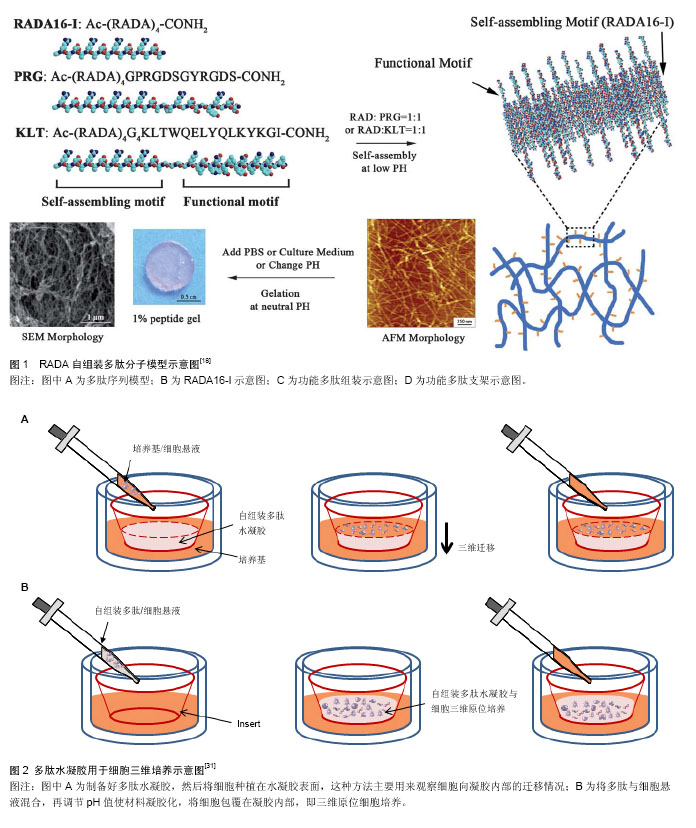
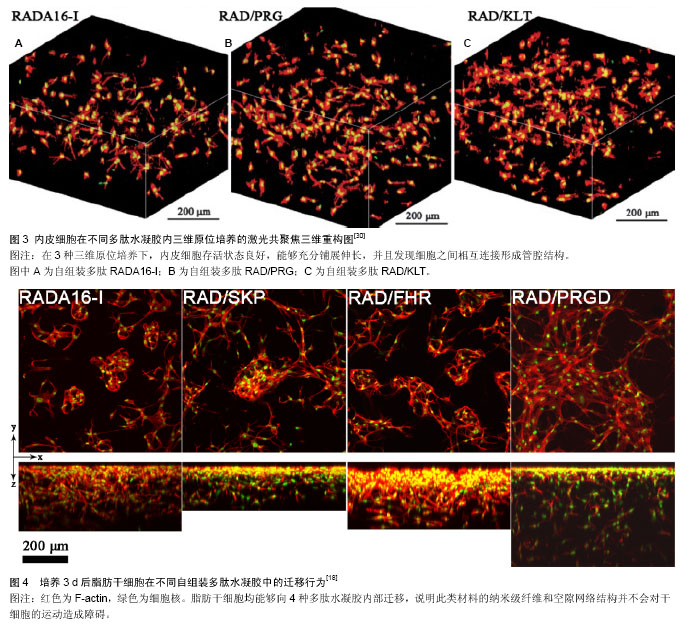
| [1] Lutolf MP,Gilbert PM,Blau HM.Designing materials to direct stem-cell fate.Nature.2009;462(7272):433-441.
[2] Marklein RA,Burdick JA.Controlling stem cell fate with material design.Adv Mater.2010;22(2):175-189.
[3] Gelain F,Horii A,Zhang S.Designer self-assembling peptide scaffolds for 3-d tissue cell cultures and regenerative medicine.Macromol Biosci.2007;7(5):544-551.
[4] Stevens MM,George JH.Exploring and engineering the cell surface interface.Science.2005;310(5751):1135-1138.
[5] Yanlian Y,Ulung K,Xiumei W,et al.Designer self-assembling peptide nanomaterials.Nano Today.2009;4(2):193-210.
[6] Matson JB,Stupp SI.Self-assembling peptide scaffolds for regenerative medicine.Chem Commun (Camb).2012;48(1): 26-33.
[7] Matson JB,Zha RH,Stupp SI.Peptide self-assembly for crafting functional biological materials.Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci. 2011;15(6):225-235.
[8] Webber MJ,Tongers J,Renault MA,et al.Development of bioactive peptide amphiphiles for therapeutic cell delivery. Acta Biomater.2010;6(1):3-11.
[9] Garty S,Kimelman-Bleich N,Hayouka Z,et al.Peptide-modified "smart" hydrogels and genetically engineered stem cells for skeletal tissue engineering.Biomacromolecules. 2010;11(6): 1516-1526.
[10] Zhang S,Holmes TC,DiPersio CM,et al.Self-complementary oligopeptide matrices support mammalian cell attachment. Biomaterials. 1995;16(18):1385-1393.
[11] Hong Y,Legge RL,Zhang S,et al.Effect of amino acid sequence and pH on nanofiber formation of self-assembling peptides EAK16-II and EAK16-IV. Biomacromolecules. 2003; 4(5):1433-1442.
[12] Zhang S,Holmes T,Lockshin C,et al.Spontaneous assembly of a self-complementary oligopeptide to form a stable macroscopic membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1993; 90(8): 3334-3338.
[13] Altman M,Lee P,Rich A,et al.Conformational behavior of ionic self-complementary peptides.Protein Sci.2000;9(6): 1095-1105.
[14] Yokoi H,Kinoshita T,Zhang S.Dynamic reassembly of peptide RADA16 nanofiber scaffold.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2005; 102(24):8414-8419.
[15] Mershin A,Cook B,Kaiser L,et al.A classic assembly of nanobiomaterials.Nat Biotechnol.2005;23(11):1379-1380.
[16] Lomander A,Hwang W,Zhang S.Hierarchical self-assembly of a coiled-coil peptide into fractal structure.Nano Lett. 2005;5(7): 1255-1260.
[17] Vauthey S,Santoso S,Gong H,et al.Molecular self-assembly of surfactant-like peptides to form nanotubes and nanovesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2002;99(8): 5355-5360.
[18] Liu X,Wang X,Horii A,et al.In vivo studies on angiogenic activity of two designer self-assembling peptide scaffold hydrogels in the chicken embryo chorioallantoic membrane. Nanoscale.2012;4(8):2720-2727.
[19] Hersel U,Dahmen C,Kessler H.RGD modified polymers: biomaterials for stimulated cell adhesion and beyond. Biomaterials.2003;24(24):4385-4415.
[20] Ruoslahti E.RGD and other recognition sequences for integrins.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.1996;12:697-715.
[21] Bab I,Gazit D,Chorev M,et al.Histone H4-related osteogenic growth peptide (OGP): a novel circulating stimulator of osteoblastic activity.The EMBO J.1992;11(5):1867.
[22] Fazzi R,Testi R,Trasciatti S,et al.Bone and bone-marrow interactions: haematological activity of osteoblastic growth peptide (OGP)-derived carboxy-terminal pentapeptide. Mobilizing properties on white blood cells and peripheral blood stem cells in mice.Leukemia Res. 2002;26(1): 19-27.
[23] Kreis TE,Vale RE.Guidebook to the extracellular matrix, anchor, and adhesion proteins.Oxford University Press.1999.
[24] Nowakowski GS,Dooner MS,Valinski HM,et al.A specific heptapeptide from a phage display peptide library homes to bone marrow and binds to primitive hematopoietic stem cells.Stem Cells.2004;22(6):1030-1038.
[25] Palou E,Pirotto F,Sole J,et al.Genomic characterization of CD84 reveals the existence of five isoforms differing in their cytoplasmic domains.Tissue Antigens.2000;55(2):118-127.
[26] Choi YJ,Lee JY,Park JH,et al.The identification of a heparin binding domain peptide from bone morphogenetic protein-4 and its role on osteogenesis.Biomaterials. 2010;31(28): 7226-7238.
[27] Chillakuri CR,Jones C,Mardon HJ.Heparin binding domain in vitronectin is required for oligomerization and thus enhances integrin mediated cell adhesion and spreading.Febs Lett.2010; 584(15):3287-3291.
[28] Harbers GM,Healy KE.The effect of ligand type and density on osteoblast adhesion,proliferation, and matrix mineralization.J Biomed Mater Res A.2005;75A(4):855-869.
[29] Tashiro K-i,Sephel G,Weeks B,et al.A synthetic peptide containing the IKVAV sequence from the A chain of laminin mediates cell attachment, migration, and neurite outgrowth.J Biol Chem.1989;264(27):16174-16182.
[30] Wang XM,Horii A,Zhang SG.Designer functionalized self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds for growth, migration, and tubulogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Soft Matter. 2008;4(12):2388-2395.
[31] 刘茜.材料调控脂肪干细胞命运及其血管生成活性的研究[D].清华大学,2013.
[32] Horii A,Wang X,Gelain F,et al.Biological designer self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds significantly enhance osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and 3-D migration.PLoS One. 2007;2(2):e190.
[33] Guillaume DJ,Johnson MA,Li XJ,et al.Human embryonic stem cell‐derived neural precursors develop into neurons and integrate into the host brain.J Neurosci Res.2006;84(6): 1165-1176.
[34] Li XJ,Du ZW,Zarnowska ED,et al.Specification of motoneurons from human embryonic stem cells.Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(2):215-221.
[35] Mueller D,Shamblott MJ,Fox HE,et al.Transplanted human embryonic germ cell-derived neural stem cells replace neurons and oligodendrocytes in the forebrain of neonatal mice with excitotoxic brain damage.J Neurosci Res.2005; 82(5):592-608.
[36] Eglitis MA,Mezey É.Hematopoietic cells differentiate into both microglia and macroglia in the brains of adult mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1997;94(8):4080.
[37] Ferrari G,Angelis D,Coletta M,et al.Muscle regeneration by bone marrow-derived myogenic progenitors. Science. 1998; 279(5356):1528-1530.
[38] Jackson KA,Majka SM,Wang H,et al.Regeneration of ischemic cardiac muscle and vascular endothelium by adult stem cells.J Clin Invest. 2001;107(11):1395-1402.
[39] Liu X,Wang X,Ren H,et al.Functionalized self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogels mimic stem cell niche to control human adipose stem cell behavior in vitro.Acta Biomaterialia. 2013;9(6):6798-6805.
[40] Hamada K,Hirose M,Yamashita T,et al.Spatial distribution of mineralized bone matrix produced by marrow mesenchymal stem cells in self-assembling peptide hydrogel scaffold.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;84(1):128-136.
[41] Cheng TY,Chen MH,Chang WH,et al.Neural stem cells encapsulated in a functionalized self-assembling peptide hydrogel for brain tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2013; 34(8):2005-2016.
[42] Cunha C,Panseri S,Villa O,et al.3D culture of adult mouse neural stem cells within functionalized self-assembling peptide scaffolds.Inte J Nanomed.2011;6:943-955.
[43] Zhang ZX,Zheng QX,Wu YC,et al.Compatibility of neural stem cells with functionalized self-assembling peptide scaffold in vitro.Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng.2010;15(4):545-551.
[44] Gelain F,Bottai D,Vescovi A,et al.Designer self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds for adult mouse neural stem cell 3-dimensional cultures.PLoS One.2006;1(1):e119.
[45] Semino CE,Kasahara J,Hayashi Y,et al.Entrapment of migrating hippocampal neural cells in three-dimensional peptide nanofiber scaffold.Tissue Eng.2004;10(3-4):643-655.
[46] Semino CE,Merok JR,Crane GG,et al.Functional differentiation of hepatocyte-like spheroid structures from putative liver progenitor cells in three-dimensional peptide scaffolds.Differentiation. 2003;71(4-5):262-270.
[47] Ellis-Behnke RG,Liang YX,You SW,et al.Nano neuro knitting: peptide nanofiber scaffold for brain repair and axon regeneration with functional return of vision.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(13):5054-5059.
[48] Davis ME,Motion JP,Narmoneva DA,et al.Injectable self-assembling peptide nanofibers create intramyocardial microenvironments for endothelial cells.Circulation.2005; 111(4):442-450. |