| [1]Cain SA,Gohritz A,Fridén J, et al.Review of Upper Extremity Nerve Transfer in Cervical Spinal Cord Injury.J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj.2015;10(1):e34-e42.[2]Rogers WK,Todd M.Acute spinal cord injury.Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol.2016;30(1):27-39. [3]Finnegan J,Ye H.Cell therapy for spinal cord injury informed by electromagnetic waves.Regen Med.2016;11(7):675-691.[4]张伟,朱肖奇,张德才.过表达Shootin1的骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(50):7507-7517. [5]Yu WY,He DW.Current trends in spinal cord injury repair.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(18):3340-3344.[6]Misra K,Sabaawy HE.Minimally manipulated autologous adherent bone marrow cells (ABMCs): a promising cell therapyof spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res.2015;10(7): 1058-1060. [7]陈胜,金正帅.不同时期局部移植人脐带间充质干细胞修复脊髓损伤的组织学观察[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(45): 6714-6719.[8]屈一鸣,李波,王群波,等.甲基强的松龙影响脊髓损伤后内源性神经干细胞的迁移[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(36): 5419-5425.[9]Schomberg D,Miranpuri G,Duellman T,et al.Spinal cord injury induced neuropathic pain: Molecular targets and therapeutic approaches.Metab Brain Dis.2015;30(3):645-658. [10]Dumont CM,Margul DJ,Shea LD.Tissue Engineering Approaches to Modulate the Inflammatory Milieu following Spinal Cord Injury.Cells Tissues Organs. 2016;202(1-2): 52-66.[11]Ji WC,Zhang XW,Qiu YS.Selected suitable seed cell, scaffold and growth factor could maximize the repair effect using tissue engineering method in spinal cord injury.World J Exp Med.2016;6(3):58-62. [12]Bartlett RD,Choi D,Phillips JB.Biomechanical properties of the spinal cord: implications for tissue engineering and clinical translation.Regen Med.2016;11(7):659-673. [13]Li X,Yuan Z,Wei X,et al.Application potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMSCs) based tissue-engineeringfor spinal cord defect repair in rat fetuses with spina bifida aperta. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2016;27(4):77. [14]Yang W,Yang Y,Yang JY,et al.Treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with plumbagin alleviates spinal cord injury by affecting oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptotis and the activation of the Nrf2 pathway.Int J Mol Med.2016;37(4):1075-1082. [15]周雪峰,任志午,陆明,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在节段性神经损伤局部微环境中的迁移和转归[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(28): 4465-4471. [16]Wang Z,Fang B,Tan Z,et al.Hypoxic preconditioning increases the protective effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cellson spinal cordischemia/reperfusion injury.Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3):1953-1960. [17]王月福,于锡欣.骨髓间充质干细胞在微损伤环境中修复骨不连[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(41):6677-6682. [18]Aras Y,Sabanci PA,Kabatas S,et al.The Effects of AdiposeTissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation During the Acute and Subacute Phases Following Spinal Cord Injury.Turk Neurosurg. 2016;26(1): 127-139.[19]张静,詹琪,黄艳.磁场对骨髓间充质干细胞分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(23):3744-3749. [20]Hur JW,Cho TH,Park DH,et al.Intrathecal transplantation ofautologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treatingspinal cord injury: A human trial.J Spinal Cord Med. 2016;39(6):655-664.[21]羊书勇,杜敏,郑维银,等.大鼠脂肪干细胞诱导培养成为神经细胞并鉴定的实验研究[J].西南国防医药, 2016,26(4):349-353.[22]Zhao Y,Jiang H,Liu XW,et al.Neurogenic differentiation from adipose-derived stem cells and application for autologous transplantation in spinal cord injury.Cell Tissue Bank. 2015; 16(3):335-342. [23]Nowotny J,Aibibu D,Farack J,et al.Novel fiber-based pure chitosanscaffold for tendon augmentation: biomechanical and cell biological evaluation.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2016; 27(10):917-936. [24]Zakhem E,Bitar KN.Development of Chitosan Scaffolds with Enhanced Mechanical Properties for Intestinal Tissue Engineering Applications.J Funct Biomater. 2015;6(4): 999-1011.[25]Vázquez N,Chacón M,Meana Á,et al.Keratin-chitosan membranes as scaffoldfor tissue engineering of human cornea.Histol Histopathol.2015;30(7):813-821.[26]薛震,牛丽媛,安刚,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/半水硫酸钙为可注射骨组织工程支架材料的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(8):1160-1164. [27]莫弼凡,莫碧文.重结晶法制备壳聚糖/磷酸三钙组织工程支架及性能研究[J].中外医学研究,2014,12(20):3-5. [28]Kühn PT,Meijer TL,Schiavon I,et al.Non-Covalently Stabilized AlginateHydrogels as Functional Cell Scaffold Material. Macromol Biosci.2016;16(11):1693-1702. |
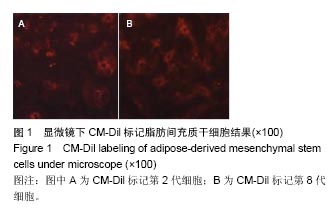
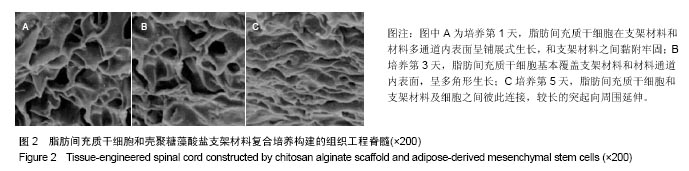
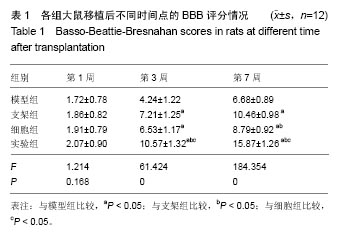
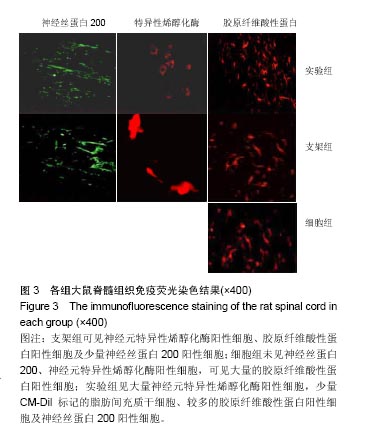
.jpg)
.jpg)