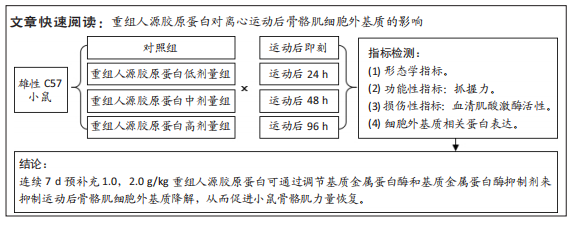
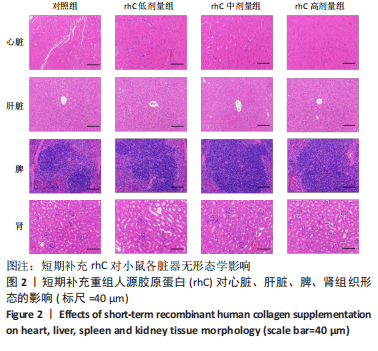
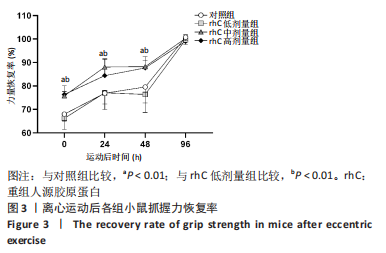
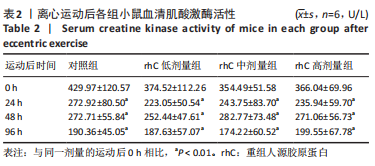
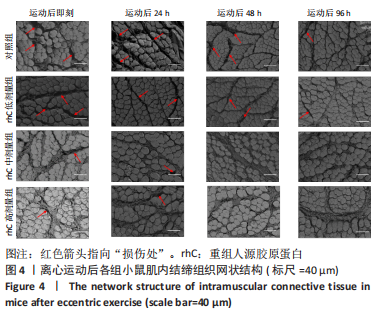
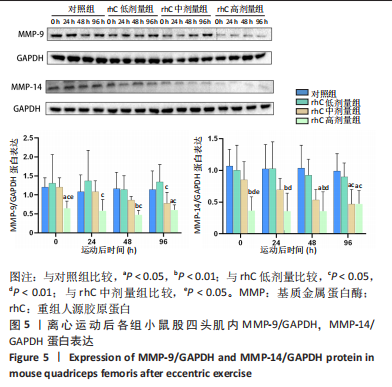
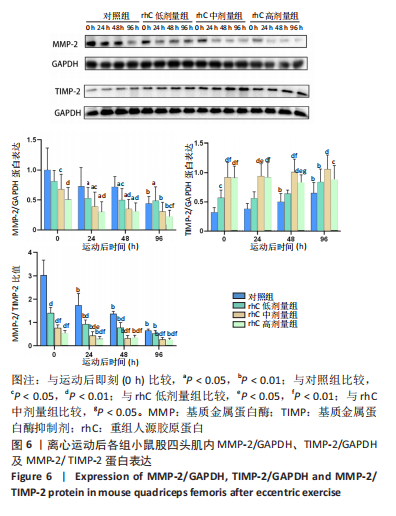
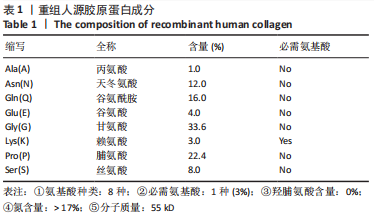
[1] MAHDY MAA. Skeletal muscle fibrosis: an overview. Cell Tissue Res. 2019;375(3):575-588.
[2] MUKUND K, SUBRAMANIAM S. Skeletal muscle: A review of molecular structure and function, in health and disease. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2020;12(1):e1462.
[3] KIM J, LEE J. Matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase responses to muscle damage after eccentric exercise. J Exerc Rehabil. 2016;12(4):260-265.
[4] 张翔,张学林,孔梅,等.急性离心运动引起的骨骼肌横向张力传递变化及针刺干预效应[J].中国体育科技,2018,54(4):92-106.
[5] PURSLOW PP. Muscle fascia and force transmission. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2010;14(4):411-417.
[6] CSAPO R, GUMPENBERGER M, WESSNER B. Skeletal Muscle
Extracellular Matrix - What Do We Know About Its Composition, Regulation, and Physiological Roles? A Narrative Review. Front Physiol. 2020;11:253.
[7] WANG X, KHALIL RA. Matrix Metalloproteinases, Vascular Remodeling, and Vascular Disease. Adv Pharmacol. 2018;81:241-330.
[8] ASTILL BD, KATSMA MS, CAUTHON DJ, et al. Sex-based difference in Achilles peritendinous levels of matrix metalloproteinases and growth factors after acute resistance exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017;122(2):361-367.
[9] CARMELI E, MOAS M, LENNON S, et al. High intensity exercise increases expression of matrix metalloproteinases in fast skeletal muscle fibres. Exp Physiol. 2005;90(4):613-619.
[10] HEINEMEIER KM, OLESEN JL, HADDAD F, et al. Expression of collagen and related growth factors in rat tendon and skeletal muscle in response to specific contraction types. J Physiol. 2007;582(Pt 3):1303-1316.
[11] KOSKINEN SO, HÖYHTYÄ M, TURPEENNIEMI-HUJANEN T, et al. Serum concentrations of collagen degrading enzymes and their inhibitors after downhill running. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2001;11(1):9-15.
[12] KOSKINEN SO, WANG W, AHTIKOSKI AM, et al. Acute exercise induced changes in rat skeletal muscle mRNAs and proteins regulating type IV collagen content. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001; 280(5):R1292-R1300.
[13] MACKEY AL, DONNELLY AE, TURPEENNIEMI-HUJANEN T, et al. Skeletal muscle collagen content in humans after high-force eccentric contractions. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004;97(1):197-203.
[14] WELSH MC, ALLEN DL, BYRNES WC. Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 response to downhill running in humans. Int J Sports Med. 2014;35(5): 363-370.
[15] DO AMARAL RJFC, ZAYED NMA, PASCU EI, et al. Functionalising Collagen-Based Scaffolds With Platelet-Rich Plasma for Enhanced Skin Wound Healing Potential. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:371.
[16] XU L, LIU Y, TANG L, et al. Preparation of Recombinant Human Collagen III Protein Hydrogels with Sustained Release of Extracellular Vesicles for Skin Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6289.
[17] TAKENAKA-NINAGAWA N, KIM J, ZHAO M, et al. Collagen-VI supplementation by cell transplantation improves muscle regeneration in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy model mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):446.
[18] HARADA A, GOTO M, KATO A, et al. Systemic Supplementation of Collagen VI by Neonatal Transplantation of iPSC-Derived MSCs Improves Histological Phenotype and Function of Col6-Deficient Model Mice. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:790341.
[19] TONELOTTO V, CONSORTI C, FACCHINELLO N, et al. Collagen VI ablation in zebrafish causes neuromuscular defects during developmental and adult stages. Matrix Biol. 2022;112:39-61.
[20] 吴迎,伊木清,曾凡星.MG53基因敲除对小鼠延迟性肌肉酸痛期骨骼肌损伤的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(6):636-642.
[21] FANG W, NASIR Y. The effect of curcumin supplementation on recovery following exercise-induced muscle damage and delayed-onset muscle soreness: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother Res. 2021;35(4):1768-1781.
[22] LOPEZ HL, ZIEGENFUSS TN, PARK J. Evaluation of the Effects of BioCell Collagen, a Novel Cartilage Extract, on Connective Tissue Support and Functional Recovery From Exercise. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2015; 14(3):30-38.
[23] CLIFFORD T, VENTRESS M, ALLERTON DM, et al. The effects of collagen peptides on muscle damage, inflammation and bone turnover following exercise: a randomized, controlled trial. Amino Acids. 2019;51(4): 691-704.
[24] WATANABE-KAMIYAMA M, SHIMIZU M, KAMIYAMA S, et al. Absorption and effectiveness of orally administered low molecular weight collagen hydrolysate in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58(2):835-841.
[25] IWAI K, HASEGAWA T, TAGUCHI Y, et al. Identification of food-derived collagen peptides in human blood after oral ingestion of gelatin hydrolysates. J Agric Food Chem. 2005;53(16):6531-6536.
[26] LEÓN-LÓPEZ A, MORALES-PEÑALOZA A, MARTÍNEZ-JUÁREZ VM, et al. Hydrolyzed Collagen-Sources and Applications. Molecules. 2019; 24(22):4031.
[27] OHARA H, MATSUMOTO H, ITO K, et al. Comparison of quantity and structures of hydroxyproline-containing peptides in human blood after oral ingestion of gelatin hydrolysates from different sources. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55(4):1532-1535.
[28] LIS DM, BAAR K. Effects of Different Vitamin C-Enriched Collagen Derivatives on Collagen Synthesis. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2019; 29(5):526-531.
[29] SORUSHANOVA A, DELGADO LM, WU Z, et al. The Collagen Suprafamily: From Biosynthesis to Advanced Biomaterial Development. Adv Mater. 2019;31(1):e1801651.
[30] ZHAO C, XIAO Y, LING S, et al. Synthesis and Assembly of Recombinant Collagen. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2347:83-96.
[31] 刘玉倩,杨雯茜,殷娟娟.运动营养研究的新进展[J].北京体育大学学报,2015,38(8):58-64,79.
[32] FRY CS, KIRBY TJ, KOSMAC K, et al. Myogenic Progenitor Cells Control Extracellular Matrix Production by Fibroblasts during Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;20(1):56-69.
[33] GILLIES AR, LIEBER RL. Structure and function of the skeletal muscle extracellular matrix. Muscle Nerve. 2011;44(3):318-331.
[34] PASSERIEUX E, ROSSIGNOL R, CHOPARD A, et al. Structural organization of the perimysium in bovine skeletal muscle: Junctional plates and associated intracellular subdomains. J Struct Biol. 2006;154(2):206-216.
[35] CAO BY, RAO Y, ZHUANG W, et al. Interpretation of therapeutic effect of fan-ashi point based on tension transmission of skeletal muscle. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2021;41(2):217-220.
[36] OWENS DJ, TWIST C, COBLEY JN, et al. Exercise-induced muscle damage: What is it, what causes it and what are the nutritional solutions? Eur J Sport Sci. 2019;19(1):71-85.
[37] 欧阳谭亮,武志娟,钟金城.MMP-2和MMP-9在骨骼肌组织中的研究进展[J].生命科学,2021,33(10):1286-1295.
[38] RULLMAN E, RUNDQVIST H, WÅGSÄTER D, et al. A single bout of exercise activates matrix metalloproteinase in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007;102(6):2346-2351.
[39] HJORTH M, NORHEIM F, MEEN AJ, et al. The effect of acute and long-term physical activity on extracellular matrix and serglycin in human skeletal muscle. Physiol Rep. 2015;3(8):e12473.
[40] IWANAGA Y, AOYAMA T, KIHARA Y, et al. Excessive activation of matrix metalloproteinases coincides with left ventricular remodeling during transition from hypertrophy to heart failure in hypertensive rats. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39(8):1384-1391.
[41] LANG T, LEBLANC A, EVANS H, et al. Cortical and trabecular bone mineral loss from the spine and hip in long-duration spaceflight. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(6):1006-1012. |