中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (11): 1951-1958.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.11.008
• 组织构建与生物活性因子 tissue construction and bioactive factors • 上一篇 下一篇
低氧训练与低氧大鼠心肌细胞凋亡及凋亡因子的表达
林喜秀1, 2,周 桔3,罗自强1,瞿树林3,赵用强2,邱继旺2
- 1 中南大学基础医学院博士后流动站,湖南省长沙市 410000
2 湖南工业大学体育学院,湖南省株洲市 412000
3 湖南师范大学医学院生理应用教研室,湖南省长沙市 410000
Hypoxia training regulates myocardial apoptosis and apoptotic factor expression in rats
Lin Xi-xiu1, 2, Zhou Ju3, Luo Zi-qiang1, Qu Shu-lin3, Zhao Yong-qiang2, Qiu Ji-wang2
- 1 Postdoctoral Research Station, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Central South University, Changsha 410000, Hunan Province, China
2 Sports Academy of Hunan University of Technology, Zhuzhou 412000, Hunan Province, China
3 Department of Physiological Applications, School of Medical Science, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410012, Hunan Province, China
摘要:
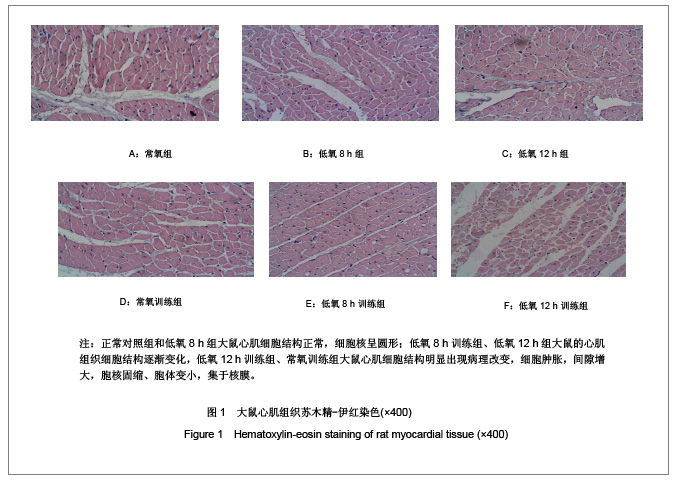
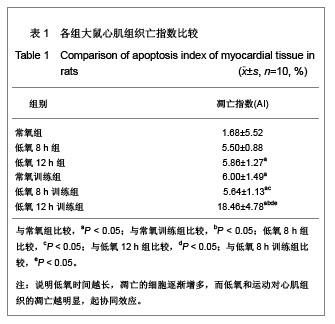
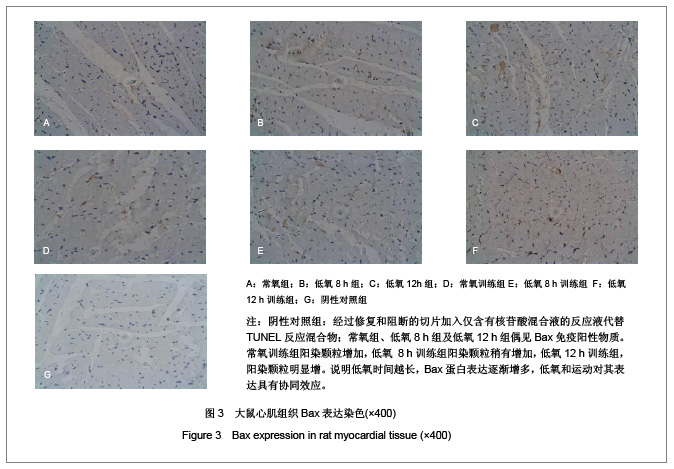
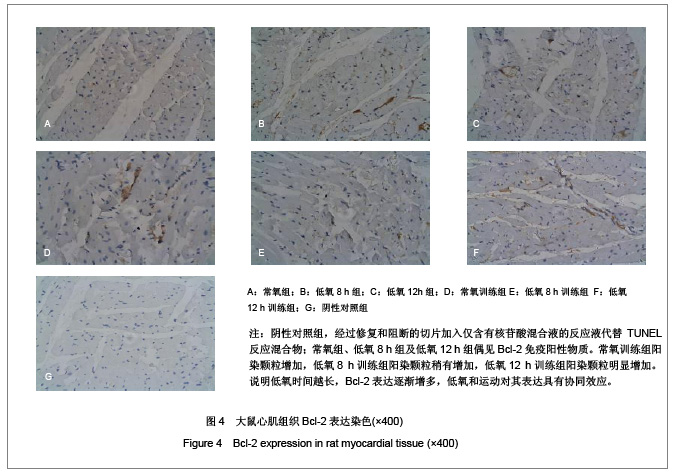
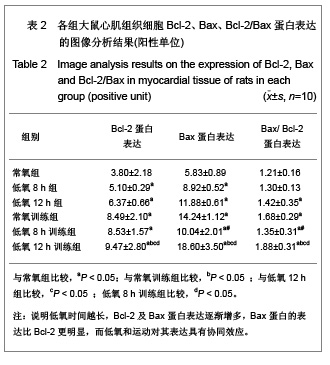
背景:低氧训练时,机体既要承受运动负荷,同时处于外界的低氧环境,此时, 心组织将如何适应其变化?其机制研究国内外较少。 目的:观察低氧与低氧训练对大鼠心肌细胞凋亡及Bax及Bcl-2表达的影响。 方法:SD大鼠共60只随机分为6组,常氧组、低氧8 h组、低氧12 h组、常氧训练组、低氧8 h训练组和低氧12 h训练组,每组10只。后3组大鼠每天在坡度为0的动物跑台上以25 m/min的速度训练1 h。训练完后,将低氧8 h组、低氧8 h训练组和低氧12 h组、低氧12 h训练组放入氧体积分数为12.5%(相当于海拔4 000 m)的低氧舱内8 h和12 h。实验期为4周,5 d/周。最后1次实验结束后24 h,大鼠均实施速眠新Ⅱ腹腔麻醉后取材,采用苏木精-伊红染色、原位末端脱氧核糖核苷酸转移酶介导的dUTP缺口末端标记法及蛋白免疫组织化学法检测各组大鼠心肌细胞凋亡和Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达。 结果与结论:①与常氧组相比, 低氧12h组、常氧训练组、低氧训练组心肌细胞凋亡指数均显著增加 (P < 0.05) ;低氧12 h训练组心肌细胞凋亡指数显著多于常氧训练组和低氧8h训练组(P < 0.05) 。②与常氧组比较,其他各组Bcl-2、Bax、Bcl-2/Bax均显著性增高(P < 0.05) ;常氧训练组Bcl-2、Bax、Bcl-2/Bax表达显著高于低氧 8 h组,显著低于低氧12 h训练组(P < 0.05) ;低氧12 h训练组Bcl-2、Bax、Bcl-2/Bax表达比低氧12 h组、低氧8 h训练组显著增加(P < 0.05)。提示低氧、低氧训练可诱导大鼠心肌细胞Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达, 运动时低氧刺激与细胞凋亡率、凋亡指数及病理损伤有关,其中以低氧12 h后运动训练组最明显,心肌细胞的凋亡调控与Bcl-2和Bax相关。
中图分类号:



.jpg)

