| [1] Liu Y,Zhang H,Liang N,et al.Prevalence and associated factors of knee osteoarthritis in a rural Chinese adult population: an epidemiological survey. BMC Public Health. 2016;16(1):94.[2] Ackerman IN, Osborne RH.Obesity and increased burden of hip and knee joint disease in Australia: results from a national survey.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2012;13:254.[3] Raederstorff D,Kunz I,Schwager J.Resveratrol, from experimental data to nutritional evidence: the emergence of a new food ingredient. Ann N Y Acad Sci.2013;1290:136-141.[4] Yu W, Fu YC, Wang W. Cellular and molecular effects of resveratrol in health and disease. J Cell Biochem.2012; 113(3):752-759.[5] Nakata R, Takahashi S, Inoue H. Recent advances in the study on resveratrol. Biol Pharm Bull.2012;35(3):273-279.[6] Maepa M,Razwinani M,Motaung S.Effects of resveratrol on collagen type II protein in the superficial and middle zone chondrocytes of porcine articular cartilage. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;178:25-33.[7] 夏睿,董启榕. MMP13在骨性关节炎患者滑膜细胞中的表达[J]. 苏州大学学报(医学版),2006,26(5):815-817.[8] Kostopoulou F, Gkretsi V, Malizos K N, et al. Central role of SREBP-2 in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e35753.[9] Qiu XM, Jin CT, Wang W.Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms of sterol regulatory element binding protein-2 gene and risk of knee osteoarthritis in a Chinese Han population. J Int Med Res.2014;42(2):320-328.[10] Pullig O, Kladny B, Weseloh G, et al.[Metabolic activation of chondrocytes in human osteoarthritis. Expression of type II collagen].Z OrthopIhre Grenzgeb.1999;137(1):67-75.[11] 刘弼,肖德明,雷鸣,等. 白藜芦醇对硝普钠诱导的软骨细胞凋亡bax及bcl-2表达的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2012,20(13): 1235-1238.[12] Shakibaei M, John T, Seifarth C, et al. Resveratrol inhibits IL-1 beta-induced stimulation of caspase-3 and cleavage of PARP in human articular chondrocytes in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1095:554-563.[13] Chang CH, Hsu YM, Chen YC, et al.Anti-inflammatory effects of hydrophilic and lipophilic statins with hyaluronic acid against LPS-induced inflammation in porcine articular chondrocytes. J Orthop Res.2014;32(4):557-565.[14] 刘维,吴沅皞.青藤碱对炎性刺激下体外培养关节软骨细胞的保护作用[J]. 国际免疫学杂志,2011,34(5):309-312.[15] Suri P, Morgenroth DC, Hunter DJ. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis and associated comorbidities. PM R.2012; 4(5 Suppl):S10-S19.[16] Davies-Tuck ML, Hanna F, Davis SR, et al. Total cholesterol and triglycerides are associated with the development of new bone marrow lesions in asymptomatic middle-aged women - a prospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther.2009;11(6): R181.[17] Miller GD, Jenks MZ, Vendela M,et al.Influence of weight loss, body composition, and lifestyle behaviors on plasma adipokines: a randomized weight loss trial in older men and women with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. J Obes.2012; 2012:708505.[18] Iwata M, Ochi H, Hara Y, et al. Initial responses of articular tissues in a murine high-fat diet-induced osteoarthritis model: pivotal role of the IPFP as a cytokine fountain. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60706.[19] Infantino V, Iacobazzi V, De Santis F, et al. Transcription of the mitochondrial citrate carrier gene: role of SREBP-1, upregulation by insulin and downregulation by PUFA. BiochemBiophys Res Commun.2007;356(1):249-254.[20] Eberle D, Hegarty B, Bossard P, et al. SREBP transcription factors: master regulators of lipid homeostasis. Biochimie. 2004;86(11):839-848.[21] 翁鉴,曾晖,肖德明,等. 固醇调节元件结合蛋白2在软骨细胞退变过程中的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(29):4624-4628.[22] 张亚峰,王骏飞,陈东阳,等. 核因子κB信号转导途径在大鼠实验性骨性关节炎软骨细胞中被激活[J]. 中国临床康复, 2006, 10(37):71-73, 图34-图37.[23] Lei M, Liu SQ, Liu YL. Resveratrol protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell derived chondrocytes cultured on chitosan-gelatin scaffolds from the inhibitory effect of interleukin-1beta. ActaPharmacol Sin.2008;29(11): 1350-1356.[24] Torzilli PA, Bhargava M, Park S, et al. Mechanical load inhibits IL-1 induced matrix degradation in articular cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2010;18(1):97-105. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
固醇调节元件结合蛋白(SREBP):是位于内质网的细胞内胆固醇敏感器,通过Insig-Srebp-Scap途径对细胞内胆固醇进行反馈调节。
白藜芦醇:是多酚类化合物,主要来源于花生、葡萄(红葡萄酒)、虎杖、桑椹等植物。白藜芦醇是一种生物性很强的天然多酚类物质,又称为芪三酚,是肿瘤的化学预防剂,同时也可降低血小板聚集,预防和治疗动脉粥样硬化、心脑血管疾病。
文题释义:
固醇调节元件结合蛋白(SREBP):是位于内质网的细胞内胆固醇敏感器,通过Insig-Srebp-Scap途径对细胞内胆固醇进行反馈调节。
白藜芦醇:是多酚类化合物,主要来源于花生、葡萄(红葡萄酒)、虎杖、桑椹等植物。白藜芦醇是一种生物性很强的天然多酚类物质,又称为芪三酚,是肿瘤的化学预防剂,同时也可降低血小板聚集,预防和治疗动脉粥样硬化、心脑血管疾病。.jpg) 文题释义:
固醇调节元件结合蛋白(SREBP):是位于内质网的细胞内胆固醇敏感器,通过Insig-Srebp-Scap途径对细胞内胆固醇进行反馈调节。
白藜芦醇:是多酚类化合物,主要来源于花生、葡萄(红葡萄酒)、虎杖、桑椹等植物。白藜芦醇是一种生物性很强的天然多酚类物质,又称为芪三酚,是肿瘤的化学预防剂,同时也可降低血小板聚集,预防和治疗动脉粥样硬化、心脑血管疾病。
文题释义:
固醇调节元件结合蛋白(SREBP):是位于内质网的细胞内胆固醇敏感器,通过Insig-Srebp-Scap途径对细胞内胆固醇进行反馈调节。
白藜芦醇:是多酚类化合物,主要来源于花生、葡萄(红葡萄酒)、虎杖、桑椹等植物。白藜芦醇是一种生物性很强的天然多酚类物质,又称为芪三酚,是肿瘤的化学预防剂,同时也可降低血小板聚集,预防和治疗动脉粥样硬化、心脑血管疾病。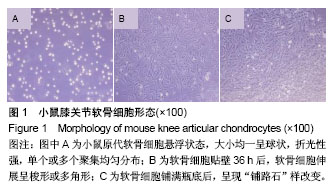
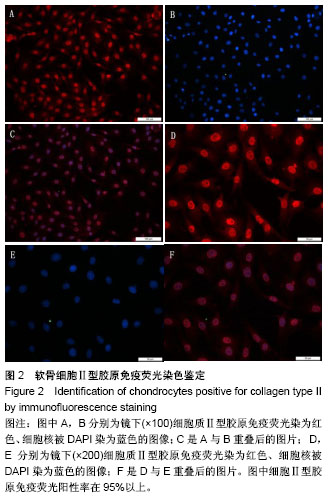
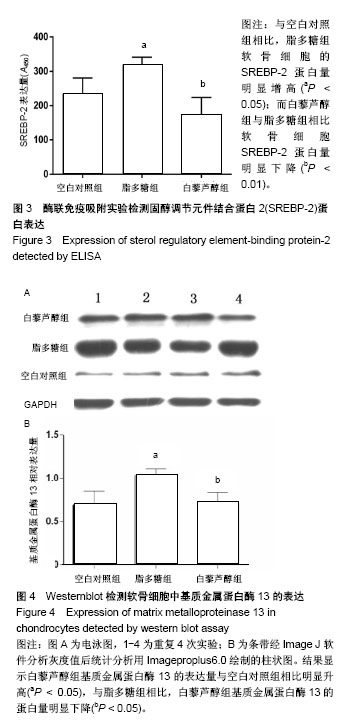
.jpg) 文题释义:
固醇调节元件结合蛋白(SREBP):是位于内质网的细胞内胆固醇敏感器,通过Insig-Srebp-Scap途径对细胞内胆固醇进行反馈调节。
白藜芦醇:是多酚类化合物,主要来源于花生、葡萄(红葡萄酒)、虎杖、桑椹等植物。白藜芦醇是一种生物性很强的天然多酚类物质,又称为芪三酚,是肿瘤的化学预防剂,同时也可降低血小板聚集,预防和治疗动脉粥样硬化、心脑血管疾病。
文题释义:
固醇调节元件结合蛋白(SREBP):是位于内质网的细胞内胆固醇敏感器,通过Insig-Srebp-Scap途径对细胞内胆固醇进行反馈调节。
白藜芦醇:是多酚类化合物,主要来源于花生、葡萄(红葡萄酒)、虎杖、桑椹等植物。白藜芦醇是一种生物性很强的天然多酚类物质,又称为芪三酚,是肿瘤的化学预防剂,同时也可降低血小板聚集,预防和治疗动脉粥样硬化、心脑血管疾病。