中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (36): 5741-5746.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.36.001
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 下一篇
不同浓度荨麻提取物对骨关节炎作用的差异
郑晓芬
- 深圳市龙华区人民医院,广东省深圳市 518109
Anti-osteoarthritis activity of urtica extracts at different concentrations
Zheng Xiao-fen
- Longhua People’s Hospital in Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518109, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
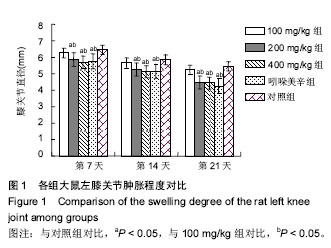
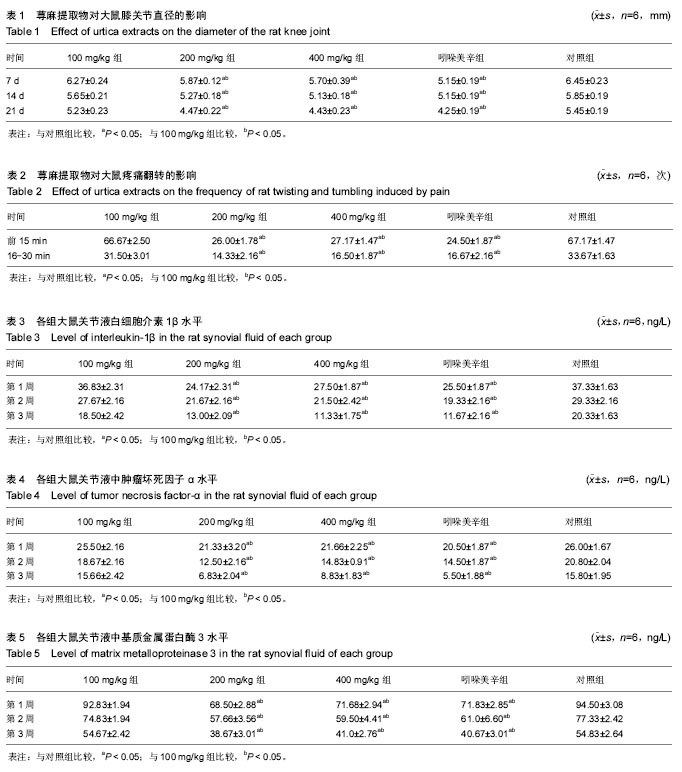
摘要 背景:荨麻作为一种传统中药,有抗炎、消肿和抗风湿作用,其对骨关节炎的效果目前尚未见相关研究。 目的:探讨不同浓度荨麻对骨关节炎的治疗效果及其机制。 方法:①取18只大鼠剔除表面部分毛,行皮肤刺激实验,分为液体石蜡组、荨麻组和甲醛组,每组6只,分别在大鼠皮肤上面涂石蜡、荨麻胶体和0.8%的甲醛,观察皮肤皮疹和红肿情况;②取30只大鼠,使用木瓜蛋白酶诱导法建立大鼠骨关节炎模型,根据荨麻提取物的浓度,实验分为100 mg/kg组、200 mg/kg组、400 mg/kg组和阳性对照组,每组6只,给药1,2,3周分别测定大鼠左膝关节直径,判断膝关节肿胀情况;用0.6%的醋酸溶液建立大鼠急性疼痛模型,分别给予不同浓度荨麻,对照组给予生理盐水;③对比观察大鼠翻滚及扭转次数,判断荨麻对大鼠止痛效果;给药后第1,2,3周分别用Elisa法测大鼠左膝关节的关节液中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和基质金属蛋白酶3的含量,检测大鼠关节炎症因子情况。 结果与结论:①荨麻作用于大鼠皮肤后,皮肤表面未见水肿及红疹;②质量浓度为200 mg/kg及400 mg/kg的荨麻与对照组相比能减少关节肿胀、其对关节肿胀的减轻作用和吲哚美辛相比无明显差别;③质量浓度200 mg/kg及400 mg/kg的荨麻能减轻大鼠痛疼,其减轻疼痛效果和吲哚美辛相当;④荨麻在质量浓度为200 mg/kg及400 mg/kg时,与对照组相比能减大少鼠关节液中炎症因子白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和基质金属蛋白酶3的含量;⑤结果表明,荨麻具有抗炎、止痛、消肿和抗骨关节炎的作用。
中图分类号:
.jpg)