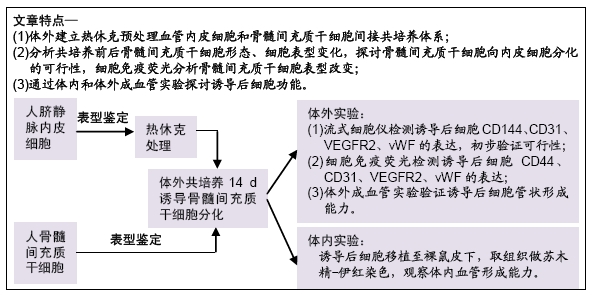
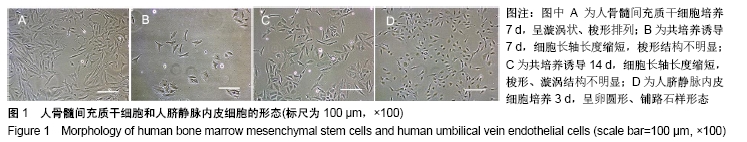
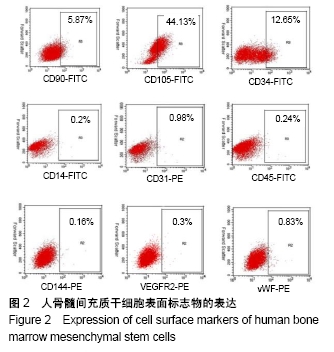
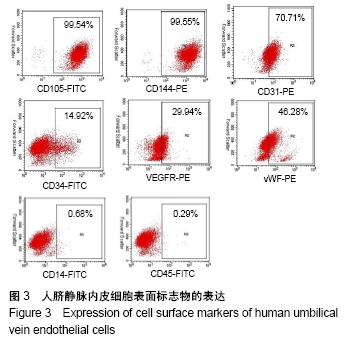
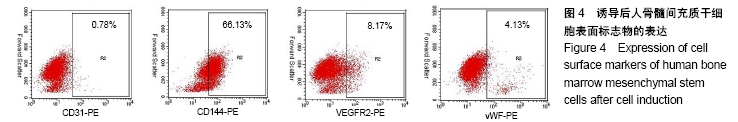
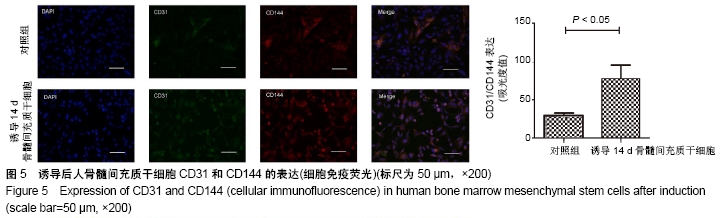
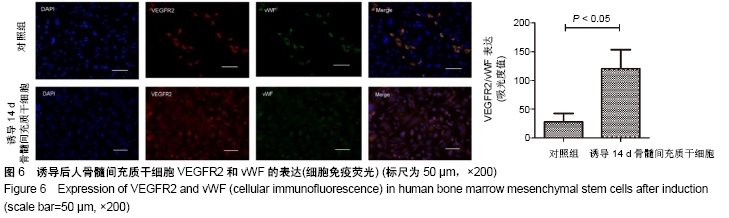
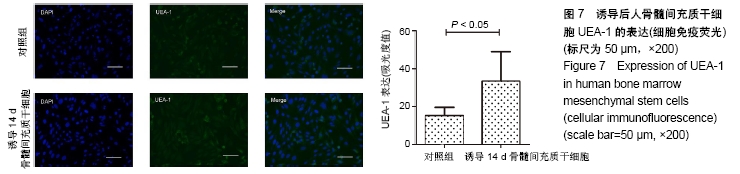
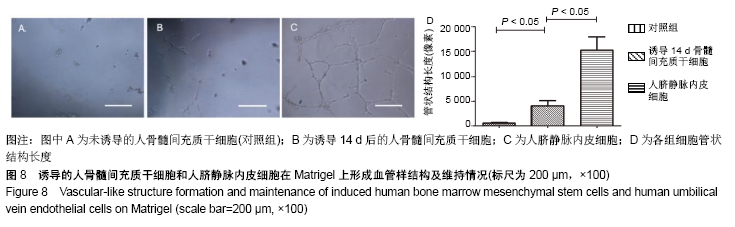
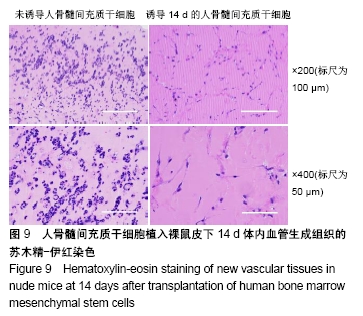
[1] 彭长铁,邓礼明, 熊国祚,等. JAK2-STAT3信号通路在缺血性疾病的研究进展[J].临床与病理杂志, 2019, 39(1):159-164.
[2] 王承恩,杨敏,佟小强, 等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗下肢缺血性疾病疗效的Meta分析[J].中国介入影像与治疗学, 2019, 16(1):26-31.
[3] 董晨露,刘笑涵,吴琳.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究与进展[J].中国骨伤, 2019,32(3):99-103.
[4] 蒋长青,蓝蔚仁,李海音,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体对退变髓核细胞的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2019, 29(2):147-155.
[5] 王怡晴,刘如明,王诺鑫,等.天然小分子化合物诱导间充质干细胞向成骨分化的研究进展[J].中草药, 2019,50(11):2728-2735.
[6] 龚业莉,走近神奇的干细胞移植[M].西安:西安交通大学出版社, 2014:97.
[7] LIN Q, WANG L, BAI Y, et al. Effect of the co-culture of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells with human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2016;36(3): 221-224.
[8] 罗淑平,杜玉婷,白驹.骨髓间充质干细胞与人脐静脉内皮细胞的共培养[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(45):7370-7374.
[9] 王俊力,许慧芳,冯莉,等.不同组织来源间充质干细胞向血管内皮细胞诱导分化的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(36): 5466-5472.
[10] 艾丽,翁立新,孙同柱.热休克汗腺细胞诱导人骨髓间充质干细胞的表型转化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(6):985-991.
[11] 李锦. 热休克培养对bFGF转染骨髓间充质干细胞FGFRs及凋亡相关蛋白的影响[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2018,9(16):134-137.
[12] LIANG T, ZHU L, GAO W, et al. Coculture of endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells enhanced their proliferation and angiogenesis through PDGF and Notch signaling. FEBS Open Bio. 2017;7(11):1722-1736.
[13] WU L, ZHAO X, HE B, et al. The Possible Roles of Biological Bone Constructed with Peripheral Blood Derived EPCs and BMSCs in Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016: 8168943.
[14] CARVALHO MS, SILVA JC, CABRAL JMS, et al. Cultured cell-derived extracellular matrices to enhance the osteogenic differentiation and angiogenic properties of human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2019;13(9): 1544-1558.
[15] FAN X, TENG Y, YE Z, et al. The effect of gap junction-mediated transfer of miR-200b on osteogenesis and angiogenesis in a co-culture of MSCs and HUVECs. J Cell Sci. 2018;131(13): jcs216135.
[16] SONG M, ZHOU Y, LIU Y. VEGF heparinized-decellularized adipose tissue scaffolds enhance tissue engineering vascularization in vitro. RSC Advances. 2018;8(59):33614-33624.
[17] GUO S, ZHEN Y, WANG A. Transplantation of bone mesenchymal stem cells promotes angiogenesis and improves neurological function after traumatic brain injury in mouse. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017; 13:2757-2765.
[18] 王斯琪,卢海源,程腊梅.3种不同组织来源的间充质干细胞促内皮祖细胞血管形成作用的比较[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2018,42(2): 184-191.
[19] 刘春晓,吴欢欢,马慧雨,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞与脐静脉内皮细胞体外共培养的研究[J].组织工程与重建外科, 2011,7(2):65-69.
[20] SALEH FA, WHYTE M, ASHTON P, et al. Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell activity by endothelial cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(3): 391-403.
[21] 郑心田,孟恒星,李广平,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞向血管内皮细胞诱导分化的实验研究[J].天津医科大学学报, 2009,15(3):357-361.
[22] 陈小莹,李欣然,王清,等.热休克预处理骨髓间充质干细胞对化疗性卵巢早衰的疗效观察[J].解放军医学杂志, 2018,43(5):403-408.
[23] GRAINGER SJ, CARRION B, CECCARELLI J, et al. Stromal cell identity influences the in vivo functionality of engineered capillary networks formed by co-delivery of endothelial cells and stromal cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(9-10):1209-1222.
[24] MA J, YANG F, BOTH SK, et al. In vitro and in vivo angiogenic capacity of BM-MSCs/HUVECs and AT-MSCs/HUVECs cocultures. Biofabrication. 2014;6(1):015005.
[25] 辛毅,李娜,黄益民,等.小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞定向诱导分化血管内皮细胞的实验研究[J].新乡医学院学报, 2014,31(1):8-14.
[26] SHOU K, NIU Y, ZHENG X, et al. Enhancement of Bone-Marrow- Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Angiogenic Capacity by NPWT for a Combinatorial Therapy to Promote Wound Healing with Large Defect. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7920265.
[27] BLACHE U, VALLMAJO-MARTIN Q, HORTON ER, et al. Notch-inducing hydrogels reveal a perivascular switch of mesenchymal stem cell fate. EMBO Rep. 2018;19(8): e45964.
[28] SHAFIEE A, PATEL J, WONG HY, et al. Priming of endothelial colony-forming cells in a mesenchymal niche improves engraftment and vasculogenic potential by initiating mesenchymal transition orchestrated by NOTCH signaling. FASEB J. 2017;31(2):610-624.
[29] JIANG YN, ZHAO J, CHU FT, et al. Tension-loaded bone marrow stromal cells potentiate the paracrine osteogenic signaling of co-cultured vascular endothelial cells. Biol Open. 2018;7(6): bio032482.
[30] BAYER EA, FEDORCHAK MV, LITTLE SR. The Influence of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor and Bone Morphogenetic Protein Presentation on Tubule Organization by Human Umbilical Vascular Endothelial Cells and Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Coculture. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(21-22):1296-1304.
[31] KHODEER DM, BILASY SE, FARAG NE, et al. Sitagliptin protects diabetic rats with acute myocardial infarction through induction of angiogenesis: role of IGF-1 and VEGF. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;97(11):1053-1063.
|