| [1] 舒文,王栋栋,陈凯,等.微创经皮锁定钢板与髓内钉治疗胫骨下段骨折的疗效观察[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2016,13(2):37-39.
[2] Gülabi D,Bekler H,Sa?lam F,et al.Surgical treatment of distal tibia fractures: open versus MIPO.Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg.2016;22(1):52-57.
[3] Van den Berg J,Monteban P,Roobroeck M,et al.Functional outcome and general health status after treatment of AO type 43 distal tibial fractures. Injury.2016.doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.04.009
[4] 梁博伟,赵劲民,殷国前,等.经皮微创钢板固定治疗胫骨下段骨折:与髓内钉固定和切开复位钢板内固定的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3116-3120.
[5] Lakhotia D,Sharma G,Khatri K,et al.Minimally invasive osteosynthesis of distal tibial fractures using anterolateral locking plate: Evaluation of results and complications.Chin J Traumatol.2016;19(1):39-44.
[6] Vidovic D,Matejcic A,Ivica M,et al.Minimally-invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibial fractures: Results and complications.Injury.2015;46 Suppl 6:S96-99.
[7] Mao Z,Wang G,Zhang L,et al.Intramedullary nailing versus plating for distal tibia fractures without articular involvement: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res.2015;10:95.
[8] Li B,Yang Y,Jiang LS.Plate fixation versus intramedullary nailing for displaced extra-articular distal tibia fractures: a system review.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(1):53-63.
[9] Gustilo RB,Merkow RL,Templeman D.Current concepts in the management of open fractures.Instr Course Lect.1987;36:359-366.
[10] Johner R,Wruh O.Classification of tibia shaft fractures and correlation with results after rigid fixation.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1983;178:7-25.
[11] Merianos,cambouridis P,Smyrnis P.The treatment of 143 tibia shaft fractures by Ender’s nailing and early weight bearing.J Bone Joint surg (Br).1985;67(4): 576-580.
[12] 王志伟,吴岳嵩,纪方,等.矩形髓内钉治疗胫腓骨远端骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,1999,15(6):820-821.
[13] 秦煜,Henry DeGroot III.极远端胫骨交锁髓内钉结合阻挡螺钉技术微创治疗胫骨远端骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(9):835-837.
[14] 姬洪全,周方,张志山,等.单臂外固定架和锁定加压钛板治疗胫骨远端骨折的比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008, 10(5):417-420.
[15] Richmond J,Colleran K,Borens O,et al. Nonunions of the distal tibia treated by reamed intramedullary nailing.J Orthop Trauma.2004;18(9):603-610.
[16] 李增炎,张英泽,闰金成.阻挡钉加强交锁髓内钉固定长骨干髓端骨折的疗效观察[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2003, 18(7): 484-485.
[17] Krettek C,Stepah C,Schandelmaier P,et al.The use of Poller screws as blocking screws in stabilizing tibial fractures treated with small diameter nails.JBJS(Br). 1999;81(6):963-968.
[18] Krettek C,Miclau T,Schandelmaier P,et al.The mechanical effect of blocking screws ("Poller screws") in stabilizing tibia fractures with short proximal or distal fragments after insertion of small-diameter intramedullary nails.J Orthop Trauma.1999;13(8): 550-553.
[19] Seyhan M ,Cakmak S,Donmez F,et al.Blocking screws for the treatment of distal femur fractures.Orthopedics.2013;36(7):e936-941.
[20] Zhu HB,Wu LG,Fang ZS,et al.Clinical application of blocking screws and rooting technique in the treatment of distal tibial fracture with interlocking intramedullary nail.Zhongguo Gu Shang.2012;25(7):569-571.
[21] Chan DS,Nayak AN,Blaisdell G,et al.Effect of distal interlocking screw number and position after intramedullary nailing of distal tibial fractures: a biomechanical study simulating immediate weight-bearing. J Orthop Trauma.2015;29(2):98-104.
[22] 王秋根,高堪达,高伟,等.下肢髓内钉术后非感染性骨不连的对策:内植骨结合阻挡钉技术[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2008,16(14):1045-1047.
[23] Stedtfeld HW,Thomas M,Peter L,et al.The logic and clinical applications of blocking screws.J Bone Joint Surg(Am).2004;86:17-25.
[24] Guthrie HC,Bellringer SF,Nicol S.Fine-tuning of blocking screws in long bone nailing.Ann R Coll Surg Engl.2015;97(3):240-241.
[25] Wang L,Fan M,Liu C,et al.Observation of curative effect in treatment of distal tibial fractures with minimall invasive percutaneous technique.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.2015;95(35):2865-2867.
[26] Muzaffar N,Bhat R,Yasin M.Plate on plate technique of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis in distal tibial fractures, an easy and inexpensive method of fracture fixation.Arch Trauma Res.2014;3(3): e18325.
[27] Rijal L,Sagar G,Mani K,et al.Minimizing radiation and incision in minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) of distal tibial fractures.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2013;23(3):361-365.
[28] Tong DK,Ji F,Cai XB.Locking internal fixator withminimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for the proximaland distal tibial fractures.Chin J Traumatol. 2011;14(43):233-236.
[29] Ahmad MA,Sivaraman A,Zia A,et al.Percutaneous locking plates for fractures of the distal tibia: our experience and a review of the literature.J Trauma Acute Care Surg.2012;72(2):E81-E87.
[30] Hannah A,Aboelmagd T,Yip G,et al.A novel technique for accurate Poller (blocking) screw placement. Injury. 2014;45(6):1011-1014. |
.jpg)
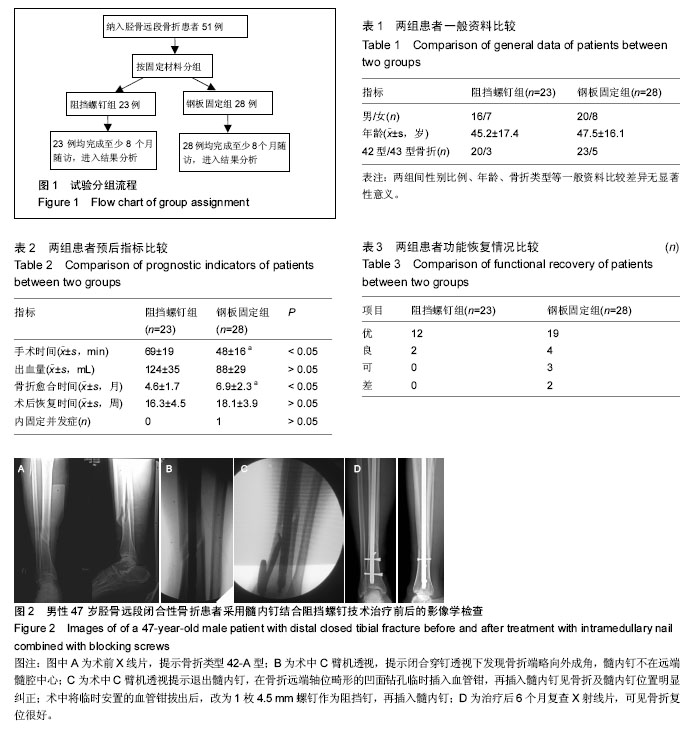
.jpg)