| [1] Wood ML,Kelley SS.Cement supplementation as a treatment for osteonecrosis. Curr Opin Orthop. 2003; 14:23-29.[2] 方志,陈曦,刘树平.髓芯减压结合自体皮质支撑骨及松质颗粒骨植骨治疗成人股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(3):266-269.[3] Fu K, Xu Q,Czernuszka J,et al. Prolonged osteogenesis from human mesenchymal stem cells implanted in immunodeficient mice by using coralline hydroxyapatite incorporating rhBMP2 microspheres.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;92(4):1256-6124.[4] 付昆,孟志斌,邵增务,等.表面置换珊瑚羟基磷灰石的表征及结构分析[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2008,11(21):3126-3129.[5] Erwin WM,Ashman K,O'Donnel P,et al.Nucleus pulposus notochord cells secrete connective tissue growth factor and up-regulate proteoglycan expression by intervertebral disc chondrocytes.Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(12):3859-3867.[6] 中华医学会骨科分会显微修复学组.成人股骨头坏死诊疗标准专家共识(2012年版)[J].中华骨科杂志, 2012, 32(6):606-609.[7] 王程,徐小龙,袁雪,等.人股骨头坏死微观结构及成骨、破骨细胞活性的区域性分布特征[J].中华骨科杂志, 2014, 34(4):417-424.[8] Thiel GSV,Mather RC.The Treatment of Osteonecrosis in the Hip.Oper Techn Sports Med. 2015;23(3):222-230.[9] Aarvold A,Smith JO,Tayton ER,et al.A tissue engineering strategy for the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head.Surgeon. 2013;11(6): 319-325.[10] Huang G,Chen HY,Liu ZX,et al.Effect of percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2010; 30(12):2729-2732.[11] Molina GS,Campero A,Feito R,et al.Kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures (VCF) : procedure description and analysis of the outcomes in 128 patients.Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2011;108:163-170.[12] Chen G,Luo ZP,Zhang H,et al.Percutaneous kyphoplasty in the treatment of painful osteoblastic metastatic spinal lesions.J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20(7): 948-950. [13] Kolk A,Handschel J,Drescher W,et al.Current trends and future perspectives of bone substitute materials - from space holders to innovative biomaterials.J Craniomaxillofac Surg.2012;40(8):706-718.[14] Fu K,Xu Q,Czernuszka J,et al.Prolonged osteogenesis from human mesenchymal stem cells implanted in immunodeficient mice by using coralline hydroxyapatite incorporating rhBMP2 microspheres.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;92(4):1256-1264.[15] Zafranskaya MM,Nizheharodova DB,Yurkevich MY,et al.In vitro assessment of mesenchymal stem cells immunosuppressive potential in multiple sclerosis patients.Immunol Lett.2013;149(1-2):9-18. [16] Fukui K,Kaneuji A,Matsumoto T.Occult fracture of the femoral neck associated with extensive osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;14:136-140.[17] Carli A,Albers A,Séguin C,et al.The Medical and Surgical Treatment of ARCO Stage-I and II Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head.A Critical Analysis Review.JBJS Rev.2014;2(2):135-138.[18] Hausdorf J,Lutz A,Mayer-Wagner S,et al.Shock wave therapy for femoral head necrosis-Pressure measurements inside the femoralhead.J Biomech. 2010;43:2065-2069.[19] Yang S,Wu X,Xu W,et al.Structural augmentation with biomaterial-loaded allograft threaded cage for the treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis.J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(8):1223-1230.[20] Song HJ,Lan BS,Cheng B,et al.Treatment of early avascular necrosis of femoral head by small intestinal submucosal matrix with peripheral blood stem cells. Transplant Proc. 2011;43(5):2027-2032. [21] 杨静,康鹏,德沈彬,等.小孔径多通道髓芯钻孔减压治疗早中期股骨头坏死[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(1):58-61.[22] Rothenberg SS.Developing neonatal minimally invasive surgery: Innovation, techniques, and helping an industry to change.J Pediatr Surg. 2015;50(2):232-235.[23] Gomes-da-Silveira GG,Cidade PR,Dibi R.TTT – A Systematic Management Model for Development of Minimally Invasive Surgery.J Minim Invas Gyn. 2014; 21(6):120-S120. |
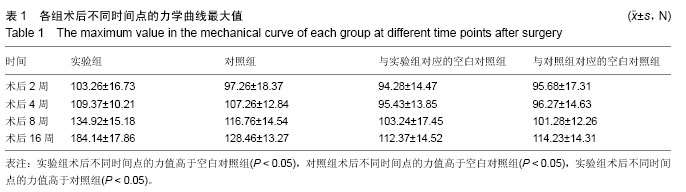
.jpg)
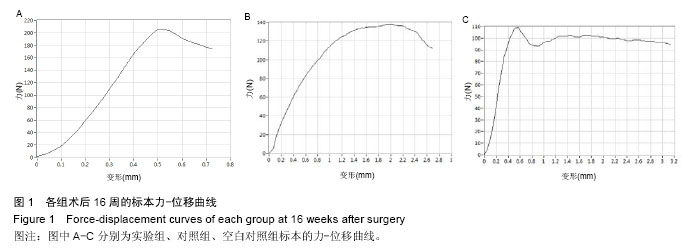
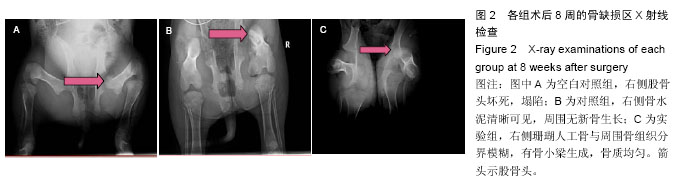
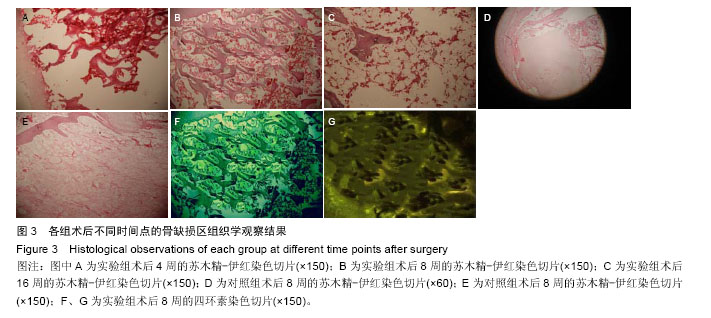
.jpg)
.jpg)