| [1] Xu ZQ, Li J, Deng J, et al. Effects of proBDNF on cell proliferation and differentiation in hippocampal dentate gyrus in Alzheimer' disease rat model. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;90(19):1353-1356.[2] 薛小燕,郭小华,李敏,等.神经营养因子研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(12):3463-3466.[3] 郭雨霁,李盛芳.神经营养因子家族及其受体的研究进展[J].神经解剖学杂志,2001,17(3):288-294.[4] Ascano M, Bodmer D, Kuruvilla R. Endocytic trafficking of neurotrophins in neural development. Trends Cell Biol. 2012; 22(5):266-273.[5] Shakhbazau A, Martinez JA, Xu QG, et al. Evidence for a systemic regulation of neurotrophin synthesis in response to peripheral nerve injury. J Neurochem. 2012;122(3): 501-511. [6] Hempstead BL. Dissecting the diverse actions of pro- and mature neurotrophins. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2006;3(1):19-24.[7] Barde YA, Edgar D, Thoenen H. Purification of a new neurotrophic factor from mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1982; 1(5):549-553.[8] Mandel AL, Ozdener H, Utermohlen V. Identification of pro- and mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor in human saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 2009;54(7):689-695. [9] 张露,崔晓燕,李俊敏,等.糖氧剥夺对海马神经元中成熟脑源性神营养因子及其前体蛋白和突触素的影响[J].中国实用医刊,2016, 43(19):5-8.[10] Salehi A, Delcroix JD, Swaab DF. Alzheimer's disease and NGF signaling. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2004;111(3):323-345.[11] 周莉,李小刚.神经生长因子在脑缺血后的变化及治疗展望[J].西南军医,2011,13(6):1094-1096.[12] Zhou FQ, Zhou J, Dedhar S, et al. NGF-induced axon growth is mediated by localized inactivation of GSK-3beta and functions of the microtubule plus end binding protein APC. Neuron. 2004;42(6):897-912.[13] Bierl MA, Jones EE, Crutcher KA, et al. 'Mature' nerve growth factor is a minor species in most peripheral tissues. Neurosci Lett. 2005;380(1-2):133-137. [14] Song W, Volosin M, Cragnolini AB, et al. ProNGF induces PTEN via p75NTR to suppress Trk-mediated survival signaling in brain neurons. J Neurosci. 2010;30(46): 15608-15615. [15] Dicou E, Pflug B, Magazin M, et al. Two peptides derived from the nerve growth factor precursor are biologically active. J Cell Biol. 1997;136(2):389-398.[16] Yano H, Torkin R, Martin LA, et al. Proneurotrophin-3 is a neuronal apoptotic ligand: evidence for retrograde-directed cell killing. J Neurosci. 2009;29(47):14790-14802. [17] Pang PT, Teng HK, Zaitsev E, et al. Cleavage of proBDNF by tPA/plasmin is essential for long-term hippocampal plasticity. Science. 2004;306(5695):487-491.[18] Ethell IM, Ethell DW. Matrix metalloproteinases in brain development and remodeling: synaptic functions and targets. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85(13):2813-2823.[19] Mowla SJ, Farhadi HF, Pareek S, et al. Biosynthesis and post-translational processing of the precursor to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Biol Chem. 2001;276 (16):12660-12666. [20] Ivanova T, Beyer C. Pre- and postnatal expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA/protein and tyrosine protein kinase receptor B mRNA in the mouse hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 2001;307(1):21-24.[21] Zafra F, Lindholm D, Castrén E, et al. Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor mRNA in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci. 1992;12(12):4793-4799.[22] Lu B. BDNF and activity-dependent synaptic modulation. Learn Mem. 2003;10(2):86-98.[23] Mandel AL, Ozdener H, Utermohlen V. Identification of pro- and mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor in human saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 2009;54(7):689-695. [24] Pang PT, Teng HK, Zaitsev E, et al. Cleavage of proBDNF by tPA/plasmin is essential for long-term hippocampal plasticity. Science. 2004;306(5695):487-491.[25] Nagappan G, Zaitsev E, Senatorov VV Jr, et al. Control of extracellular cleavage of ProBDNF by high frequency neuronal activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(4): 1267-1272.[26] Gray K, Ellis V. Activation of pro-BDNF by the pericellular serine protease plasmin. FEBS Lett. 2008;582(6):907-910.[27] Keifer J, Sabirzhanov BE, Zheng Z, et al. Cleavage of proBDNF to BDNF by a tolloid-like metalloproteinase is required for acquisition of in vitro eyeblink classical conditioning. J Neurosci. 2009;29(47):14956-14964. [28] Bergami M, Santi S, Formaggio E, et al. Uptake and recycling of pro-BDNF for transmitter-induced secretion by cortical astrocytes. J Cell Biol. 2008;183(2):213-221. [29] Seidah NG, Mowla SJ, Hamelin J, et al. Mammalian subtilisin/kexin isozyme SKI-1: A widely expressed proprotein convertase with a unique cleavage specificity and cellular localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96(4):1321-1326.[30] Zhou XF, Song XY, Zhong JH, et al. Distribution and localization of pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor-like immunoreactivity in the peripheral and central nervous system of the adult rat. J Neurochem. 2004;91(3):704-715.[31] Perovic M, Tesic V, Mladenovic Djordjevic A, et al. BDNF transcripts, proBDNF and proNGF, in the cortex and hippocampus throughout the life span of the rat. Age (Dordr). 2013;35(6):2057-2070. [32] Tognoli C, Rossi F, Di Cola F, et al. Acute stress alters transcript expression pattern and reduces processing of proBDNF to mature BDNF in Dicentrarchus labrax. BMC Neurosci. 2010;11:4. [33] Cui X, Chen L, Ren Y, et al. Genetic modification of mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury repair strategies. Biosci Trends. 2013;7(5):202-208.[34] Hondermarck H. Neurotrophins and their receptors in breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012;23(6):357-365. [35] Schecterson LC, Bothwell M. Neurotrophin receptors: Old friends with new partners. Dev Neurobiol. 2010;70(5): 332-338. [36] Skaper SD. The neurotrophin family of neurotrophic factors: an overview. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;846:1-12. [37] Aloe L. Rita Levi-Montalcini and the discovery of NGF, the first nerve cell growth factor. Arch Ital Biol. 2011;149(2):175-181. [38] Matusica D, Skeldal S, Sykes AM, et al. An intracellular domain fragment of the p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75(NTR)) enhances tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA) receptor function. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(16):11144-11154. [39] Petrie CN, Smithson LJ, Crotty AM, et al. Overexpression of nerve growth factor by murine smooth muscle cells: role of the p75 neurotrophin receptor on sympathetic and sensory sprouting. J Comp Neurol. 2013;521(11):2621-2643. [40] 彭凤玲,莫中成,郑翔,等.神经生长因子及其受体相关信号传导通路的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(31):6190-6193.[41] Matsumoto T, Rauskolb S, Polack M, et al. Biosynthesis and processing of endogenous BDNF: CNS neurons store and secrete BDNF, not pro-BDNF. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11(2): 131-133. [42] He XL, Garcia KC. Structure of nerve growth factor complexed with the shared neurotrophin receptor p75. Science. 2004;304(5672):870-875.[43] Gargano N, Levi A, Alema S. Modulation of nerve growth factor internalization by direct interaction between p75 and TrkA receptors. J Neurosci Res. 1997;50(1):1-12.[44] Vega CJ, Peterson DA. Stem cell proliferative history in tissue revealed by temporal halogenated thymidine analog discrimination. Nat Methods. 2005;2(3):167-169.[45] Strohmaier C, Carter BD, Urfer R, et al. A splice variant of the neurotrophin receptor trkB with increased specificity for brain-derived neurotrophic factor. EMBO J. 1996;15(13): 3332-3337.[46] Meloni M, Caporali A, Graiani G, et al. Nerve growth factor promotes cardiac repair following myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2010;106(7):1275-1284. [47] Vicario A, Kisiswa L, Tann JY, et al. Neuron-type-specific signaling by the p75NTR death receptor is regulated by differential proteolytic cleavage. J Cell Sci. 2015;128(8): 1507-1517.[48] Xu G, He J, Guo H, et al. Activin A prevents neuron-like PC12 cell apoptosis after oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(11):1016-1024. [49] Huang CS, Zhou J, Feng AK, et al. Nerve growth factor signaling in caveolae-like domains at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(51):36707-36714.[50] Iacaruso MF, Galli S, Martí M, et al. Structural model for p75(NTR)-TrkA intracellular domain interaction: a combined FRET and bioinformatics study. J Mol Biol. 2011;414(5): 681-698. [51] 路露,陈美婉,罗焕敏.神经营养因子受体的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(1):126-131.[52] 卞雷斯,刘振国,王文安.神经营养因子受体Trk小分子激动剂研究进展[J].国际脑血管病杂志,2006,14(11):865-869.[53] Bachis A, Rabin SJ, Del Fiacco M, et al. Gangliosides prevent excitotoxicity through activation of TrkB receptor. Neurotox Res. 2002;4(3):225-234.[54] Nakamura K, Namekata K, Harada C, et al. Intracellular sortilin expression pattern regulates proNGF-induced naturally occurring cell death during development. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14(8):1552-1554.[55] Sarret P, Krzywkowski P, Segal L, et al. Distribution of NTS3 receptor/sortilin mRNA and protein in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 2003;461(4):483-505.[56] 姜万梅,苗文哲,柳鹏,等.神经生长因子(NGF)对周围神经损伤的再生及恢复作用(综述)[J].伤残医学杂志,2003(4):74-76.[57] Ledesma MD, Da Silva JS, Crassaerts K, et al. Brain plasmin enhances APP alpha-cleavage and Abeta degradation and is reduced in Alzheimer's disease brains. EMBO Rep. 2000;1(6): 530-535.[58] Fahnestock M, Michalski B, Xu B, et al. The precursor pro-nerve growth factor is the predominant form of nerve growth factor in brain and is increased in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2001;18(2):210-220.[59] Harrington AW, Leiner B, Blechschmitt C, et al. Secreted proNGF is a pathophysiological death-inducing ligand after adult CNS injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(16): 6226-6230.[60] Lee R, Kermani P, Teng KK, et al. Regulation of cell survival by secreted proneurotrophins. Science. 2001;294(5548): 1945-1948.[61] Jansen P, Giehl K, Nyengaard JR, et al. Roles for the pro-neurotrophin receptor sortilin in neuronal development, aging and brain injury. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10(11):1449-1457.[62] Nykjaer A, Lee R, Teng KK, et al. Sortilin is essential for proNGF-induced neuronal cell death. Nature. 2004;427(6977): 843-848.[63] Masoudi R, Ioannou MS, Coughlin MD, et al. Biological activity of nerve growth factor precursor is dependent upon relative levels of its receptors. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(27): 18424-18433.[64] 周健,孙克华.神经损伤后的再生与神经营养因子[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2006,11(1):36-38.[65] Yang JW, Ru J, Ma W, et al. BDNF promotes the growth of human neurons through crosstalk with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via GSK-3β. Neuropeptides. 2015;54: 35-46.[66] Tashima R, Mikuriya S, Tomiyama D, et al. Bone marrow-derived cells in the population of spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23701.[67] Huang EJ, Reichardt LF. Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24: 677-736.[68] [68] Koshimizu H, Hazama S, Hara T, et al. Distinct signaling pathways of precursor BDNF and mature BDNF in cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2010;473(3): 229-232.[69] [Taylor AR, Gifondorwa DJ, Robinson MB, et al. Motoneuron programmed cell death in response to proBDNF. Dev Neurobiol. 2012;72(5):699-712.[70] Fan YJ, Wu LL, Li HY, et al. Differential effects of pro-BDNF on sensory neurons after sciatic nerve transection in neonatal rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27(9):2380-2390.[71] Gibon J, Buckley SM1, Unsain N1, et al. proBDNF and p75NTR Control Excitability and Persistent Firing of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons. J Neurosci. 2015;35(26):9741-9753.[72] Yang M, Lim Y, Li X, et al. Precursor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (proBDNF) forms a complex with Huntingtin-associated protein-1 (HAP1) and sortilin that modulates proBDNF trafficking, degradation, and processing. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(18):16272-16284. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
神经生长因子:是最早被发现的神经营养因子,主要来源于中枢神经系统、胎盘组织、唾液腺、前列腺、蛇毒腺以及脑内胆碱能神经元支配区,能促进神经元的存活与生长,保护损伤神经元,促进受损神经元的修复,其受体可被分为高亲和力受体Trk A和低亲和力受体p75NTR。
脑源性神经生长因子:是神经营养因子家族中第2个被发现的因子,主要分布在中枢神经系统,在海马和大脑皮质组织中含量最高,通过与高亲和受体TrkB结合发挥促进中枢神经系统和外周神经系统的神经元与胶质细胞的分化和存活、髓鞘形成、神经元迁移和轴突伸缩,以及保护损伤后的神经元等生物学作用。
文题释义:
神经生长因子:是最早被发现的神经营养因子,主要来源于中枢神经系统、胎盘组织、唾液腺、前列腺、蛇毒腺以及脑内胆碱能神经元支配区,能促进神经元的存活与生长,保护损伤神经元,促进受损神经元的修复,其受体可被分为高亲和力受体Trk A和低亲和力受体p75NTR。
脑源性神经生长因子:是神经营养因子家族中第2个被发现的因子,主要分布在中枢神经系统,在海马和大脑皮质组织中含量最高,通过与高亲和受体TrkB结合发挥促进中枢神经系统和外周神经系统的神经元与胶质细胞的分化和存活、髓鞘形成、神经元迁移和轴突伸缩,以及保护损伤后的神经元等生物学作用。.jpg) 文题释义:
神经生长因子:是最早被发现的神经营养因子,主要来源于中枢神经系统、胎盘组织、唾液腺、前列腺、蛇毒腺以及脑内胆碱能神经元支配区,能促进神经元的存活与生长,保护损伤神经元,促进受损神经元的修复,其受体可被分为高亲和力受体Trk A和低亲和力受体p75NTR。
脑源性神经生长因子:是神经营养因子家族中第2个被发现的因子,主要分布在中枢神经系统,在海马和大脑皮质组织中含量最高,通过与高亲和受体TrkB结合发挥促进中枢神经系统和外周神经系统的神经元与胶质细胞的分化和存活、髓鞘形成、神经元迁移和轴突伸缩,以及保护损伤后的神经元等生物学作用。
文题释义:
神经生长因子:是最早被发现的神经营养因子,主要来源于中枢神经系统、胎盘组织、唾液腺、前列腺、蛇毒腺以及脑内胆碱能神经元支配区,能促进神经元的存活与生长,保护损伤神经元,促进受损神经元的修复,其受体可被分为高亲和力受体Trk A和低亲和力受体p75NTR。
脑源性神经生长因子:是神经营养因子家族中第2个被发现的因子,主要分布在中枢神经系统,在海马和大脑皮质组织中含量最高,通过与高亲和受体TrkB结合发挥促进中枢神经系统和外周神经系统的神经元与胶质细胞的分化和存活、髓鞘形成、神经元迁移和轴突伸缩,以及保护损伤后的神经元等生物学作用。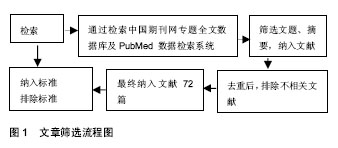
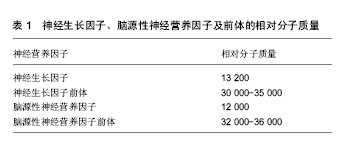
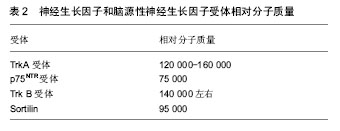
.jpg) 文题释义:
神经生长因子:是最早被发现的神经营养因子,主要来源于中枢神经系统、胎盘组织、唾液腺、前列腺、蛇毒腺以及脑内胆碱能神经元支配区,能促进神经元的存活与生长,保护损伤神经元,促进受损神经元的修复,其受体可被分为高亲和力受体Trk A和低亲和力受体p75NTR。
脑源性神经生长因子:是神经营养因子家族中第2个被发现的因子,主要分布在中枢神经系统,在海马和大脑皮质组织中含量最高,通过与高亲和受体TrkB结合发挥促进中枢神经系统和外周神经系统的神经元与胶质细胞的分化和存活、髓鞘形成、神经元迁移和轴突伸缩,以及保护损伤后的神经元等生物学作用。
文题释义:
神经生长因子:是最早被发现的神经营养因子,主要来源于中枢神经系统、胎盘组织、唾液腺、前列腺、蛇毒腺以及脑内胆碱能神经元支配区,能促进神经元的存活与生长,保护损伤神经元,促进受损神经元的修复,其受体可被分为高亲和力受体Trk A和低亲和力受体p75NTR。
脑源性神经生长因子:是神经营养因子家族中第2个被发现的因子,主要分布在中枢神经系统,在海马和大脑皮质组织中含量最高,通过与高亲和受体TrkB结合发挥促进中枢神经系统和外周神经系统的神经元与胶质细胞的分化和存活、髓鞘形成、神经元迁移和轴突伸缩,以及保护损伤后的神经元等生物学作用。