, CHEN X, et al. Preparation of core‐sheath composite nanofibers by emulsion electrospinning. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2006;27(19):1637-1642. [20] TEO WE, GOPAL R, RAMASESHAN R, et al. A dynamic liquid support system for continuous electrospun yarn fabrication. Polymer. 2007;48(12):3400-3405. [21] ALI U, ZHOU Y, WANG X, et al. Direct electrospinning of highly twisted, continuous nanofiber yarns. J Text Inst. 2012;103(1):80-88. [22] SI Y, YU J, TANG X, et al. Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality. Nat Commun. 2014;5(1):5802. [23] WU J, LIU S, HE L, et al. Electrospun nanoyarn scaffold and its application in tissue engineering. Mater Lett. 2012;89:146-149. [24] WU J, HUANG C, LIU W, et al. Cell infiltration and vascularization in porous nanoyarn scaffolds prepared by dynamic liquid electrospinning. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10(4):603-614. [25] PIEZ KA, REDDI AH. Extracellular matrix biochemistry. Elsvier Science Publishing Co., Inc., New York. 1984. [26] NISHIDA T, YASUMOTO K, OTORI T, et al. The network structure of corneal fibroblasts in the rat as revealed by scanning electron microscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci. 1988;29(12):1887-1890. [27] KIM BS, MOONEY DJ. Development of biocompatible synthetic extracellular matrices for tissue engineering. Tibtechnol. 1998;16:224. [28] PATTISON MA, WURSTERS, Webster TJ, et al. Three-dimensional, nano-structured PLA-PLGA scaffolds for bladder tissue replacement applications. Biomaterials. 2005;26(15):2491-2500. [29] ELIAS KL, PRICE RL, WEBSTER TJ. Enhanced functions of osteoblasts on nanometer diameter carbon fibers. Biomaterials. 2002;23:3279-3287. [30] STEVENS MM, GEORGE JH. Exploring and engineering the cell surface interface. Science. 2005;310:1135-1138. [31] WANG Y, FU C, WU Z, et al. A chitin film containing basic fibroblast growth factor with a chitin-binding domain as wound dressings. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;174:723-730. [32] BAO L, YANG W, MAO X, et al. Agar/collagen membrane as skin dressing for wounds. Biomed Mater. 2008;3(4):044108. [33] YU PJ, GUO JA, LI JJ, et al. Repair of skin defects with electrospun collagen/chitosan and fibroin/chitosan compound nanofiber scaffolds compared with gauze dressing. J Biomater Tissue Eng. 2017;7(5):386-392. [34] LI D, GAO Y, WANG Y, et al. Evaluation of biocompatibility and immunogenicity of micro/nanofiber materials based on tilapia skin collagen. J Biomater Appl. 2019;33(8):1118-1127. [35] MA L, ZHANG D, YANG X, et al. Cirsium Japonicum DC ingredients-loaded silk fibroin nanofibrous matrices with excellent hemostatic activity. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2018;4(2):025035. [36] ZHOU T, SUI B, MO X, et al. Multifunctional and biomimetic fish collagen/bioactive glass nanofibers: fabrication, antibacterial activity and inducing skin regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:3495-3507. [37] YU H, CHEN X, CAI J, et al. Novel porous three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffolds for accelerating wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2019;369:253-262. [38] BROWNING MB, DEMPSEY D, GUIZA V, et al. Multilayer vascular grafts based on collagen-mimetic proteins. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(3):1010-1021. [39] DESMET W, VANHAECKE J, VROLIX M, et al. Isolated single coronary artery: a review of 50 000 consecutive coronary angiographies. Eur Heart J. 1992;13(12):637-1640. [40] HUANG C, WANG S, QIU L, et al. Heparin loading and pre-endothelialization in enhancing the patency rate of electrospun small-diameter vascular grafts in a canine model. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(6):2220-2226. [41] CHEN X, WANG J, AN Q, et al. Electrospun poly (l-lactic acid-co-ɛ-caprolactone) fibers loaded with heparin and vascular endothelial growth factor to improve blood compatibility and endothelial progenitor cell proliferation. Colloids Surf BBiointerfaces. 2015;128:106-114. [42] YIN A, ZHANG K, MCCLURE MJ, et al. Electrospinning collagen/chitosan/poly (L‐lactic acid‐co‐ϵ‐caprolactone) to form a vascular graft: mechanical and biological characterization. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(5):1292-1301. [43] WU T, JIANG B, WANG Y, et al. Electrospun poly (l-lactide-co-caprolactone)-collagen-chitosan vascular graft in a canine femoral artery model. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(28):5760-5768. [44] KUANG H, WANG Y, HU J, et al. A method for preparation of an internal layer of artificial vascular graft co-modified with Salvianolic acid B and heparin. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(23):19365-19372. [45] WU T, ZHANG J, WANG Y, et al. Development of dynamic liquid and conjugated electrospun poly(L-lactide-co-caprolactone)/collagen nanoyarns for regulating vascular smooth muscle cells growth. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2017;13(3):303-312. [46] WU T, ZHANG JL, WANG YF, et al. Design and fabrication of a biomimetic vascular scaffold promoting in situ endothelialization and tunica media regeneration. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2018;1:833-844. [47] WU T, ZHANG JL, WANG YF, et al. Fabrication and preliminary study of a biomimetic tri-layer tubular graft based on fibers and fiber yarns for vascular tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;82:121-129. [48] XIE J, MACEWAN MR, LIU W, et al. Nerve guidance conduits based on double-layered scaffolds of electrospun nanofibers for repairing the peripheral nervous system. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2014;6(12):9472-9480. [49] GU X, DING F, WILLIAMS DF. Neural tissue engineering options for peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomaterials. 2014;35(24):6143-6156. [50] ZHANG K, WANG H, HUANG C, et al. Fabrication of silk fibroin blended P (LLA‐CL) nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93(3):984-993. [51] WANG CY, ZHANG KH, FAN CY, et al. Aligned natural-synthetic polyblend nanofibers for peripheral nerve regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(2):634-643. [52] ZHANG KH, WANG CY, FAN CY, et al. Aligned SF-P (LLA-CL)-blended nanofibers encapsulating nerve growth factor for peripheral nerve regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(8):2680-2691. [53] ZHANG J, QIU K, SUN B, et al. The aligned core-sheath nanofibers with electrical conductivity for neural tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(45):7945-7954. [54] SUN B, WU T, WANG J, et al. Polypyrrole-coated poly (l-lactic acid-co-ε-caprolactone)/silk fibroin nanofibrous membranes promoting neural cell proliferation and differentiation with electrical stimulation. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(41):6670-6679. [55] LI D, PAN X, SUN B, et al. Nerve conduits constructed by electrospun P (LLA-CL) nanofibers and PLA nanofiber yarns. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(45):8823-8831. [56] WU T, LI D, WANG Y, et al. Laminin-coated nerve guidance conduits based on poly (l-lactide-co-glycolide) fibers and yarns for promoting Schwann cells’ proliferation and migration. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(17):3186-3194. [57] SUN B, ZHOU Z, WU T, et al. Development of nanofiber sponges-containing nerve guidance conduit for peripheral nerve regeneration in vivo. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(32):26684-26696. [58] BERNER A, REICHERT JC, MÜLLER MB, et al. Treatment of long bone defects and non-unions:from research to clinical practice. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;347:501-519. [59] LIU W, ZHANG J, RETHORE G, et al. A novel injectable, cohesive and toughened Si-HPMC (silanized-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) composite calcium phosphate cement for bone substitution. Acta biomater. 2014;10(7):3335-3345. [60] LANGER RS, VACANTI JP. Tissue engineering:the challenges ahead. Sci Am. 1999;280(4):86-89. [61] SHAO S, ZHOU S, LI L, et al. Osteoblast function on electrically conductive electrospun PLA/MWCNTs nanofibers. Biomaterials. 2011;32(11):2821-2833. [62] CUI W, ZHOU Y, CHANG J. Electrospun nanofibrous materials for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2010;11(1):014108. [63] WEINER S, WAGNER HD. The material bone:structure-mechanical function relations. Annu Rev Mater Sci. 1998;28(1):271-298. [64] RAJZER I, MENASZEK E, KWIATKOWSKI R, et al. Electrospun gelatin/poly (ε-caprolactone) fibrous scaffold modified with calcium phosphate for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;44:183-190. [65] YE K, LIU D, KUANG H, et al. Three-dimensional electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds displaying bone morphogenetic protein-2-derived peptides for the promotion of osteogenic differentiation of stem cells and bone regeneration. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019;534:625-636. [66] WANG Y, CUI W, ZHAO X, et al. Bone remodeling-inspired dual delivery electrospun nanofibers for promoting bone regeneration. Nanoscale. 2019;11(1):60-71. [67] GUTIÉRREZ-SÁNCHEZ M, ESCOBAR-BARRIOS VA, POZOS-GUILLÉN A, et al. RGD-functionalization of PLA/starch scaffolds obtained by electrospinning and evaluated in vitro for potential bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;96:798-806. [68] KO E, LEE JS, KIM H, et al. Electrospun silk fibroin nanofibrous scaffolds with two-stage hydroxyapatite functionalization for enhancing the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;10(9):7614-7625. [69] MARINS NH, LEE BEJ, SILVA RM, et al. Niobium pentoxide and hydroxyapatite particle loaded electrospun polycaprolactone/gelatin membranes for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;182:110386. [70] NUKAVARAPU SP, DORCEMUS DL. Osteochondral tissue engineering: current strategies and challenges. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(5):706-721. [71] ZHANG S, CHEN L, JIANG Y, et al. Bi-layer collagen/microporous electrospun nanofiber scaffold improves the osteochondral regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7236-7247. [72] CHEN W, CHEN S, MORSI Y, et al. Superabsorbent 3D scaffold based on electrospun nanofibers for cartilage tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(37):24415-24425. [73] CHEN Y, XU W, SHAFIQ M, et al. Three-dimensional porous gas-foamed electrospun nanofiber scaffold for cartilage regeneration. J Colloid Interf Sci. 2021;603:94-109. [74] CHEN Y, XU W, SHAFIQ M, et al. Chondroitin sulfate cross-linked three-dimensional tailored electrospun scaffolds for cartilage regeneration. Biomater Adv. 2022;134:112643. [75] CHEN W, XU Y, LIU Y, et al. Three-dimensional printed electrospun fiber-based scaffold for cartilage regeneration. Mater Des. 2019;179:107886. [76] YIN H, WANG J, GU Z, et al. Evaluation of the potential of kartogenin encapsulated poly (L-lactic acid-co-caprolactone)/collagen nanofibers for tracheal cartilage regeneration. J Biomater Appl. 2017;32(3):331-341. [77] BASS E. Tendinopathy: why the difference between tendinitis and tendinosis matters. Int J Ther Massage Bodywork. 2012;5(1):14. [78] LJUNGQVIST A, SCHWELLNUS MP, BACHL N, et al. International Olympic committee consensus statement:molecular basis of connective tissue and muscle injuries in sport. Clin. Sports Med. 2008;27(1):231-239. [79] OLENDER E, UHRYNOWSKA-TYSZKIEWICZ I, KAMINSKI A, et al. Revitalization of biostatic tissue allografts: new perspectives in tissue transplantology. Transplant Proc. 2011;43(8):3137-3141. [80] YANG G, LIN H, ROTHRAUFF BB, et al. Multilayered polycaprolactone/gelatin fiber-hydrogel composite for tendon tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2016;35:68-76. [81] RINOLDI C, KIJEŃSKA E, CHLANDA A, et al. Nanobead-on-string composites for tendon tissue engineering. J Mater Chem. 2018;6(19):3116-3127. [82] LARANJEIRA M, DOMINGUES RMA, COSTA-ALMEIDA R, et al. 3D mimicry of native‐tissue‐fiber architecture guides tendon‐derived cells and adipose stem cells into artificial tendon constructs. Small. 2017;13(31):1700689. [83] ZHANG C, WANG X, ZHANG E, et al. An epigenetic bioactive composite scaffold with well-aligned nanofibers for functional tendon tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018;66:141-156. [84] SENSINI A, CRISTOFOLINI L. Biofabrication of electrospun scaffolds for the regeneration of tendons and ligaments. Materials. 2018;11(10):1963. [85] LINDERMAN SW, GOLMAN M, GARDNER TR, et al. Enhanced tendon-to-bone repair through adhesive films. Acta Biomater. 2018;70:165-176. [86] MADHURAKKAT PERIKAMANA SK, LEE J, AHMAD T, et al. Harnessing biochemical and structural cues for tenogenic differentiation of adipose derived stem cells (ADSCs) and development of an invitro tissue interface mimicking tendon-bone insertion graft. Biomaterials. 2018;165:79-93. [87] XIE X, CAI J, YAO Y, et al. A woven scaffold with continuous mineral gradients for tendon-to-bone tissue engineering. Compos part B-Eng. 2021;212:108679. [88] LI X, CHENG R, SUN Z, et al. Flexible bipolar nanofibrous membranes for improving gradient microstructure in tendon-to-bone healing. Acta biomater. 2017;61:204-216. |
| [1] | 谷明西, 王常成, 田丰德, 安 宁, 郝瑞胡, 郭 林. 丝素蛋白/明胶/壳聚糖三维多孔软骨组织支架的制备及体外评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 366-372. |
| [2] | 许晓东, 周骥平, 张 琦, 冯 辰, 朱勉顺, 史宏灿. 明胶/氧化纳米纤维素高弹性模量高孔隙皮肤支架的3D打印工艺[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 398-403. |
| [3] | 王新民, 闫文凯, 宋亚辉, 刘 飞. 自体富白细胞-血小板纤维蛋白凝胶与腘绳肌腱修复创伤性髌骨脱位[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 404-410. |
| [4] | 毕玉杰, 马笃军, 彭力平, 周紫琼, 赵 静, 朱厚均, 钟秋辉, 杨玉鑫. 中医药联合医用水凝胶治疗疾病的策略及意义[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| [5] | 龙俊东, 史业弘, 王 成, 陈世玖. 不同冷冻技术对同种异体血管移植排斥反应的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 433-438. |
| [6] | 高雪钰, 张文涛, 孙天泽, 张 警, 李忠海. 金属离子在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 439-444. |
| [7] | 杨 杰, 胡浩磊, 李 硕, 岳 玮, 徐 弢, 李 谊. 3D打印生物墨水在组织修复与再生医学中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 445-451. |
| [8] | 陈品叡, 裴锡波, 薛轶元. 磁响应水凝胶在骨组织工程中的作用与优势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 452-457. |
| [9] | 龙智睿, 黄 雷, 肖 放, 王 琳, 王晓蓓. 骨组织工程中研究水凝胶微球的特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 472-478. |
| [10] | 孔祥宇, 王 兴, 裴志伟, 常家乐, 李斯琴, 郝 廷, 何万雄, 张葆鑫, 贾燕飞. 生物支架材料及打印技术修复骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 479-485. |
| [11] | 徐 静, 吕慧欣, 鲍 鑫, 张 逸, 王一涵, 周延民. 近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 486-492. |
| [12] | 代新语, 闫纪红, 华凌军, 郑晓鸿. 抗阻运动改善超重肥胖人群身体成分:一项伞形综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 267-271. |
| [13] | 孟志成, 乔卫平, 赵 阳, 刘洪飞, 李凯杰, 马 博. 免疫细胞及相关细胞因子在骨关节炎发病及治疗中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 280-287. |
| [14] | 龙 宜, 杨佳明, 叶 花, 钟燕彪, 王茂源. 细胞外囊泡在少肌性肥胖中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 315-320. |
| [15] | 龙清熙, 张萍淑, 刘 青, 欧 亚, 张丽丽, 元小冬. 单细胞RNA测序揭示星形胶质细胞的异质性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 139-146. |
作为替代方案,有研究者发明了一种能够利用高压电场生产纳米级聚合物纤维的装置,并于 1934 年申请了专利[5],这是首个使用电势差作为驱使力制备纳米纤维的国际专利,由此创造了“电纺”一词。静电纺丝提供了一种简单直接的方法来生产直径从纳米到微米的连续聚合物纤维[5]。典型的静电纺丝装置包括高压电源、控制聚合物流速的注射泵和喷丝头(例如,带有钝头的医用针头)和用于捕获静电纺丝纤维的导电收集器。简单地说,静电纺丝可以被认为是一种电流体动力学过程,它依赖于电位差来产生液体射流,然后进行机械拉伸、伸长和干燥以产生纤维 [6-7]。随着纤维的聚集,形成具有 3D 形态、高孔隙率和大表面积的电纺膜,同时保持机械完整性和纤维连续性[8]。因此,静电纺丝膜的独特结构在许多领域都有广泛的应用,但作为组织工程的支架特别受关注[9-10]。 这种组织工程应用是因为大多数人体组织和器官都是由细胞外基质中的纳米纤维组成的,这使得电纺纳米纤维可以作为模拟物用于组织和器官修复[11-12]。更重要的是,多种天然和合成聚合物可以电纺,具有生物相容性和生物降解性,并被人体重新吸收。总之,静电纺丝纳米纤维的这些特性引起了生物医学研究人员的注意,并导致研究用于皮肤、骨骼、软骨、神经、血管、肌腱和其他组织再生应用。
组织工程领域尝试使用细胞、生物大分子以及支架这3种基本成分恢复或再生健康组织或器官的功能[13]。组织工程支架提供了因疾病、受伤或先天性缺陷损伤的细胞生长所需的3D微环境,材料的选择在很大程度上取决于组织特异性应用[14]。然而,无论预期应用如何,一个主要的挑战是如何将生物材料扩展成三维结构以再现组织微环境的生理、化学以及机械性能[15]。因此,文章重点综述了静电纺丝支架的制备工艺,探讨了利用静电纺工艺生产的纳米纤维支架在皮肤、血管、神经、骨骼、软骨和肌腱/韧带等组织中的应用,并从而证明了电纺纳米纤维支架应用于软组织和硬组织再生的巨大潜力,为相关领域疾病的治疗提供一定的理论参考。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2022年8月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库自建库起至2022 年8月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 Google学术、PubMed和中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“静电纺丝、电纺纳米纤维、电纺纳米纤维支架、组织再生”;英文检索词为“Electrospinning,electrospun nanofibers,electrospun nanofiber scaffolds,tissue regeneration”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。

1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 与静电纺丝、电纺纳米纤维、电纺纳米纤维支架及组织再生有关的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 与研究内容不相关的文献及重复性文献。
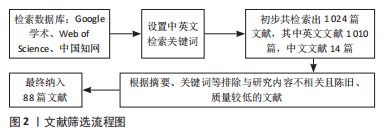
1.3 文献质量评估及数据的提取 初步检索文献数为1 024篇,排除与研究内容不相关且陈旧、质量较低的文献,最终纳入符合标准的88 篇来自PubMed和谷歌学术数据库英文文献进行综述,见图2。
然而,现有的研究也还存在着不足。目前的研究成果多是基于体外的细胞实验,体内动物实验也多仅限于兔、鼠和犬等中小型动物,但毕竟人类与动物生理上存在着显著差异,且存在着诸如伦理、安全等实际问题,研究成果能否最终应用于人体还需要经历漫长的验证过程。另外,电纺产品虽然具有重要的经济效益,但其商品化过程却是耗时甚久,如何将这些基础研究转化为实际产品,仍需投入更多的人力财力,开展更深层次、多角度的临床研究。
3.2 作者综述区别于别篇的特点 较以往研究而言,这篇综述以全面的视角系统阐述了电纺纳米支架应用于皮肤、骨骼、软骨、神经、血管、肌腱和其他组织等再生的基础和产品转化等多方向的研究进展,并证明了电纺纳米纤维支架在不同疾病领域治疗中的重要潜力。
3.3 综述的局限性 作者虽然尽可能检索了目前发表的文献,但主要探讨的是电纺纳米支架应用于不同组织再生的研究策略,以及如何根据组织的生理特点利用不同的静电纺工艺制备具有特定结构的电纺纳米纤维支架。而对支架的特定结构和特殊成分对组织再生中的作用机制及在疾病应用的总结分析相对有限,生物活性因子和生物信号对组织再生的调控也未能进行深入探讨。最终,静电纺丝和静电纺丝纳米纤维支架的进一步发展为各种组织工程应用带来了广阔的前景,并可能改善世界各地患者的生活质量。
3.4 综述的重要意义 该文章重点总结了静电纺丝的工艺、原理以及由此产生的静电纺丝纳米纤维在组织工程中的应用,纵向电纺纳米纤维在组织工程中应用的相关进展,包括其在皮肤、血管、神经、骨骼、软骨和肌腱/韧带中的应用,从而为提高疾病的治疗效果和产品开发提供思路借鉴。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 电纺纳米纤维支架值得引起科研人员的关注,在已有研究的基础上,期待未来有更多的研究者拓宽电纺纳米纤维支架在不同疾病领域的应用,开发更多的商业化产品。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
电纺纳米纤维支架:是用静电纺丝法制备的由纳米纤维丝交织而成的组织再生用支架材料,为膜状、管状及块状等,用于皮肤、血管、神经、肌腱、骨和软骨等的组织再生。组织再生:是机体对由某种原因引起死亡的细胞进行补偿与恢复的过程。组织不断地进行更新,称为生理性再生。
纤维对人类来说并不陌生。天然纤维来自植物和动物,包括棉、麻、羊毛和丝,已经使用了上千年。随着现代复合材料的出现,合成纤维逐渐流行起来。它们被持续大范围使用,包括每天的消费产品、环境应用、过滤系统以及保护设备。近年来,不同的构建方法出现用来制备纤维,例如相分离、自组装以及模板合成。然而,这些方法受到其技术复杂性、成本、产量和控制所得纤维规模的能力的限制。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||