| [1] Pogliacomi F, Schiavi P, Pedrazzini A, et al. Modified Mason type III and IV radial head fractures: results of different surgical treatments. Acta Biomed. 2015;86(3):242-250.[2] 李晓东,王玉海,孙国锋,等.第三代可吸收棒治疗成年人MasonⅡ-Ⅳ型桡骨头骨折的疗效探讨[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2014, 22(12):1072-1076.[3] Ertürer E, Seçkin F, Akman S, et al. The results of open reduction and screw or K-wire fixation for isolated type II radial head fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010; 44(1):20-26.[4] Kodde IF, Kaas L, Flipsen M, et al. Current concepts in the management of radial head fractures. World J Orthop. 2015;6(11):954-960.[5] Berry M. Bioresorbable composite materials for orthopaedic devices. Med Device Technol. 2008;19(5):69-70, 72.[6] 谢阳江,陈恩涛,吴波,等.生物可吸收材料在关节骨折内固定中的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(34):5076-5081.[7] Barber FA. Complications of Biodegradable Materials: Anchors and Interference Screws. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2015;23(3):149-155.[8] 任慧文,段炼,史小涛,等.可吸收内固定材料治疗关节周围骨折的手术技巧[J]. 中国老年学, 2016, 36(21):5388-5390.[9] Cusick MC, Bonnaig NS, Azar FM, et al. Accuracy and reliability of the Mayo Elbow Performance Score. J Hand Surg Am. 2014;39(6):1146-1150.[10] 王敏,平立原,王卫,等. MayoⅡB型尺骨鹰嘴粉碎骨折的手术治疗[J].中国骨伤, 2016, 29(2):184-186.[11] 魏素红,张建忠.桡骨小头内侧骨折成伤机制分析1例[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2009, 8(1):143-143.[12] Abdulla I, Langohr GD, Gladwell M, et al. The effect of fracture comminution on the reliability and accuracy of radial head sizing. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(3):364-368.[13] Pavi? R, Margeti? P, Hnatešen D. Diagnosis of occult radial head and neck fracture in adults. Injury. 2015;46(S6):119-124.[14] LZwingmann J , Bode G , Hammer T, et al. Radial head prosthesis after radial head and neck fractures-current literature and quality of evidence. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2015;82(3):177-185.[15] Schnetzke M , Aytac S , Deuss M, et al. Radial head prosthesis in complex elbow dislocations: effect of oversizing and comparison with ORIF. Int Orthop. 2014;38(11): 2295-2301.[16] Pogliacomi F, Schiavi P, Pedrazzini A, et al. Modified Mason type III and IV radial head fractures: results of different surgical treatments. Acta Biomed. 2015;86(3):242-250.[17] 宋晖,曾智,杨俊涛,等. 桡骨头损伤后应力传导有限元分析[J]. 医学临床研究, 2013, 30(5):978-981.[18] 曹洪邹海兵,张磊,等.克氏针经皮撬拨治疗JudetⅡ型桡骨颈骨折的临床效果观察[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2016, 13(6):55-57.[19] Kodde IF, Kaas L, Flipsen M, et al. Current concepts in the management of radial head fractures. World J Orthop. 2015; 6(11):954-960.[20] 云文科,王剑,曹磊光,等.可吸收钉与克氏针内固定治疗 MasonⅡ型桡骨小头骨折12例[J]. 武警医学, 2015, 26(5):511-512.[21] 王松,刘孟军,杨青山,等. 克氏针与钢板置入内固定修复老年桡骨远端骨折安全及有效性的 Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(9):1361-1368.[22] Kim JH , Nam DH. Losed reduction of displaced or dislocated mandibular condyle fractures in children using threaded Kirschner wire and external rubber traction. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;44(10):1255-1259.[23] 刘俊涛,王小勇,王畅,等. O'BrienⅡ型、Ⅲ型儿童桡骨近端骨折的治疗[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2016,22(1):53-54.[24] 刘长发,汪少春,姚亮, 等. 克氏针辅助外固定架与掌侧入路钢板内固定治疗AOC型桡骨远端骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016,31(7):770-771.[25] 王东建,张鑫,张延栋. 克氏针经皮固定治疗桡骨远端骨折[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2017,20(1):80-81.[26] 陈鹏,傅德皓. Herbert螺钉与钢板治疗Mason Ⅱ型桡骨小头骨折临床分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2015,21(2):160-162.[27] Elliott MJ, Slakey JB. CT provides precise size assessment of implanted titanium alloy pedicle screws. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(5):1605-1609.[28] 常小波,汤峰,王勤业,等. 手术内固定治疗MasonⅡ、Ⅲ型桡骨头骨折[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2017,23(1):63-65.[29] 尹爱民,黄建锋,杨述华. 桡骨头假体置换术与切开复位内固定术治疗MasonⅢ型桡骨头骨折的临床对比研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2016,15(10):944-948.[30] Katsoulis J, Mericske-Stern R, Rotkina L, et al. Precision of fit of implant-supported screw-retained 10-unit computer-aided-designed and computer-aided-manufactured frameworks made from zirconium dioxide and titanium: an in vitro study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25(2):165-174.[31] Pogliacomi F, Schiavi P, Pedrazzini A, et al. Modified Mason type III and IV radial head fractures: results of different surgical treatments. Acta Biomed. 2015;86(3):242-250.[32] 赵华国,马维虎,刘观燚.桡骨头骨折研究进展[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015, 30(9):1004-1006.[33] Santoshi JA , Chaware PN , Pakhare AP,et al. An Anatomical Study to Demonstrate the Proximity of Kirschner Wires to Structures at Risk in Percutaneous Pinning of Distal Radius Fractures. J Hand Microsurg. 2015;7(1):73-78.[34] 邢丹谋,勘武生,任东,等. 可吸收自身增强软骨钉治疗桡骨小头骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(1):50-54.[35] 王思成,张友忠,杨国庆,等. 可吸收棒与Herbert螺钉修复桡骨小头骨折:治疗效应及经济学的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(26):4153-4157.[36] 代杰志,柴益民. MasonⅢ型桡骨头骨折治疗研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2016,37(3):145-148.[37] Nestorson J, Josefsson PO, Adolfsson L. A radial head prosthesis appears to be unnecessary in Mason-IV fracture dislocation. Acta Orthop. 2017;88(3):315-319. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: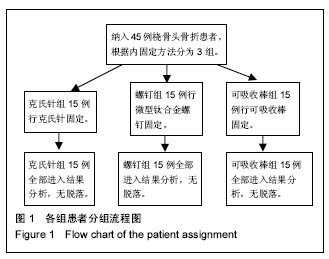
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: