| [1] Chen XY, Hao YR, Wang Z, et al. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on aggrecan and type II collagen expression in rat articular chondrocytes. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(11):3359-3364.
[2] Yamairi F, Utsumi H, Ono Y, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) associated with histopathological changes in rodent models of osteoarthritis. J Toxicol Pathol. 2011;24(2):137-142.
[3] Yudoh K, Shi Y, Karasawa R. Angiogenic growth factors inhibit chondrocyte ageing in osteoarthritis: potential involvement of catabolic stress-induced overexpression of caveolin-1 in cellular ageing. Int J Rheum Dis. 2009;12(2): 90-99.
[4] 李雪峰,宋雄英,甄志强,等.关节炎患者血管内皮生长因子的检测及其临床意义[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(7):615-617.
[5] Bonnet CS, Walsh DA. Osteoarthritis, angiogenesis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44(1):7-16.
[6] Lingaraj K, Poh CK, Wang W. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is expressed during articular cartilage growth and re-expressed in osteoarthritis. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2010;39(5):399-403.
[7] Landry JP, Fei Y, Zhu X, et al. Discovering small molecule ligands of vascular endothelial growth factor that block VEGF-KDR binding using label-free microarray-based assays. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2013;11(5):326-332.
[8] Cramer T, Schipani E, Johnson RS, et al. Expression of VEGF isoforms by epiphyseal chondrocytes during low-oxygen tension is HIF-1 alpha dependent. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(6):433-439.
[9] Enomoto H, Inoki I, Komiya K, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms and their receptors are expressed in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Am J Pathol. 2003;162(1): 171-181.
[10] Murphy CL. HIF-2alpha--a mediator of osteoarthritis? Cell Res. 2010;20(9):977-979.
[11] Pfander D, Körtje D, Zimmermann R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in articular cartilage of healthy and osteoarthritic human knee joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001; 60(11):1070-1073.
[12] Enomoto H, Inoki I, Komiya K, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms and their receptors are expressed in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Am J Pathol. 2003;162(1): 171-181.
[13] 邱波,陈宣银,周建林.骨关节炎软骨中血管内皮生长因子mRNA表达[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2011,32(1): 52-55.
[14] Yano K, Brown LF, Detmar M. Control of hair growth and follicle size by VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2001;107(4):409-417.
[15] 陈勇,周正炎,季振威.组织修复中血管内皮生长因子作用及应用的研究进展[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2003,24(4):285-287.
[16] Knudsen LS, Hetland ML, Johansen JS, et al. Changes in plasma IL-6, plasma VEGF and serum YKL-40 during treatment with etanercept and methotrexate or etanercept alone in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate therapy. Biomark Insights. 2009;4:91-95.
[17] Maeda K, Chung YS, Ogawa Y, et al. Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1996;77(5):858-863.
[18] Amarilio R, Viukov SV, Sharir A, et al. HIF1alpha regulation of Sox9 is necessary to maintain differentiation of hypoxic prechondrogenic cells during early skeletogenesis. Development. 2007;134(21):3917-3928.
[19] Ray BK, Shakya A, Ray A. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in arthritic joint is regulated by SAF-1 transcription factor. J Immunol. 2007;178(3):1774-1782.
[20] Tibesku CO, Daniilidis K, Skwara A, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor on chondrocytes increases with osteoarthritis - an animal experimental investigation. Open Orthop J. 2011;5:177-180.
[21] Okubo M, Kimura T, Fujita Y, et al. Semaphorin 3A is expressed in human osteoarthritic cartilage and antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor 165-promoted chondrocyte migration: an implication for chondrocyte cloning. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(10):3000-3009.
[22] Mohan S, Baylink DJ. Bone growth factors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(263):30-48.
[23] 王松,张睨,陈国庆,等.骨质疏松骨折愈合中软骨细胞凋亡与血管内皮生长因子的表达[J].解剖学杂志,2004,27(2):162-165.
[24] Kim WU, Kang SS, Yoo SA, et al. Interaction of vascular endothelial growth factor 165 with neuropilin-1 protects rheumatoid synoviocytes from apoptotic death by regulating Bcl-2 expression and Bax translocation. J Immunol. 2006; 177(8):5727-5735.
[25] Surendran S, Kim SH, Jee BK, et al. Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 gene transfection of human articular chondrocytes protects against nitric oxide-induced apoptosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88(12):1660-1665.
[26] Horner A, Bishop NJ, Bord S, et al. Immunolocalisation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in human neonatal growth plate cartilage. J Anat. 1999;194 ( Pt 4):519-524.
[27] Ropert S, Vignaux O, Mir O, et al. VEGF pathway inhibition by anticancer agent sunitinib and susceptibility to atherosclerosis plaque disruption. Invest New Drugs. 2011;29(6):1497-1499.
[28] Murphy CL, Sambanis A. Effect of oxygen tension on chondrocyte extracellular matrix accumulation. Connect Tissue Res. 2001;42(2):87-96.
[29] Semenza GL, Wang GL. A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12(12):5447- 5454.
[30] Tian H, McKnight SL, Russell DW. Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 (EPAS1), a transcription factor selectively expressed in endothelial cells. Genes Dev. 1997;11(1):72-82.
[31] Saito T, Kawaguchi H. HIF-2α as a possible therapeutic target of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(12):1552- 1556.
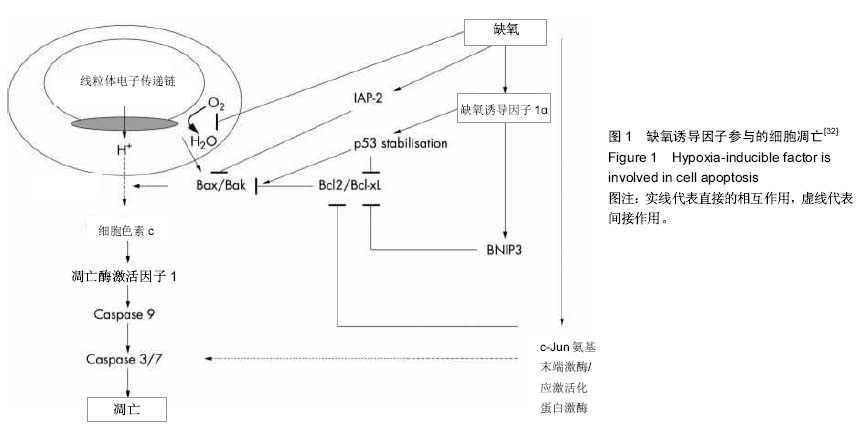
[32] Greijer AE, van der Wall E. The role of hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) in hypoxia induced apoptosis. J Clin Pathol. 2004;57(10):1009-1014.
[33] 任步方,邓廉夫,王君,等.低氧环境对小鼠未成熟关节透明软骨细胞培养的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2008,28(1):56-62.
[34] Percy MJ, Furlow PW, Lucas GS, et al. A gain-of-function mutation in the HIF2A gene in familial erythrocytosis. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(2):162-168.
[35] Pietras A, Johnsson AS, Påhlman S. The HIF-2α-driven pseudo-hypoxic phenotype in tumor aggressiveness, differentiation, and vascularization. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;345:1-20. |