| [1] Sherman MF, Warren RF, Marshall JL, et al. A clinical and radiographical analysis of 127 anterior cruciate insufficient knees. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;227:229-237.[2] Johnson DL, Urban WJ, Caborn DN, et al. Articular cartilage changes seen with magnetic resonance imaging-detected bone bruises associated with acute anterior cruciate ligament rupture. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26(3):409-414.[3] Nielsen A B, Yde J. Epidemiology of acute knee injuries: a prospective hospital investigation. J Trauma. 1991;31(12): 1644-1648.[4] Ritter MA, Lutgring JD, Davis KE, et al. Total knee arthroplasty effectiveness in patients 55 years old and younger: osteoarthritis vs. rheumatoid arthritis. Knee. 2007;14(1):9-11.[5] Swanik CB, Lephart SM, Rubash HE. Proprioception, kinesthesia, and balance after total knee arthroplasty with cruciate-retaining and posterior stabilized prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(2):328-334.[6] Conditt MA, Noble PC, Bertolusso R, et al. The PCL significantly affects the functional outcome of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(7 Suppl 2):107-112.[7] Straw R, Kulkarni S, Attfield S, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament at total knee replacement. Essential, beneficial or a hindrance? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(5):671-674.[8] Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12.[9] Clark CR, Rorabeck CH, MacDonald S, et al. Posterior-stabilized and cruciate-retaining total knee replacement: a randomized study. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2001(392):208-212.[10] Tanzer M, Smith K, Burnett S. Posterior-stabilized versus cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty: balancing the gap. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(7):813-819.[11] Wang CJ, Wang JW, Chen HS. Comparing cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty and cruciate-substituting total knee arthroplasty: a prospective clinical study. Chang Gung Med J. 2004;27(8):578-585.[12] Maruyama S, Yoshiya S, Matsui N, et al. Functional comparison of posterior cruciate-retaining versus posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(3): 349-353.[13] Catani F, Leardini A, Ensini A, et al. The stability of the cemented tibial component of total knee arthroplasty: posterior cruciate-retaining versus posterior-stabilized design. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(6):775-782.[14] Chaudhary R, Beaupre LA, Johnston DW. Knee range of motion during the first two years after use of posterior cruciate-stabilizing or posterior cruciate-retaining total knee prostheses. A randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(12):2579-2586.[15] Harato K, Bourne RB, Victor J, et al. Midterm comparison of posterior cruciate-retaining versus -substituting total knee arthroplasty using the Genesis II prosthesis. A multicenter prospective randomized clinical trial. Knee. 2008;15(3): 217-221.[16] Kim YH, Choi Y, Kwon OR, et al. Functional outcome and range of motion of high-flexion posterior cruciate-retaining and high-flexion posterior cruciate-substituting total knee prostheses. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(4):753-760.[17] Seon JK, Park JK, Shin YJ, et al. Comparisons of kinematics and range of motion in high-flexion total knee arthroplasty: cruciate retaining vs. substituting designs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(12):2016-2022.[18] Yagishita K, Muneta T, Ju YJ, et al. High-flex posterior cruciate-retaining vs posterior cruciate-substituting designs in simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(3):368-374.[19] Matsumoto T, Muratsu H, Kubo S, et al. Intraoperative soft tissue balance reflects minimum 5-year midterm outcomes in cruciate-retaining and posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(9):1723-1730.[20] Thomsen MG, Husted H, Otte KS, et al. Do patients care about higher flexion in total knee arthroplasty? A randomized, controlled, double-blinded trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:127.[21] van den Boom LG, Halbertsma JP, van Raaij JJ, et al. No difference in gait between posterior cruciate retention and the posterior stabilized design after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(12):3135-3141.[22] Vermesan D, Trocan I, Prejbeanu R, et al. Reduced operating time but not blood loss with cruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty. J Clin Med Res. 2015;7(3):171-175.[23] Ozturk A, Akalin Y, Cevik N, et al. Posterior cruciate-substituting total knee replacement recovers the flexion arc faster in the early postoperative period in knees with high varus deformity: a prospective randomized study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(7):999-1006.[24] Beaupre LA, Sharifi B, Johnston D. A Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Posterior Cruciate-Stabilizing vs Posterior Cruciate-Retaining Prostheses in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: 10-Year Follow-Up. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(3): 818-823.[25] 汪锡龙,尚希福,李国远,等. 个体化股骨远端外翻角度截骨技术在初次人工全膝关节置换术中的应用[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015,29(1):27-30.[26] 吴彦生,李永胜,陈百成. 后交叉韧带保留与否对膝关节本体感觉的影响[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013,27(7):851-854.[27] Matsumoto T, Muratsu H, Kubo S, et al. Soft tissue tension in cruciate-retaining and posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(5):788-795.[28] 吴伟山. 应用CR型和PS型人工膝关节假体置换术后早期临床疗效分析[D]. 济南:山东中医药大学, 2016.[29] 吕新凯. CR型假体与PS型假体全膝置换的早期临床疗效对比[D]. 济南:山东大学, 2014.[30] White SH, O'Connor JJ, Goodfellow JW. Sagittal plane laxity following knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(2): 268-270.[31] Lee SM, Seong SC, Lee S, et al. Outcomes of the different types of total knee arthroplasty with the identical femoral geometry. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2012;24(4):214-220.[32] Chaudhary R, Beaupre LA, Johnston DW. Knee range of motion during the first two years after use of posterior cruciate-stabilizing or posterior cruciate-retaining total knee prostheses. A randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(12):2579-2586.[33] Lee SM, Seong SC, Lee S, et al. Outcomes of the different types of total knee arthroplasty with the identical femoral geometry. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2012;24(4):214-220.[34] Becker R, Hirschmann MT, Karlsson J. The role of ligament tension and sensomotoric system in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(6):1663-1665.[35] Callaghan JJ, O'Rourke MR, Goetz DD, et al. Tibial post impingement in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(404):83-88.[36] 罗世兴,赵劲民,苏伟,等. 保留和不保留后交叉韧带全膝置换疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2010,18(14):1145-1149.[37] 陈良军. 保留和不保留后交叉韧带的全膝关节置换术的系统评价[D]. 南宁:广西医科大学, 2010.[38] Victor J, Banks S, Bellemans J. Kinematics of posterior cruciate ligament-retaining and -substituting total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised outcome study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(5):646-655.[39] Vermesan D, Prejbeanu R, Laitin S, et al. Meniscal tears left in situ during anatomic single bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014; 18(2):252-256.[40] 王林,宋磊,韩伟峰. 全膝关节置换术中后交叉韧带保留与切除与否的对比研究[J]. 首都医科大学学报, 2017,38(6):915-918.[41] Pang HN, Yeo SJ, Chong HC, et al. Joint line changes and outcomes in constrained versus unconstrained total knee arthroplasty for the type II valgus knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10):2363-2369.[42] Abdel MP, Morrey ME, Jensen MR, et al. Increased long-term survival of posterior cruciate-retaining versus posterior cruciate-stabilizing total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(22):2072-2078.[43] 凌卓彦,李柳炳,董启榕. 全膝关节置换术中切除后交叉韧带的优缺点[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2009,24(10):958-960.[44] Ishii Y, Noguchi H, Takeda M, et al. Prediction of range of motion 2 years after mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: PCL-retaining versus PCL-sacrificing. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(12):2002-2008. |
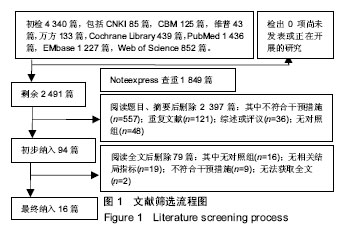
.jpg)
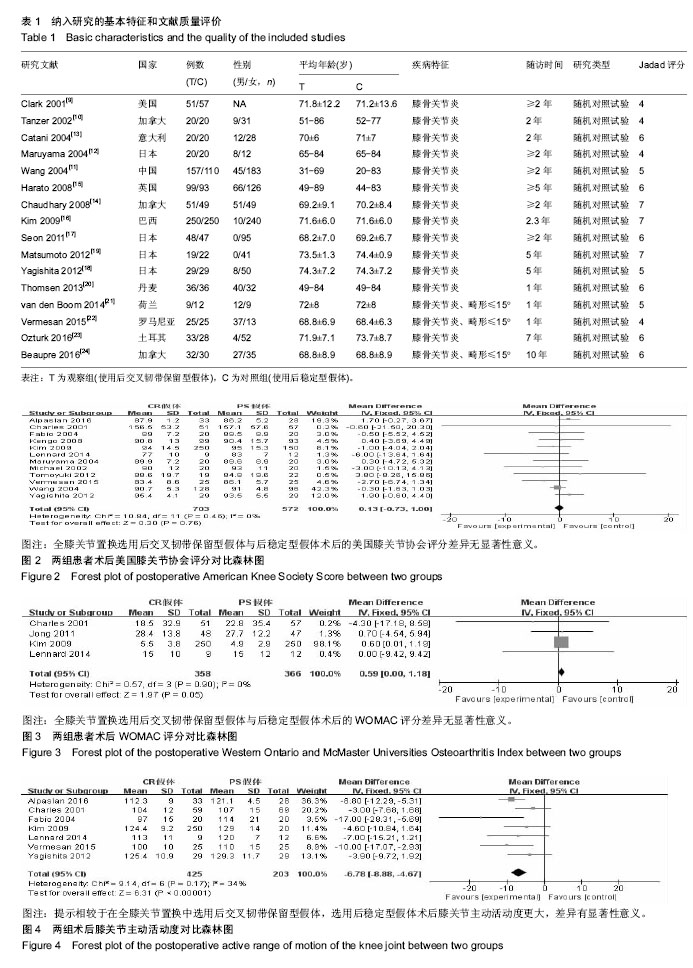

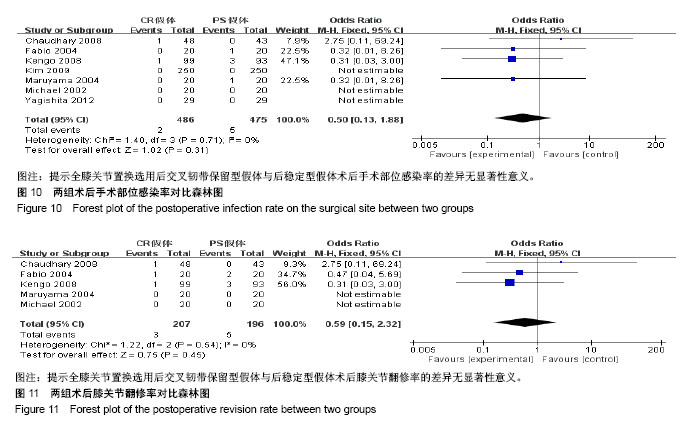
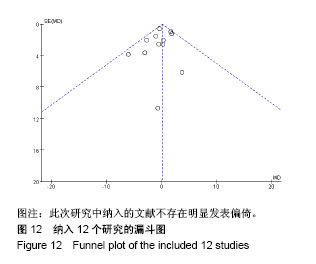
.jpg)