| [1] 傅崇辉,张玲华,李玉柱. 从第六次人口普查看中国人口生育变化的新特点[J]. 统计研究,2013,30(1):68-75.[2] Hagino H, Kishimoto H, Ohishi H, et al. Efficacy, tolerability and safety of once-monthly administration of 75mg risedronate in Japanese patients with involutional osteoporosis: a comparison with a 2.5mg once-daily dosage regimen. Bone.2014;59:44-52.[3] Khosla S, Hofbauer LC. Osteoporosis treatment: recent developments and ongoing challenges. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.2017;7: S2213-8587(17)30188-30182.[4] 李洁.阿仑膦酸钠治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的临床疗效及不良反应[J].临床合理用药杂志,2016,9(19):54-55.[5] 杨艳,李蓬秋,朱显军,等.重组人甲状旁腺激素(1-34)和依降钙素治疗原发性骨质疏松症的随机对照研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014, 20(2):137-141+155.[6] 王非,荆莉,石卫峰,等.抗骨质疏松药物的不良反应[J].药品评价, 2013,10(23):23-28.[7] 林雪源,欧阳国豪.鲑降钙素的临床应用及不良反应研究进展[J].中国实用医药,2011,6(33):244-245.[8] 苑文杰.雌激素替代疗法治疗妇女绝经后骨质疏松症疗效观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2011,20(32):4082-4083.[9] 刘月芬,尤琳,李恩泽,等.阿仑膦酸钠不良反应[J].中国误诊学杂志,2011,11(16):3804.[10] 余伯龙,李义凯.使用双膦酸盐类药物的不良反应[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(1):80-85.[11] Costa CR,Amorim BR,de Magalhaes P,et al.Effects of Plants on Osteogenic Differentiation and Mineralization of Periodontal Ligament Cells: A Systematic Review. Phytother Res.2016;30(4):519-531.[12] 赵晓玲,彭勇.中药防治骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国现代中药, 2012,14(8):16-20.[13] 杜贵友,曹春雨.中药治疗骨质疏松症实验研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2011,36(4):401-404.[14] 郭冰凌,李法琦.老年人骨质疏松症的药物治疗进展[J].重庆医学, 2014,43(33):4542-4544.[15] 严红梅,张振海,孙娥,等.中药治疗骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中草药,2014,45(8):1174-1178.[16] 郭杨,马勇.中医药治疗骨质疏松症的常用处方分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2010,16(7):188-191.[17] Gao F, Hu Y,Ye X, et al.Optimal extraction and fingerprint analysis of Cnidii fructus by accelerated solvent extraction and high performance liquid chromatographic analysis with photodiode array and mass spectrometry detections. Food Chem.2013;141(3):1962-1971.[18] Zhang ZR,Leung WN,Li G,et al.Osthole Enhances Osteogenesis in Osteoblasts by Elevating Transcription Factor Osterix via cAMP/CREB Signaling In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients.2017;9(6):588.[19] Li XX, Hara I,Matsumiya T.Effects of osthole on postmenopausal osteoporosis using ovariectomized rats; comparison to the effects of estradiol.Biol Pharm Bull.2002; 25(6):738-742.[20] Jia M,Li Y,Xin HL,et al.Estrogenic activity of osthole and imperatorin in MCF-7 cells and their osteoblastic effects in Saos-2 cells.Chin J Nat Med.2016;14(6):413-420.[21] Zhai YK,Pan YL,Niu YB,et al.The importance of the prenyl group in the activities of osthole in enhancing bone formation and inhibiting bone resorption in vitro. Intern J Endocrinol. 2014; 2014;(9):921954.[22] Ming LG,Zhou J,Cheng GZ, et al.Osthol, a coumarin isolated from common cnidium fruit, enhances the differentiation and maturation of osteoblasts in vitro. Pharmacology.2011;88(1-2):33-43.[23] Zhang W,Ma D,Zhao Q, et al.The effect of the major components of Fructus Cnidii on osteoblasts in vitro. J Acupunct Meridian Stud.2010;3(1):32-37.[24] Tang DZ, Hou W, Zhou Q, et al. Osthole stimulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation by activation of beta-catenin-BMP signaling.J Bone Miner Res.2010;25(6): 1234-1245.[25] Kuo PL, Hsu YL, Chang CH, et al. Osthole-mediated cell differentiation through bone morphogenetic protein-2/p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway in human osteoblast cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther.2005;314(3): 1290-1299.[26] An J, Yang H, Zhang Q, et al. Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis: The effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone formation. Life Sci.2016;147: 46-58.[27] Roussel BD, Kruppa AJ,Miranda E,et al.Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in neurological disease. The Lancet Neurol.2013;12(1):105-118.[28] Ryoo HD. Long and short (timeframe) of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death. FEBS J. 2016;283(20): 3718-3722. [29] Moreno JA, Tiffany-Castiglioni E. The chaperone Grp78 in protein folding disorders of the nervous system. Neurochem Res.2015;40(2):329-335.[30] Rao RV, Bredesen DE.Misfolded proteins, endoplasmic reticulum stress and neurodegeneration. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16(6):653-662.[31] Zhu G, Lee AS.Role of the unfolded protein response, GRP78 and GRP94 in organ homeostasis. J Cell Physiol. 2015; 230(7):1413-1420.[32] Okumura M, Kadokura H, Inaba K. Structures and functions of protein disulfide isomerase family members involved in proteostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum. Free Radic Biol Med.2015;83:314-322.[33] Kranz P,Neumann F,Wolf A,et al.PDI is an essential redox-sensitive activator of PERK during the unfolded protein response (UPR). Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(8):e2986.[34] Gutiérrez T, Simmen T.Endoplasmic reticulum chaperones and oxidoreductases: critical regulators of tumor cell survival and immunorecognition. Front Oncol. 2014;4:291.[35] Marciniak SJ, Yun CY, Oyadomari S,et al.CHOP induces death by promoting protein synthesis and oxidation in the stressed endoplasmic reticulum.Genes Dev.2004;18(24): 3066-3077.[36] Southwood CM,Garbern J,Jiang W, et al. The unfolded protein response modulates disease severity in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Neuron.2002;36(4):585-596.[37] Rozpedek W,Pytel D,Mucha B,et al.The Role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP Signaling Pathway in Tumor Progression During Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Curr mol med.2016;16(6):533-544.[38] Hiramatsu N,Kasai A,Hayakawa K,et al.Real-time detection and continuous monitoring of ER stress in vitro and in vivo by ES-TRAP: evidence for systemic, transient ER stress during endotoxemia.Nucleic acids Rre.2006;34(13):e93.[39] 王青,张云,毛红娇,等. 蛇床子素对TCP颗粒诱导小鼠颅骨溶解的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015,31(12):2265-2270. [40] Adler S, Pellizzer C, Paparella M, et al. The effects of solvents on embryonic stem cell differentiation. Toxicol In Vitro. 2006; 20(3):265-271.[41] Gardner BM,Pincus D,Gotthardt K,et al.Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensing in the unfolded protein response. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(3):a013169. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
内质网应激:是细胞在应激条件下做出的一系列适应性调节反应。内质网的能量供应不足或负荷过高会扰乱内质网的正常功能从而诱发内质网应激。适度的内质网应激有助于减轻细胞的损伤,但是持久或强烈的内质网应激会导致细胞凋亡。CHOP是内质网应激的标志性蛋白。
分子伴侣:是细胞质中一类蛋白,能够识别并结合不完全折叠或装配的蛋白质,帮助这些多肽正确折叠、转运或防止他们聚集,其本身不参与最终产物的形成。
文题释义:
内质网应激:是细胞在应激条件下做出的一系列适应性调节反应。内质网的能量供应不足或负荷过高会扰乱内质网的正常功能从而诱发内质网应激。适度的内质网应激有助于减轻细胞的损伤,但是持久或强烈的内质网应激会导致细胞凋亡。CHOP是内质网应激的标志性蛋白。
分子伴侣:是细胞质中一类蛋白,能够识别并结合不完全折叠或装配的蛋白质,帮助这些多肽正确折叠、转运或防止他们聚集,其本身不参与最终产物的形成。.jpg) 文题释义:
内质网应激:是细胞在应激条件下做出的一系列适应性调节反应。内质网的能量供应不足或负荷过高会扰乱内质网的正常功能从而诱发内质网应激。适度的内质网应激有助于减轻细胞的损伤,但是持久或强烈的内质网应激会导致细胞凋亡。CHOP是内质网应激的标志性蛋白。
分子伴侣:是细胞质中一类蛋白,能够识别并结合不完全折叠或装配的蛋白质,帮助这些多肽正确折叠、转运或防止他们聚集,其本身不参与最终产物的形成。
文题释义:
内质网应激:是细胞在应激条件下做出的一系列适应性调节反应。内质网的能量供应不足或负荷过高会扰乱内质网的正常功能从而诱发内质网应激。适度的内质网应激有助于减轻细胞的损伤,但是持久或强烈的内质网应激会导致细胞凋亡。CHOP是内质网应激的标志性蛋白。
分子伴侣:是细胞质中一类蛋白,能够识别并结合不完全折叠或装配的蛋白质,帮助这些多肽正确折叠、转运或防止他们聚集,其本身不参与最终产物的形成。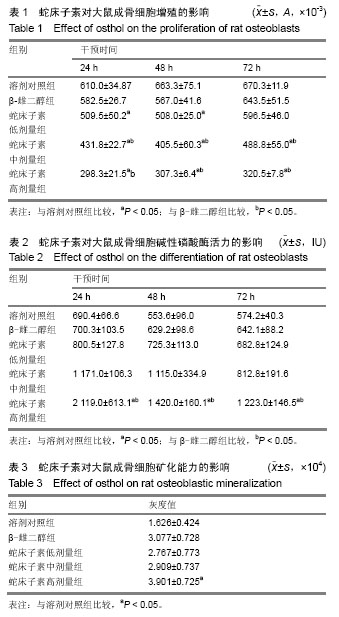
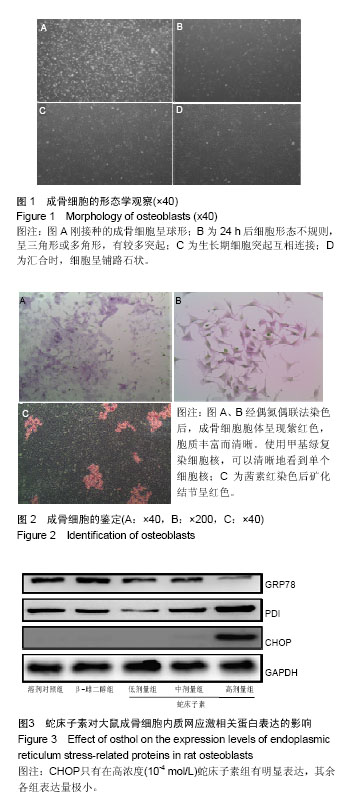
.jpg) 文题释义:
内质网应激:是细胞在应激条件下做出的一系列适应性调节反应。内质网的能量供应不足或负荷过高会扰乱内质网的正常功能从而诱发内质网应激。适度的内质网应激有助于减轻细胞的损伤,但是持久或强烈的内质网应激会导致细胞凋亡。CHOP是内质网应激的标志性蛋白。
分子伴侣:是细胞质中一类蛋白,能够识别并结合不完全折叠或装配的蛋白质,帮助这些多肽正确折叠、转运或防止他们聚集,其本身不参与最终产物的形成。
文题释义:
内质网应激:是细胞在应激条件下做出的一系列适应性调节反应。内质网的能量供应不足或负荷过高会扰乱内质网的正常功能从而诱发内质网应激。适度的内质网应激有助于减轻细胞的损伤,但是持久或强烈的内质网应激会导致细胞凋亡。CHOP是内质网应激的标志性蛋白。
分子伴侣:是细胞质中一类蛋白,能够识别并结合不完全折叠或装配的蛋白质,帮助这些多肽正确折叠、转运或防止他们聚集,其本身不参与最终产物的形成。