中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (19): 3039-3043.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0284
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
股骨头外移、上移及泪滴基线外移指数对成人髋臼发育不良的诊断价值:自身对照,诊断性试验及预试验结果
秦 迪,胡世伟,李会杰,何丽英,吴啸波,吴 涛,马文辉,韩永台
- 河北医科大学第三医院,河北省石家庄市 050051
Offshoring index, moving up index and teardrop baseline offshoring index of the femoral head for diagnosis of adult acetabular dysplasia: study protocol for a self-controlled, diagnostic trial and preliminary results
Qin Di, Hu Shi-wei, Li Hui-jie, He Li-ying, Wu Xiao-bo, Wu Tao, Ma Wen-hui, Han Yong-tai
- the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义:泪滴基线外移指数:即股骨头中心点与髋臼外上缘点分别到泪滴的垂直距离的比值×100%。
头臼指数:从股骨头内侧缘到髋臼外缘点的距离 A 与股骨头的横径 B 的比值,表示股骨头的大小与髋臼深度不相称的状态。
摘要
背景:髋臼发育不良患者常合并髋臼骨质增生、股骨头坏死,会使股骨头中心点位置发生改变,这样在使用骨盆X射线成像测量影像学诊断指标——中心边缘角、髋臼角、头臼指数时就会存在误差,从而影响髋臼发育不良诊断的准确性。
目的:试验提出了3种新的X射线指标测量方法,分别测量股骨头外移指数、上移指数、泪滴基线外移指数的变化,这些结果指标均用相对比值表示,可规避测量角度带来诊断成人髋臼发育不良导致的误差,以期对髋臼发育不良做出更准确的诊断。
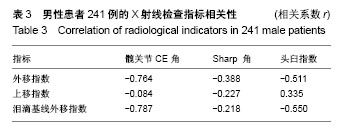
方法:试验在中国河北省,河北医科大学第三医院完成。纳入行骨盆正位X射线片检查的成人患者200例,男女各100例,采用Photoshop CS5软件对X射线图像进行健侧及患侧影像学指标测量及分析。试验的主要观察指标为股骨头外移指数对成人髋臼发育不良诊断的敏感度;次要观察指标为股骨头外移指数对成人髋臼发育不良诊断的特异度、阳性预测值、阴性预测值、阳性似然比、阴性似然比及诊断正确率,股骨头上移指数、泪滴基线外移指数对成人髋臼发育不良诊断的敏感度特异度,特异、阳性预测值、阴性预测值、阳性似然比、阴性似然比及诊断正确率,股骨头外移指数、上移指数、泪滴基线外移指数与中心边缘角、髋臼角、头臼指数的相关性,影响髋关节功能的危险因素Logistic回归分析结果。目前试验已得到241例骨盆正位X射线检查的男性患者的数据结果,显示患侧外移指数、上移指数、泪滴基线外移指数分别为(86.8±0.6)%,(75.8±2.0)%及(76.2±0.5)%,此3个指数与髋关节CE角、Sharp 角及头臼指数具有一定相关性。试验经中国河北医科大学第三医院伦理委员会批准(批准单位:河北医科大学第三医院,批准号:KE2016-011-1)。研究符合世界医学会制定的《赫尔辛基宣言》的要求。参与者对试验方案和过程均知情同意,并签署知情同意书。文章结果将以科学会议报告,或在同行评议的期刊上发表传播。试验已在中国临床试验注册中心注册(注册号:ChiCTR1800016375),注册方案版本号1.0。
讨论:试验结果旨在证实采用3种新的X射线指标(股骨头外移指数、上移指数、泪滴基线外移指数)的测量方法,与单纯指标测量中心边缘角、髋臼角,头臼指数相比较,可提高成人髋臼发育不良的诊断准确率,有效避免诊断误差。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: