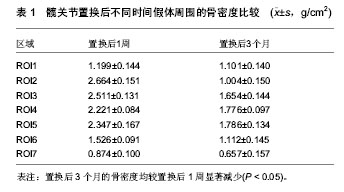
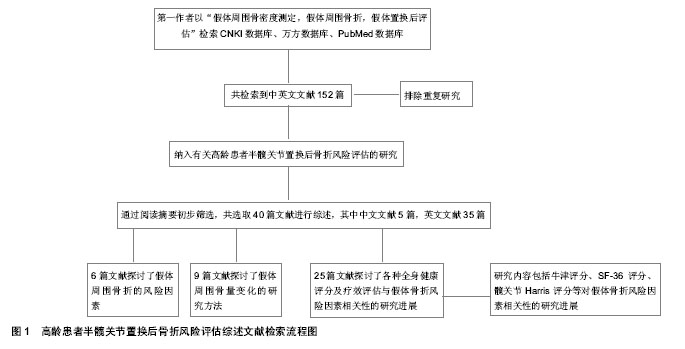
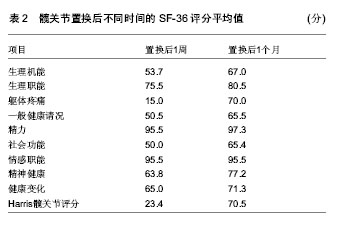
| [1] Kynaston-Pearson F, Ashmore AM, Malak TT, et al. Primary hip replacement prostheses and their evidence base: systematic review of literature. BMJ. 2013;347:f6956.
[2] 范卫民,王青,陶松年,等.人工关节松动病因的研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1998,18(9):518-521.
[3] 刘志宏,王毅,杨庆铭,等.人工髋关节置换术失败原因分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2000,20(12):723-727.
[4] Burghardt AJ, Issever AS, Schwartz AV, et al. High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomographic imaging of cortical and trabecular bone microarchitecture in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95: 5045-5055.
[5] Singh JA, Jensen MR, Harmsen SW, et al. Are gender, comorbidity, and obesity risk factors for postoperative periprosthetic fractures after primary total hip arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(1):126-131.e1-2.
[6] Napoli N, Schwartz AV, Palermo L, et al. Risk factors for subtrochanteric and diaphyseal fractures: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(2): 659-667.
[7] Rizzoli R, Akesson K, Bouxsein M, et al. Subtrochanteric fractures after long-term treatment with bisphosphonates: a European Society on Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis, and International Osteoporosis Foundation Working Group Report. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22:373-390.
[8] 林剑浩,吕厚山,寇伯龙,等.股骨头假体置换术后假体周围骨量变化的观察[J].中华骨科杂志,1995 ,15(8):494-499.
[9] Melton 3rd LJ, Riggs BL, Leibson CL, et al. A bone structural basis for fracture risk in diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:4804-4809.
[10] Palazzo C, Jourdan C, Descamps S, et al. Determinants of satisfaction 1 year after total hip arthroplasty: the role of expectations fulfilment. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014; 15:53.
[11] 王文昊.人工全髋关节置换术失败原因及翻修术的疗效观察[D]. 山东大学,2013.
[12] Callaghan JJ, Dysart HD, Savory CF, et al. Assessing theresults of hip replacement. Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990; 72(10): 1008- 1009.
[13] Baker P, Muthumayandi K, Gerrand C, et al. Influence of body mass index (BMI) on functional improvements at 3 years following total knee replacement: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59079.
[14] Li MG, Nilsson KG. Changes in bone mineral density at theproximal tibia after total knee arthroplasty: a 2- year followupof 28 knees using dual energy X- ray absorptiometry.J Orthop Res. 2000;18(1): 40-47.
[15] Karachalios T, Tsatsaronis C, Efraimis G, et al. The long- term clinical relevance of calcar atrophy caused by stress shielding in total hip arthroplasty: a 10-year, prospective, randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19: 469-475.
[16] Sangha O, Stucki G, Liang MH, et al. The Self-Administered Comorbidity Questionnaire: a new method to assess comorbidity for clinical and health services research. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49(2): 156-163.
[17] Anderson JG, Wilson RL, Tsai D, et al. Functional outcome and patient satisfaction in total knee patients over the age of 75. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11(7): 831-840.
[18] 沈霖, Sabo D, Ewerbeck V. 全髋关节置换术后假体周围骨密度动态观察[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2001,9(3):1-4.
[19] World Health Organisation BMI classification. 2012.
[20] Ethgen O, Bruyère O, Richy F, et al. Health-related quality of life in total hip and total knee arthroplasty. A qualitative and systematic review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(5):963-974.
[21] Jones CA, Voaklander DC, Johnston DW, et al. Health related quality of life outcomes after total hip and knee arthroplasties in a community based population. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(7): 1745-1752.
[22] Singh HJ, Nimarpreet K, Ashima Das S, et al. Study of bone mineral density in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7(12):2832-2835.
[23] Korkosz M , G?sowski J , Grzanka P ,et al. Baseline new bone formation does not predict bone loss in ankylosing spondylitis as assessed by quantitative computed tomography (QCT): 10-year follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:121.
[24] Moritomo H , Imaeda T , Gotani H , et al. Reliability of the hand20 questionnaire: comparison with the 36-item short-form health survey. Hand Surg. 2014;19(1):1-6.
[25] Bruyère O , Ethgen O , Neuprez A , et al. Health-related quality of life after total knee or hip replacement for osteoarthritis: a 7-year prospective study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(11):1583-1587.
[26] Chiu HC, Mau LW, Hsu YC, et al. Postoperative 6-month and 1-year evaluation of health-related quality of life in total hipreplacement patients. J Formos Med Associ. 2001; 100(7): 461-465.
[27] Towheed TE, Hochberg MC. Health-related quality of life after total hip replacement. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1996; 26(1): 483-491.
[28] Cleary PD, Reilly DT, Greenfield S, et al. Using patient reports to assess health-related quality of life after total hip replacement. Qual Life Res. 1993; 2(1):3-11.
[29] Shi HY , Chiu HC , Chang JK , et al. Evaluation and prediction of health-related quality of life for total hip replacement among Chinese in Taiwan. Int Orthop. 2008; 32(1):27-32.
[30] Uesugi Y, Makimoto K, Fujita K, et al. Validity and responsiveness of the Oxford hip score in a prospective study with Japanese total hiparthroplasty patients. J Orthop Sci. 2009; 14(1):35-39.
[31] Badura-Brzoza K, Zajac P, Brzoza Z, et al. Psychological and psychiatric factors related to health-related quality of life after total hip replacement - preliminary report. Eur Psychiatry. 2009;24(2):119-124.
[32] Shi HY, Khan M, Culbertson R, et al. Health-related quality of life after total hip replacement: a Taiwan study. Int Orthop. 2009; 33(5):1217-1222.
[33] Santi? V, Legovi? D, Sestan B, et al. Measuring improvement following total hip and knee arthroplasty using the SF-36 Health Survey. Coll Antropol. 2012;36(1):207-212.
[34] Hofhuis JG , Spronk PE. Health-related quality of life and influence of age after trauma: An overview. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014;76(2):549-556.
[35] Guillemin F, Martinez L, Calvert M, et al. Fear of falling, fracture history, and comorbidities are associated with health-related quality of lifeamong European and US women with osteoporosis in a large international study. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(12):3001-3010.
[36] Liu SS, Buvanendran A, Rathmell JP, et al. A cross-sectional survey on prevalence and risk factors for persistent postsurgical pain 1 year after total hip and knee replacement. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2012;37(4):415-422.
[37] Stevens M, Paans N, Wagenmakers R, et al. The influence of overweight/obesity on patient-perceived physical functioning and health-relatedquality of life after primary total hip arthroplasty. Obes Surg. 2012;22(4):523-529.
[38] Bolton KL, Egerton T, Wark J, et al. Effects of exercise on bone density and falls risk factors in post-menopausal women with osteopenia: a randomised controlled trial. J Sci Med Sport. 2012;15(2):102-109.
[39] Garrido-Abejar M, Serrano-Parra MD, Bartolomé-Gutiérrez R, et al. [Factors associated with health-related quality of life in the institutionalised elderly: differences between men and women]. Enferm Clín. 2012;22(1):27-34.
[40] Vlak T, Kaštelan D, Lozo P,et al. Monthly or weekly bisphosphonate? Evaluation of satisfaction in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis using OPSAT-Q questionnaire during the BOOSTER study in Croatia. Clin Rheumatol. 2011; 30 (12):1549-1554. |