| [1] 李振伟,向阳明.生物力学评价颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉植入骨质疏松椎骨内的稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(35): 5718-5722.
[2] 周章彦,朱轶,连福明,等.颈后路椎弓根钉技术治疗寰枢椎创伤性失稳[J].中国医师杂志,2012,14(3):342-343.
[3] 赵刘军,徐荣明,马维虎,等.下颈椎损伤前路椎弓根螺钉固定的初步临床运用[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,28(9):780-784.
[4] Wu AM, Wang XY, Chi YL, et al. Management of acute combination atlas-axis fractures with percutaneous triple anterior screw fixation in elderly patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(8):894-899.
[5] 赵刘军,李杰,蒋伟宇,等.下颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉固定系统与普通前路椎体螺钉固定系统的静力学比较[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(2):118-122.
[6] Meyer D, Meyer F, Kretschmer T, et al. anslaminar screws of the axis: an alternative technique for rigid screw fixation in upper cervical spine instability. Neurosurg Rev. 2012;35(2):255-261.
[7] 李菊根,黄彦,杨进顺,等.寰枢椎后路短节段个体化内固定治疗上颈椎损伤[J].中华创伤杂志,2013,29(6):519-522.
[8] Gupta P, Kumar A, Gamangatti S. Mechanism and patterns of cervical spine fractures-dislocations in vertebral artery injury. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2012;3(1):11-15.
[9] Wang L, Xia T, Dong S, et al. Surgical treatment of complex axisfractures with adjacent segment instability. J Clin Neurosci. 2012;19(3):380-387.
[10] Tomaszewski R, Pyzińska M. Treatment of cervical spine fractureswith halo vest method in children and young people. OrtopTraumatol Rehabil. 2014;16(5):449-454.
[11] Li X, Song QS, Wang JY, et al. Simvastatin induces estro-gen receptor-alpha expression in bone, restores bone loss, and decreases ERα expression and uterine wet weight inovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Metab. 2011;29(4):396-403.
[12] Kato S, Hozumi T, Yamakawa K, et al. META: an MRI-based scoring system differentiating metastatic from osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Spine J. 2015; 15(7):1563-1570.
[13] 朱晓文,陈建庭.狄诺塞麦对低骨量妇女腰椎骨密度的影响及其安全性的 meta 分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2013, 33(6):913-917.
[14] Eschler A, Ender SA, Schiml K, et al. Bony healing of unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures in the elderly using percutaneously applied titanium mesh cages and a transpedicular fixation system with expandable screws. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0117122.
[15] 唐晓明,戴健,朱国太,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎体成形治疗高龄骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(47):7545-7549.
[16] Landham PR, Baker-Rand HL, Gilbert SJ, et al. Is kyphoplasty better than vertebroplasty at restoring form and function after severe vertebral wedge fractures? Spine J. 2015;15(4):721-732.
[17] Niu JJ, Shen MJ, Meng B, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures with neurological deficit: radicular pain can mimic disc herniation. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(8):2360-2364.
[18] 陈作喜,黄义星,黄皆和,等.颈胸段前路内固定器械的相关 MRI影像解剖学研究[J].温州医学院学报,2013,43(11): 701-705.
[19] 徐彦芳,孙进,周初松,等.全内置式可膨胀型脊柱前路内固定系统研制的解剖学基础[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(3): 352-354.
[20] Chen LX, Li YL, Ning GZ, et al. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of three treatments in old people with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a network meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS One. 2015; 10(4):e0123153.
[21] 丁真奇,胡生庭,康两期,等.新型胸腰椎前路内固定系统的设计与生物力学研究[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2013, 19(1):28-31.
[22] Edidin AA, Ong KL, Lau E, et al. Morbidity and Mortality After Vertebral Fractures: comparison of vertebral augmentation and nonoperative management in the medicare population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(15):1228-1241.
[23] 程云为.经椎弓根固定结合伤椎椎体内植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2012,11(8): 606-607.
[24] 路磊,陈鹏.腰椎爆裂性骨折腹腔镜辅助下前路小切口内固定技术 11 例疗效分析[J].浙江创伤外科,2014,19(1): 126-127.
[25] Xiao H, Yang J, Feng X, et al. Comparing complications of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of the randomized and non-randomized controlled studies. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25 Suppl 1:S77-S85.
[26] 李杰,赵刘军,徐荣明,等.下颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉内固定技术的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(10):873-877.
[27] 沈源彬,关宏刚,陈苑妮,等.Iso-C 3D导航系统下椎弓根钉内固定治疗颈椎骨折脱位[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012, 20(14):1278-1281.
[28] 黄晓楠,张勇.三种方式置入植入物修复腰椎爆裂性骨折后的骨性融合及矫正度和功能恢复[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(22):3498-3503.
[29] He S, Lin L, Tang X, et al. The treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar severe burst fractures with short pedicle screw fixation and vertebroplasty. Acta Orthop Belg. 2014;80(4):93-500. |
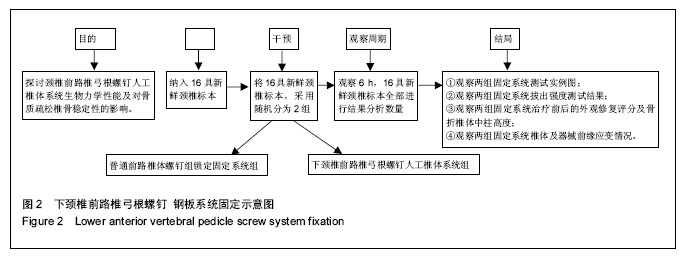
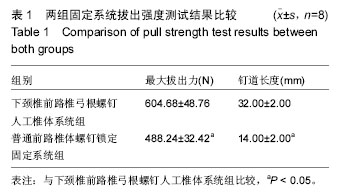
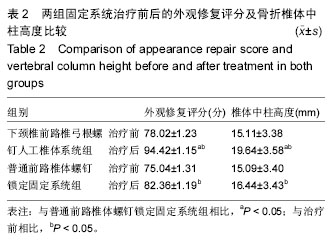
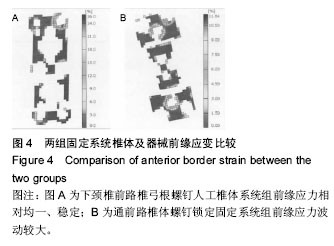
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)