| [1] Beamer GL, Turner J. Murine models of susceptibility to tuberculosis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2005;53(6): 469-483. [2] Zumla A, George A, Sharma V, et al. The WHO 2014 global tuberculosis report--further to go. Lancet Glob Health. 2015; 3(1):e10-12.[3] Rasouli MR, Mirkoohi M, Vaccaro AR, et al. Spinal tuberculosis: diagnosis and management. Asian Spine J. 2012;6(4):294-308.[4] 曹雪飞,甄平.载药磷酸钙骨水泥治疗结核性骨缺损[J].实用骨科杂2014,20(11):1009-1011.[5] Yuan J, Zhen P, Zhao HB, et al. The preliminary performance study of the 3D printing of a tricalcium phosphate scaffold for the loading of sustained release anti-tuberculosis drugs. J Mater Sci. 2015;50(5):2138-2147.[6] Langer R, Vacanti JP. Tissue Engineering. Science.1993; 260: 920-926.[7] 胡金龙.组织工程学技术治疗骨缺损的最新研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(2):150-153.[8] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.[9] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12): 4279-4295.[10] 王冠聪. 具有二级三维网络结构的壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石骨组织工 程复合支架材料的构建及其生物性能研究[D].济南:山东大学, 2012.[11] 李东亚,郑欣,邱旭升,等.新西兰兔桡骨骨缺损动物模型的制作[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(9):2012-2013.[12] 张屹,陈建常,史振满.异种骨支架及其衍生材料治疗骨缺损的研究现状与进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志志,2014,22(14): 1277-1279.[13] 邢文华,霍洪军,肖宇龙,等.不同植入物内固定修复胸腰段脊柱结核:后凸Cobb角及脊柱稳定性比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(13):2034-2039.[14] Liu J, Kerns DG. Mechanisms of guided bone regeneration: a review. Open Dent J. 2014;8:56-65.[15] 吴子征,李受珉,王泽,等.同种异体脂肪源性间充质干细胞复合β-磷酸三钙支架修复兔桡骨大段骨缺损[J].复旦学报:医学版,2015, 42(3):338-343.[16] 王贵玲,仇丽鸿,庞希宁.间充质干细胞的旁分泌作用及其在颅颌 面骨再生治疗中的应用研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2016, 9(6):373-378.[17] Liu G, Zhang Y, Liu B, et al. Bone regeneration in a canine cranial model using allogeneic adipose derived stem cells and coral scaffold. Biomaterials. 2013;34(11):2655-2664.[18] Kim BS, Park KE, Kim MH, et al. Effect of nanofiber content on bone regeneration of silk fibroin/poly(ε-caprolactone) nano/microfibrous composite scaffolds. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:485-502.[19] Seok H, Kim MK, Kim SG, et al. Comparison of silkworm-cocoon-derived silk membranes of two different thicknesses for guided bone regeneration. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(6):2066-2069.[20] Lindfors LT, Tervonen EA, Sándor GK, et al. Guided bone regeneration using a titanium-reinforced ePTFE membrane and particulate autogenous bone: the effect of smoking and membrane exposure. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(6):825-830.[21] Riggenbach MD, Jones GL, Bishop JY. Open reduction and internal fixation of clavicular nonunions with allograft bone substitute. Int J Shoulder Surg. 2011;5(3):61-67.[22] Mitchell JB, McIntosh K, Zvonic S, et al. Immunophenotype of human adipose-derived cells: temporal changes in stromal-associated and stem cell-associated markers. Stem Cells. 2006;24(2):376-385.[23] 梁求真,折胜利,宋兴华,等.体外构建抗结核骨组织工程复合体的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(19):1789-1796.[24] Tang ZB, Cao JK, Wen N, et al. Posterolateral spinal fusion with nano-hydroxyapatite-collagen/PLA composite and autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(4):325-336.[25] Lange C, Bruns H, Kluth D, et al. Hepatocytic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in cocultures with fetal liver cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(15):2394-2397.[26] 折胜利,罗兰,宋兴华,等. PLA/PLGA共聚物在组织工程中的应用[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2011,7(4):235-237.[27] 杨晓波,裴福兴,严永刚,等.聚氨基酸复合纳米羟基磷灰石的体内生 物相容性实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(21): 1809-1813.[28] Teixeira S, Fernandes H, Leusink A, et al. In vivo evaluation of highly macroporous ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93(2):567-575.[29] Khan SN, Tomin E, Lane JM. Clinical applications of bone graft substitutes. Orthop Clin North Am. 2000;31(3):389-398.[30] 李海建,龙志成,宋兴华,等HA/β-TCA复合材料与同种异体骨体外兔脂肪干细胞生物相容性的对比实验[J].新疆医科大学学报, 2015,38(8):949-953.[31] 刘正文,呼西旦,付明花,等.兔脊柱结核模型的构建[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(4):758-761. |
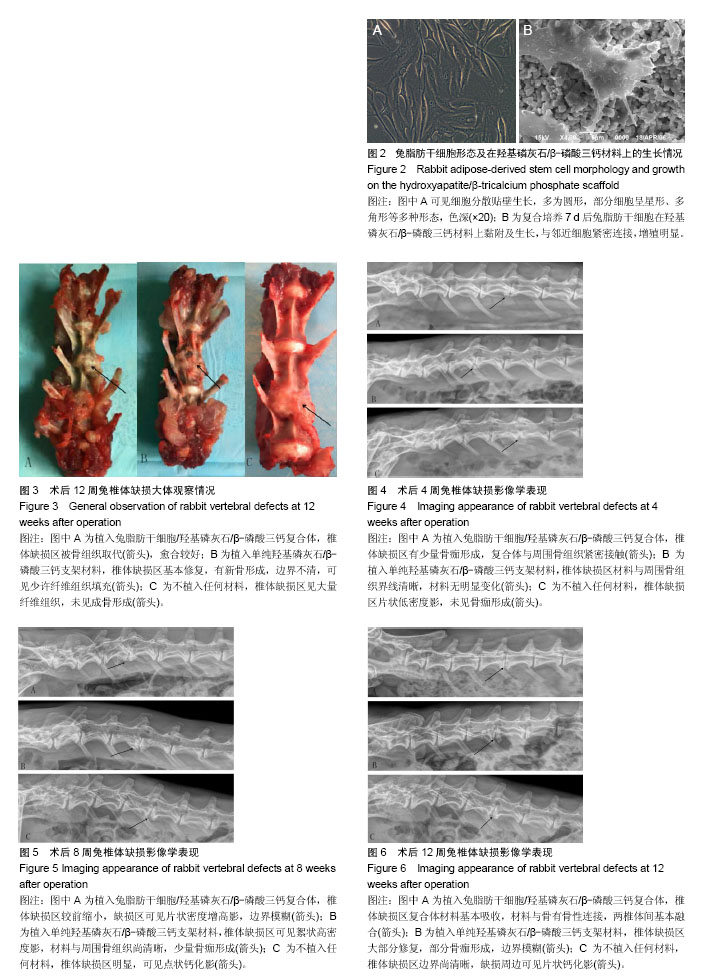
.jpg)
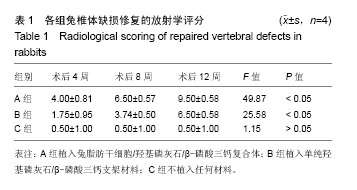
.jpg)
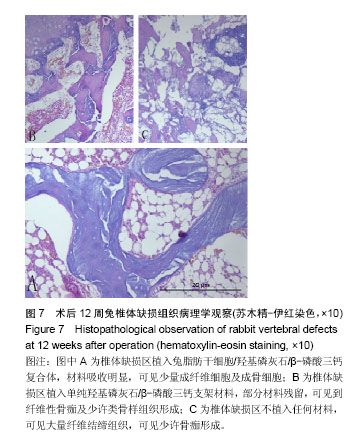
.jpg)