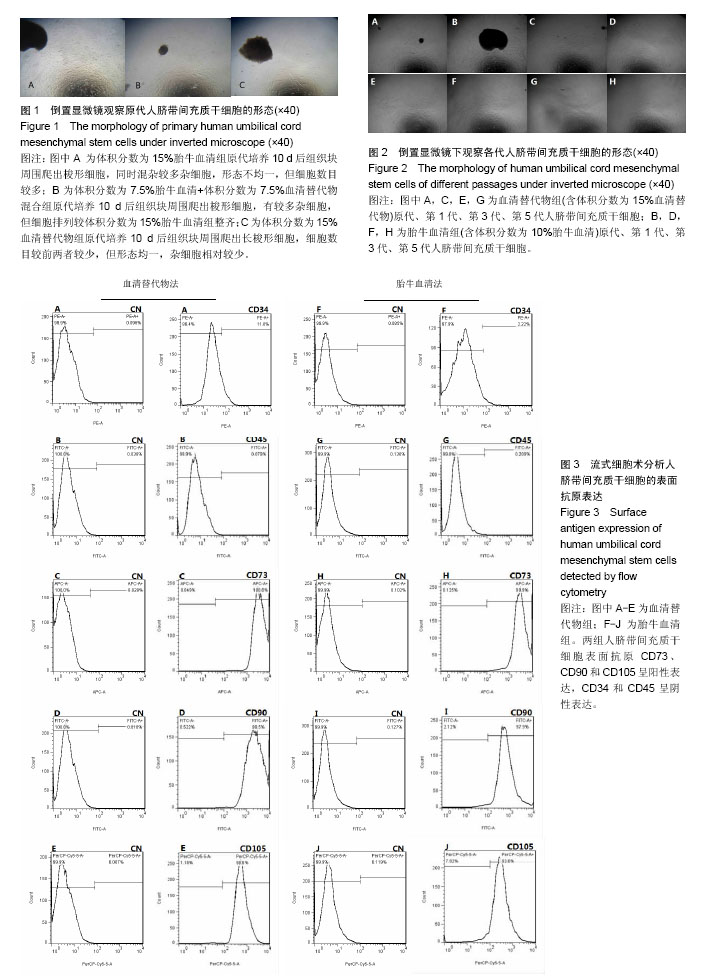
| [1] Friedenstein AJ, Gorskaja JF, Kulagina NN. Fibroblast precursors in normal and irradiated mouse hematopoietic organs. Exp Hematol. 1976;4(5):267-274.[2] Castrechini NM, Murthi P, Gude NM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in human placental chorionic villi reside in a vascular Niche. Placenta. 2010;31(3):203-212.[3] Corotchi MC, Popa MA, Remes A, et al. Isolation method and xeno-free culture conditions influence multipotent differentiation capacity of human Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(4):81.[4] Jin ES, Min J, Jeon SR, et al. Analysis of molecular expression in adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells : prospects for use in the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013;53(4):207-212.[5] Yang LM, Liu Y, Zhao J, et al. Characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells following tissue mass culture. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2014;60(1):12-18.[6] Gu F, Wang D, Zhang H, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for lupus nephritis patients refractory to conventional therapy. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33(11): 1611-1619.[7] Wang D, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in active and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicenter clinical study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R79.[8] Wang D, Zhang H, Liang J, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in severe and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: 4 years of experience. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(12):2267-2277.[9] Woodworth TG, Furst DE. Safety and feasibility of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in treatment-refractory systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis: time for a double-blind placebo-controlled trial to determine efficacy. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(4):113.[10] Sun L, Wang D, Liang J, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in severe and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(8):2467-2475. [11] Santos Nascimento D, Mosqueira D, Sousa LM, et al. Human umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate remodeling after myocardial infarction by proangiogenic, antiapoptotic, and endogenous cell-activation mechanisms. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):5.[12] Kong D, Zhuang X, Wang D, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transfusion ameliorated hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Lab. 2014;60(12):1969-1976.[13] Liu J, Han D, Wang Z, et al. Clinical analysis of the treatment of spinal cord injury with umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(2):185-191.[14] Wang S, Cheng H, Dai G, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation significantly improves neurological function in patients with sequelae of traumatic brain injury. Brain Res. 2013;1532:76-84.[15] Jiang Y, Zhu W, Zhu J, et al. Feasibility of delivering mesenchymal stem cells via catheter to the proximal end of the lesion artery in patients with stroke in the territory of the middle cerebral artery. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(12):2291-2298.[16] Lv YT, Zhang Y, Liu M, et al. Transplantation of human cord blood mononuclear cells and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in autism. J Transl Med. 2013;11: 196.[17] Buyl K, Vanhaecke T, Desmae T, et al. Evaluation of a new standardized enzymatic isolation protocol for human umbilical cord-derived stem cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2015;29(6):1254-1262.[18] Mori Y, Ohshimo J, Shimazu T, et al. Improved explant method to isolate umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their immunosuppressive properties. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015;21(4):367-372.[19] Iftimia-Mander A, Hourd P, Dainty R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell isolation from human umbilical cord tissue: understanding and minimizing variability in cell yield for process optimization. Biopreserv Biobank. 2013;11(5):291-298.[20] Medicinal and other products and human and animal transmissible spongiform encephalopathies: memorandum from a WHO meeting. Bull World Health Organ. 1997;75(6): 505-513.[21] Selvaggi TA, Walker RE, Fleisher TA. Development of antibodies to fetal calf serum with arthus-like reactions in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients given syngeneic lymphocyte infusions. Blood. 1997;89(3):776-779.[22] Spees JL, Gregory CA, Singh H, et al. Internalized antigens must be removed to prepare hypoimmunogenic mesenchymal stem cells for cell and gene therapy. Mol Ther. 2004;9(5):747-756.[23] Tuschong L, Soenen SL, Blaese RM, et al. Immune response to fetal calf serum by two adenosine deaminase-deficient patients after T cell gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 2002; 13(13):1605-1610.[24] Drach G, Maret A, Richard MF, et al. Transfer and induction of delayed hypersensitivity to methylated bovine serum albumin in the absence of adjuvant. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1977;284(23):2435-2437.[25] Kocaoemer A, Kern S, Klüter H, et al. Human AB serum and thrombin-activated platelet-rich plasma are suitable alternatives to fetal calf serum for the expansion of mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2007;25(5):1270-1278. [26] Ding Y, Yang H, Feng JB, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived MSC culture: the replacement of animal sera with human cord blood plasma. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2013;49(10):771-777.[27] Ma HY, Yao L, Yu YQ, et al. An effective and safe supplement for stem cells expansion ex vivo: cord blood serum. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(5):857-869.[28] Shetty P, Bharucha K, Tanavde V. Human umbilical cord blood serum can replace fetal bovine serum in the culture of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biol Int. 2007;31(3):293-298. [29] Murphy MB, Blashki D, Buchanan RM, et al. Adult and umbilical cord blood-derived platelet-rich plasma for mesenchymal stem cell proliferation, chemotaxis, and cryo-preservation. Biomaterials. 2012;33(21):5308-5316.[30] Schallmoser K, Bartmann C, Rohde E, et al. Human platelet lysate can replace fetal bovine serum for clinical-scale expansion of functional mesenchymal stromal cells. Transfusion. 2007;47(8):1436-1446.[31] Mohammadi S, Nikbakht M, Malek Mohammadi A, et al. Human Platelet Lysate as a Xeno Free Alternative of Fetal Bovine Serum for the In Vitro Expansion of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2016;10(3): 161-171.[32] Bieback K, Hecker A, Kocaömer A, et al. Human alternatives to fetal bovine serum for the expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2009;27(9):2331-2341.[33] Ng F, Boucher S, Koh S, et al. PDGF, TGF-beta, and FGF signaling is important for differentiation and growth of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): transcriptional profiling can identify markers and signaling pathways important in differentiation of MSCs into adipogenic, chondrogenic, and osteogenic lineages. Blood. 2008;112(2):295-307.[34] Liu ZZ, Chen P, Lu ZD, et al. Enrichment of breast cancer stem cells using a keratinocyte serum-free medium. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(18):2934-2936.[35] Huang D, Peng WJ, Ye Q, et al. Serum-Free Suspension Culture of MDCK Cells for Production of Influenza H1N1 Vaccines. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0141686.[36] O'Loughlin AJ, Woffindale CA, Wood MJ. Exosomes and the emerging field of exosome-based gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2012;12(4):262-274.[37] Qin J, Xu Q. Functions and application of exosomes. Acta Pol Pharm. 2014;71(4):537-543.[38] Wahlgren J, Statello L, Skogberg G, et al. Delivery of Small Interfering RNAs to Cells via Exosomes. Methods Mol Biol. 2016; 1364:105-125.[39] Lai RC, Chen TS, Lim SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosome: a novel stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular disease. Regen Med. 2011;6(4):481-492.[40] Phinney DG, Prockop DJ. Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair--current views. Stem Cells. 2007; 25(11):2896-2902.[41] Yu B, Zhang X, Li X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4142-4157.[42] Zhang B, Wu X, Zhang X, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance angiogenesis through the Wnt4/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(5):513-522.[43] Zhang B, Shen L, Shi H, et al. Exosomes from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Identification, Purification, and Biological Characteristics. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1929536.[44] Li T, Yan Y, Wang B, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6):845-854.[45] Zhou Y, Xu H, Xu W, et al. Exosomes released by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress and apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(2):34.[46] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[47] Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676. |
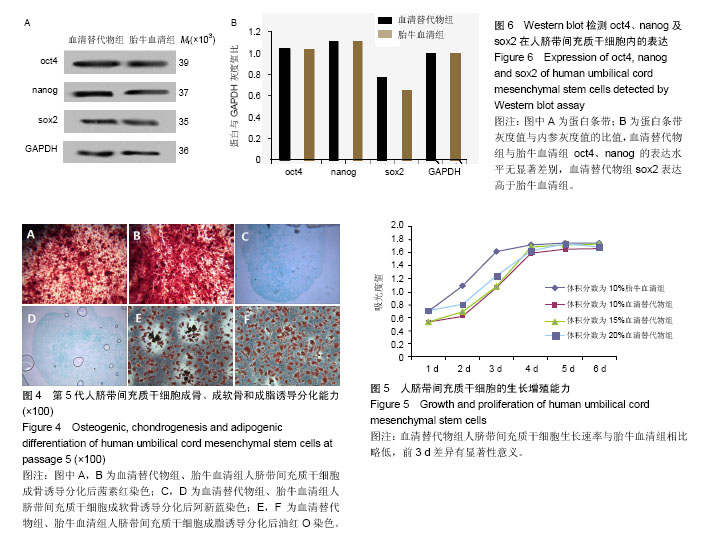
.jpg)
.jpg)