中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (48): 7747-7751.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.48.007
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
零切迹颈前路融合钢板(Zero-P)在颈椎前路减压植骨融合内固定中的应用
程俊杰,代 杰,马 原,田慧中
- 新疆医科大学第六附属医院脊柱外一科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830002
The clinical application of zero notch anterior cervical fusion plate (Zero-P) on anterior cervical decompression and bone fusion
Cheng Jun-jie, Dai Jie, Ma Yuan, Tian Hui-zhong
- First Department of Spine Surgery, the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
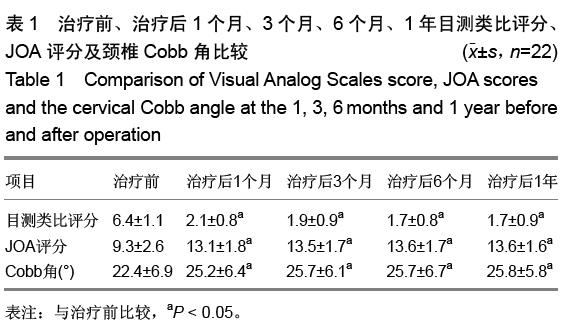
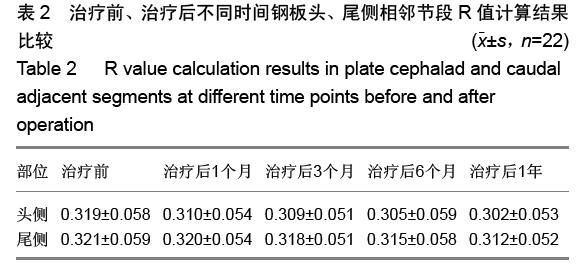
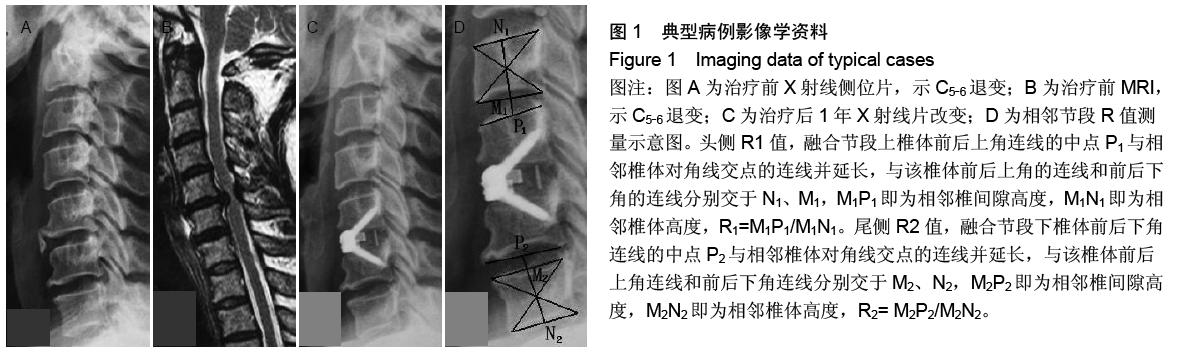
背景:近年来,内固定系统和技术不断改进,行颈椎前路减压植骨的同时行前路钢板内固定已被大多数学者所接受,但与之有关的并发症也不断出现。鉴于此,零切迹椎间植骨融合钢板(Zero-P)被批准应用于临床治疗颈椎退行性疾病。 目的:探讨Zero-P在颈椎前路减压植骨融合内固定中的早期应用效果。 方法:2014年2至12月采用零切迹颈前路融合钢板对22例颈椎病患者行颈椎前路减压植骨融合内固定治疗。C3-4,C4-5,C5-6分别置入Zero-P为1,3,18枚。治疗后应用目测类比评分和JOA评分来评价疼痛及神经功能改善情况,并拍摄颈椎正侧位及过伸过屈侧位线片,根据测量治疗后颈椎侧位X射线片上钢板头、尾侧相邻椎间隙与椎体高度的比值(R)及相邻节段骨质增生情况来判断相邻节段退变情况。根据治疗后伸屈侧位X射线片观察手术间隙有无异常活动。 结果与结论:22例患者随访10-28个月,2例患者分别于治疗后第4天和第5天出现吞咽困难(均为轻度),均于治疗后2周内症状消失。所有患者治疗后的目测类比评分均低于治疗前(P < 0.05),JOA评分均高于治疗前(P < 0.05),颈椎Cobb角均大于治疗前(P < 0.05),治疗后不同时间点的目测类比评分、JOA 评分和颈椎Cobb角差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。钢板头侧相邻椎间隙中3例(均为1级)椎体出现骨质增生,尾侧有1例(1级)出现;头、尾两侧骨质增生差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。头、尾侧R值治疗前后差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),随访期间手术间隙无异常活动, 内置物无移位。提示Zero-P修复单节段椎间盘病变效果显著,能有效改善颈椎曲度,建立良好的颈椎稳定性,治疗后吞咽困难发生率低,早期不增加相邻节段的退变。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
.jpg)