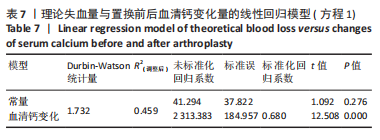
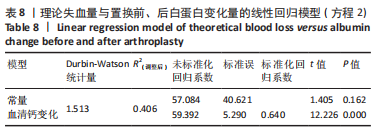
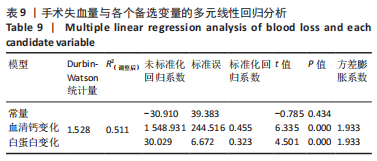
[1] LI J, ZHU H, LIAO R. Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) pathway for primary hip and knee arthroplasty: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2019;20:599.
[2] TILLE E, MYSLIWIETZ J, BEYER F, et al.Intraarticular use of tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rate after primary total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):341.
[3] LI ZJ, ZHAO MW, ZENG L. Additional Dose of Intravenous Tranexamic Acid after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty Further Reduces Hidden Blood Loss. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(6):638-642.
[4] VORA M, SING DC, YI PH, et al. Hypoalbuminemia is a risk factor for predicting early postoperative complications after proximal humerus fracture fixation. J Orthop. 2019;19:106-110.
[5] BLEVINS K, AALIREZAIE A, SHOHAT N, et al. Malnutrition and the Development of Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Patients Undergoing Primary Elective Total Joint Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(9): 2971-2975.
[6] NWACHUKWU BU, DY CJ, BURKET JC, et al. Risk for Complication after Total Joint Arthroplasty at a Center of Excellence: The Impact of Patient Travel Distance. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30:1058-1061.
[7] ROBINSON TN, RAEBURN CD, TRAN ZV, et al. Postoperative Delirium in the Elderly: Risk Factors and Outcomes. Ann Surg. Ann Surg. 2009; 249(1):173-178.
[8] YATES AJ JR; AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF HIP AND KNEE SURGEONS EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE COMMITTEE. Postoperative prophylactic antibiotics in total joint arthroplasty. Arthroplast Today. 2018;4(1): 130-131.
[9] SCHIAVON CA, BERSCH-FERREIRA AC, SANTUCCI EV, et al. Effects of Bariatric Surgery in Obese Patients With Hypertension: The GATEWAY Randomized Trial (Gastric Bypass to Treat Obese Patients With Steady Hypertension). Circulation. 2018;137(11):1132-1142.
[10] YU Q, LIU K, MA D, et al. Do Symptoms and Serum Calcium Levels Affect the Results of Surgical Treatment of Primary Hyperparathyroidism? Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:2150159.
[11] GAI P, SUN H, SUI L, et al. Hypocalcaemia After Total Knee Arthroplasty and its Clinical Significance. Anticancer Res. 2016;36(3):1309-1311.
[12] 刘子桃, 黄永明. 膝关节置换患者围手术期钠、钾、钙离子水平的变化及临床意义[J]. 当代医学,2012,18(23):22-24.
[13] MATTSSON JP, VÄÄNÄNEN K, WALLMARK B, et al. Omeprazole and bafilomycin, two proton pump inhibitors: Differentiation of their effects on gastric, kidney and bone H+-translocating ATPases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1065(2):261-268.
[14] BAHTIRI E, ISLAMI H, HOXHA R, et al. Proton pump inhibitor use for 12 months is not associated with changes in serum magnesium levels: a prospective open label comparative study. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017;28(2):104-109.
[15] LEE L, RAMOS-ALVAREZ I, ITO T, et al. Insights into Effects/Risks of Chronic Hypergastrinemia and Lifelong PPI Treatment in Man Based on Studies of Patients with Zollinger–Ellison Syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):5128.
[16] BIHORAC A, ROSS EA. Continuous Venovenous Hemofiltration With Citrate-Based Replacement Fluid: Efficacy, Safety, and Impact on Nutrition. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;46(5):908-918.
[17] KUO IY, EHRLICH BE. Signaling in muscle contraction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(2):a006023.
[18] HARVEY NC, BIVER E, KAUFMAN J, et al. The role of calcium supplementation in healthy musculoskeletal ageing : An expert consensus meeting of the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO) and the International Foundation for Osteoporosis (IOF). Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(2):447-462.
[19] ANASTASIO AT, FARLEY KX, BODEN SD, et al. Modifiable, Postoperative Risk Factors for Delayed Discharge Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: The Influence of Hypotension and Opioid Use. J Arthroplasty. 2020; 35(1):82-88.
[20] TANG MJ, DING SB, HU WY. Fibrinogen and Albumin Score Changes during Preoperative Treatment Can Predict Prognosis in Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2019; 2019:3514586.
[21] LAI R, CHEN T, WU Z, et al. Associations between body mass index and mortality in acute-on-chronic liver failure patients. Ann Hepatol. 2019;18(6):893-897.
[22] UENO K, AJIKI T, TSUGAWA D, et al. Effectiveness of omega-3 fatty acid administration on completion rate of adjuvant chemotherapy for biliary tract cancer: study protocol for a single-centre, open-label, single-arm, historically controlled study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(8):e029915.
[23] OKAMOTO N, AMANO N, NAKAMURA T, et al. Relationship between tooth loss, low masticatory ability, and nutritional indices in the elderly: a cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health. 2019;19(1):110.
[24] SŁOTWIŃSKI R, SARNECKA A, DĄBROWSKA A, et al. Innate immunity gene expression changes in critically ill patients with sepsis and disease-related malnutrition. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2015;40(3):311-324.
[25] HE Y, XIAO J, SHI Z, et al. Supplementation of enteral nutritional powder decreases surgical site infection, prosthetic joint infection, and readmission after hip arthroplasty in geriatric femoral neck fracture with hypoalbuminemia. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):292.
[26] ALFARGIENY R, BODALAL Z, BENDARDAF R, et al. Nutritional status as a predictive marker for surgical site infection in total joint arthroplasty. Avicenna J Med. 2015;5(4):117-122.
[27] KHANNA R, YI PH, SING DC, et al. Hypoalbuminemia Is Associated With Septic Revisions After Primary Surgery and Postoperative Infection After Revision Surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(6):454-460.
[28] IBRAHIM MS, TWAIJ H, GIEBALY DE, et al. Enhanced recovery in total hip replacement: a clinical review. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(12):1587-1594.
[29] PEARSON TC, GUTHRIE DL, SIMPSON J, et al. Interpretation of measured red cell mass and plasma volume in adults: Expert Panel on Radionuclides of the International Council for Standardization in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 1995;89(4):748-756.
[30] GOOD L, PETERSON E, LISANDER B. Tranexamic acid decreases external blood loss but not hidden blood loss in total knee replacement. Br J Anaesth. 2003;90(5):596-599.
[31] MARX G, SCHUERHOLZ T, PEDDER S, et al. Blood volume measurements using an integrated fiberoptic monitoring system in a porcine septic shock model. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:1483-1488.
|