| [1] Kepler CK, Ponnappan RK, Tannoury CA, et al. The molecular basis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 2013;13(3):318-330.
[2] Vo NV, Hartman RA, Yurube T, et al. Expression and regulation of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in intervertebral disc aging anddegeneration. Spine J. 2013; 13(3):331-341.
[3] Gopal D, Ho AL, Shah A, et al. Molecular basis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012; 760:114-33.
[4] 王海,黄博,王建,等.退变椎间盘生物学特性研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013; 21(17):1738-1741.
[5] 周旭,贺石生.椎间盘退行性变的分子生物学因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,7(39):7375-7379.
[6] Ding F, Shao ZW, Xiong LM. Cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration. Apoptosis. 2013;18(7):777-785.
[7] Park JB, Lee JK, Park EY, et al. Fas/FasL interaction of nucleus pulposus and cancer cells with the activation of caspases. Int Orthop. 2008;32(6):835-840.
[8] Ding F, Shao ZW, Yang SH, et al. Role of mitochondrial pathway in compression-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells. Apoptosis. 2012;17(6):579-590.
[9] Sudo H, Minami A. Caspase 3 as a therapeutic target for regulation of intervertebral disc degeneration in rabbits. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(6):1648-1657.
[10] 刘旭,车路,王海强,等.椎间盘退变的分子病理机制研究概况[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,(6):2664-2666.
[11] Wang D, Hu Z, Hao J, et al. SIRT1 inhibits apoptosis of degenerative human disc nucleus pulposus cells through activation of Akt pathway. Age (Dordr). 2013;35(5): 1741-1753.
[12] Liu G, Cao P, Chen H, et al. MiR-27a regulates apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells by targeting PI3K. PLoS One. 2013; 8(9):e75251.
[13] Niu CC, Lin SS, Yuan LJ, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment suppresses MAPK signaling and mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in degenerated human intervertebral disc cells. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(2):204-209.
[14] Hiyama A, Yokoyama K, Nukaga T, et al. A complex interaction between Wnt signaling and TNF-α in nucleus pulposus cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R189.
[15] Than KD, Rahman SU, Vanaman MJ, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins and degenerative disk disease. Neurosurgery. 2012;70(4):996-1002.
[16] Wang Z, Hutton WC, Yoon ST. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 antagonizes tumor necrosis factor-α-induced activation of nuclear factor κB and up-regulation of the ADAMTS, leading to decreased degradation of disc matrix macromolecules aggrecan and collagen II. Spine J. 2014;14(3):505-512.
[17] 辛洪奎,张超,阮狄克.骨形态发生蛋白7及其对椎间盘退变修复作用的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(5):416-418.
[18] Imai Y, Miyamoto K, An HS, et al. Recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 upregulates proteoglycan metabolism of human anulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus cells. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(12):1303-1309; discussion 1310.
[19] Griffith JF, Wang YX, Antonio GE, et al. Modified Pfirrmann grading system for lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(24):E708-E712.
[20] Yuan M, Leong KW, Chan BP. Three-dimensional culture of rabbit nucleus pulposus cells in collagen microspheres. Spine J. 2011;11(10):947-960.
[21] 王锋,郑陈静美,吴小涛.人退变椎间盘髓核细胞体外平面培养的形态学及活性观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(13): 1346-1351.
[22] Ha KY, Kim BG, Kim KW, et al. Apoptosis in the sequestrated nucleus pulposus compared to the remaining nucleus pulposusin the same patient. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(9):683-689.
[23] Wei A, Brisby H, Chung SA, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 protects human intervertebral disc cells in vitro from apoptosis. Spine J. 2008;8(3):466-474.
[24] Yu LP, Qian WW, Yin GY, et al. MRI assessment of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration with lumbar degenerative disease using the Pfirrmann grading systems. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e48074.
[25] 杨勇,梁伟,罗卓荆,等.不同Pfirrmann分级椎间盘内髓核细胞生物学特性的比较[J].脊柱外科杂志,2011,9(4):244-248.
[26] Kakoi H, Maeda S, Shinohara N, et al. Bone morphogenic protein (BMP) signaling up-regulates neutral sphingomyelinase 2 to suppress chondrocyte maturation via the akt protein signaling pathway as a negative feedback mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(12):8135-8150.
[27] Zheng Y, Wang X, Wang H, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and migration through downregulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Tumour Biol. 2014.
[28] Lim AI, Chan LY, Tang SC, et al. BMP-7 represses albumin-induced chemokine synthesis in kidney tubular epithelial cells through destabilization of NF-κB-inducing kinase. Immunol Cell Biol. 2014.
[29] Pei H, Cao D, Guo Z, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 ameliorates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via inhibiting oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(12):23441-23453.
[30] Ciumas M, Eyries M, Poirier O, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins protect pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells from apoptosis by upregulating α-B-crystallin. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33(11):2577-2584.
[31] Wang Z, Guo J. Mechanical induction of BMP-7 in osteocyte blocks glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis through PI3K/AKT/ GSK3β pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;67(2):567-574.
[32] Shimizu T, Kayamori T, Murayama C, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-4 and BMP-7 suppress granulosa cell apoptosis via different pathways: BMP4 via PI3K/PDK-1/Akt and BMP-7 via PI3K/PDK-1/PKC. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;417(2):869-873.
[33] Mehrkens A, Karim MZ, Kim S, et al. Canine notochordal cell-secreted factors protect murine and human nucleus pulposus cells from apoptosis by inhibition of activated caspase-9 and caspase-3/7. Evid Based Spine Care J. 2013; 4(2):154-156.
[34] Hiyama A, Yokoyama K, Nukaga T, et al. A complex interaction between Wnt signaling and TNF-α in nucleus pulposus cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R189.
[35] Ma Y, Qin H, Cui Y. MiR-34a targets GAS1 to promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in papillary thyroid carcinoma via PI3K/Akt/Bad pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;441(4):958-963.
[36] Iwasaki K, Sudo H, Yamada K, et al. Cytotoxic effects of the radiocontrast agent iotrolan and anesthetic agents bupivacaine and lidocaine in three-dimensional cultures of human intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cells: identification of the apoptotic pathways. PLoS One. 2014; 9(3):e92442. |
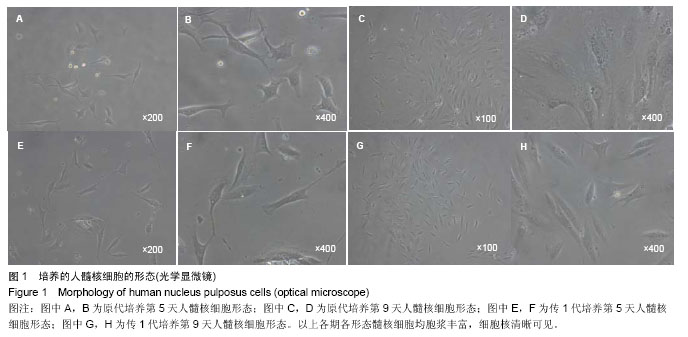
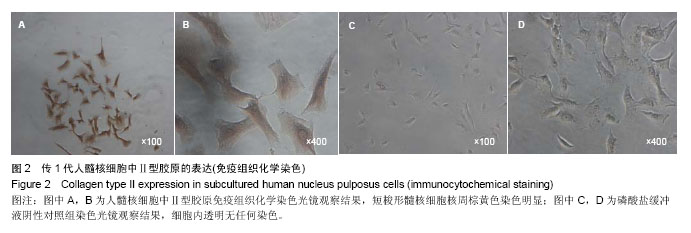
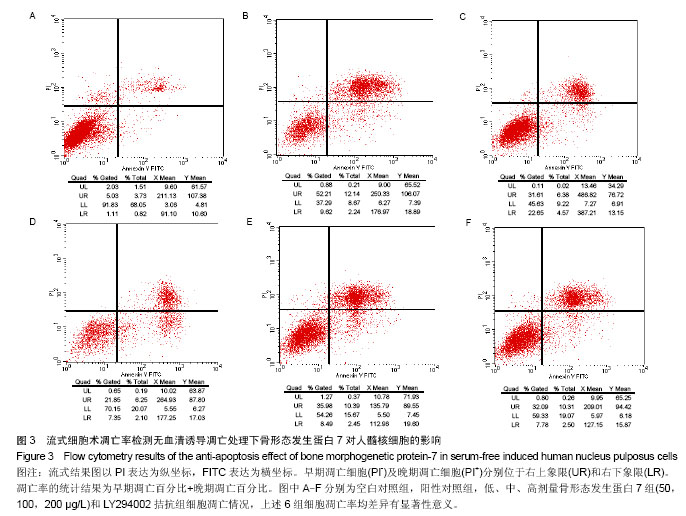
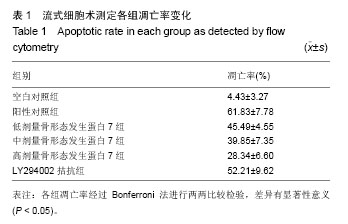
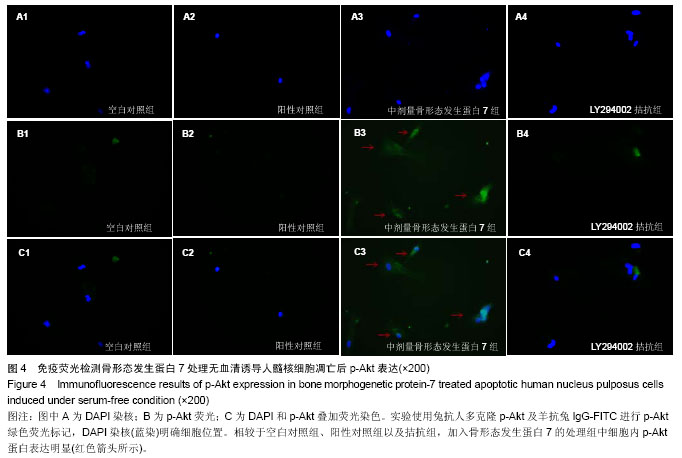
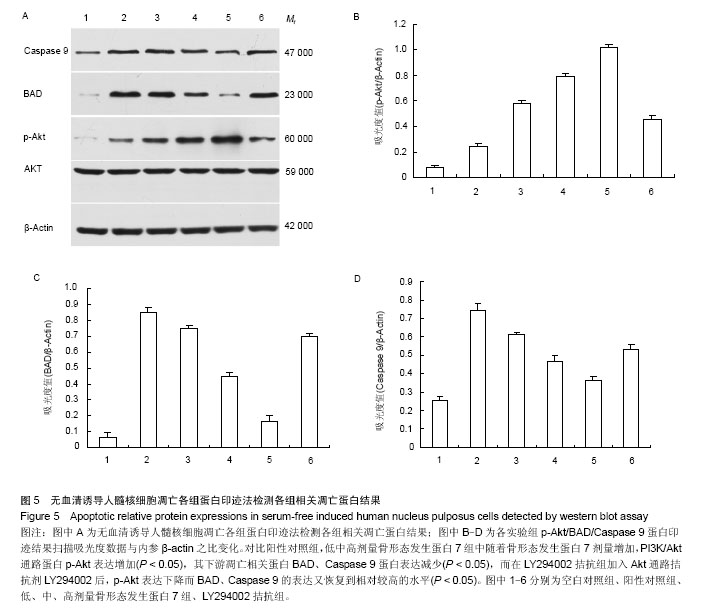
.jpg)
.jpg)