[1] KALHOR M, HOROWITZ K, BECK M, et al. Vascular supply to the acetabular labrum. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(15): 2570-2575.
[2] GEYER MR, PHILIPPON MJ, FAGRELIUS TS, et al. Acetabular labral reconstruction with an iliotibial band autograft outcome and survivorship analysis at minimum 3-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(8): 1750-1756.
[3] TAN V, SELDES RM, KATZ MA, et al. Contribution of acetabular labrum to articulating surface area and femoral head coverage in adult hip joints: an anatomic study in cadavera. Am J Orthop. 2001;30:809-812.
[4] FERGUSON SJ, BRYANT JT, GANZ R, et al. An in vitro investigation of the acetabular labral seal in hip joint mechanics. J Biomech. 2003;36(2): 171-178.
[5] CRAWFORD MJ, DY CJ, ALEXANDER JW, et al. The 2007 Frank Stinchfield Award. The biomechanics of the hip labrum and the stability of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;465: 16-22.
[6] LARSON CM, GIVEANS MR, STONE RM. Arthroscopic debridement versus refixation of the acetabular labrum associated with femoroacetabular impingement: mean 3.5-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(5): 1015-1021.
[7] KELLY BT, WEILAND DE, SCHENKER ML, et al. Arthroscopic labral repair in the hip: surgical technique and review of the literature. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21(12): 1496-1504.
[8] MASON JB. Acetabular labral tears in the athlete. Clin Sports Med 2001;20: 779-790.
[9] MATSUDA DK, BURCHETTE RJ. Arthroscopic hip labral reconstruction with a gracilis autograft versus labral refixation: 2-year minimum outcomes. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(5): 980-987.
[10] FERGUSON SJ, BRYANT JT, GANZ R, et al. The influence of the acetabular labrum on hip joint cartilage consolidation: A poroelastic finite element model. J Biomech. 2000;33: 953-960.
[11] MATSUDA DK. Acute iatrogenic dislocation following hip impingement arthroscopic surgery. Arthroscopy.2009;25(4):400-404.
[12] RATH R, MAZEK J. Arthroscopic acetabular labral reconstruction with rectus femoris tendon autograft: Our experiences and early results. J Orthop. 2018;15(3): 783-786.
[13] SHI YY, CHEN LX, XU Y, et al. Acetabular labral reconstruction with autologous tendon tissue in a porcine model: in vivo histological assessment and gene expression analysis of the healing tissue. Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44(4): 1031-1039.
[14] AL MANA L, COUGHLIN RP, DESAI V, et al. The hip labrum reconstruction: indications and outcomes-an updated systematic review. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2019;12(2):156-165.
[15] MOOK WR, BRIGGS KK, PHILIPPON MJ. Evidence and approach for management of labral deficiency: the role for labral reconstruction. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2015;23(4): 205-12.
[16] FERRO FP, PHILIPPON MJ, RASMUSSEN MT, et al. Tensile properties of the human acetabular labrum and hip labral reconstruction grafts. Am J Sports Med. 2015; 43(5): 1222-1227.
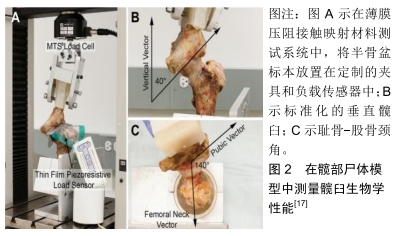
[17] LEE S, WUERZ TH, SHEWMAN E, et al. Labral reconstruction with iliotibial band autografts and semitendinosus allografts improves hip joint contact area and contact pressure: an in vitro analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2015; 43(1): 98-104.
[18] PHILIPPON MJ, BRIGGS KK, HAY CJ, et al. Arthroscopic labral reconstruction in the hip using iliotibial band autograft: technique and early outcomes. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(6): 750-756.
[19] PHILIPPON MJ, WEISS DR, KUPPERSMITH DA, et al. Arthroscopic labral repair and treatment of femoroacetabular impingement in professional hockey players. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38: 99-104.
[20] BIZZINI M, NOTZLI HP, MAFFIULETTI NA. Femoroacetabular im- pingement in professional ice hockey players: A case series of 5 athletes after open surgical decompression of the hip. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35: 1955-1959.
[21] MATSUDA DK. Arthroscopic labral reconstruction with gracilis autograft. Arthrosc Tech. 2012; 1(1): e15-21.
[22] CHANDRASEKARAN S, DARWISH N, CLOSE MR, et al. Arthroscopic reconstruction of segmental defects of the hip labrum: results in 22 patients with mean 2-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2017;33(9): 1685-1693.
[23] REDMOND JM, CREGAR WM, MARTIN TJ, et al. Arthroscopic labral reconstruction of the hip using semitendinosus allograft. Arthrosc Tech. 2015; 4(4): e323-329.
[24] PARK SE, KO Y. Use of the quadriceps tendon in arthroscopic acetabular labral reconstruction: potential and benefits as an autograft option. Arthrosc Tech. 2013;2(3): e217-219.
[25] MURDOCK CJ, AGYEMAN K. Anatomy, abdomen and pelvis, rectus femoris muscle. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019.
[26] SHARFMAN ZT, AMAR E, SAMPSON T,et al. Arthroscopic labrum reconstruction in the hip using the indirect head of rectus femoris as a local graft: surgical technique. Arthrosc Tech. 2016; 5(2): e361-364.
[27] AMAR E, SAMPSON TG, SHARFMAN ZT, et al. Acetabular labral reconstruction using the indirect head of the rectus femoris tendon significantly improves patient reported outcomes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(8): 2512-2518.
[28] COSTA ROCHA P, KLINGENSTEIN G, GANZ R, et al. Circumferential reconstruction of severe acetabular labral damage using hamstring allograft: surgical technique and case series. Hip Int. 2013;23 Suppl 9: S42-53.
[29] NHO SJ, BECK EC, KUNZE KN, et al. Contemporary management of the hip capsule during arthroscopic hip preservation surgery. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2019: 260-270.
[30] DOMB BG, GUPTA A, STAKE CE, et al. Arthroscopic labral reconstruction of the hip using local capsular autograft. Arthrosc Tech. 2014; 3(3): e355-359.
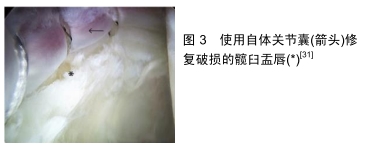
[31] NWACHUKWU BU, ALPAUGH K, MCCORMICK F, et al. All-Arthroscopic Reconstruction of the Acetabular Labrum by Capsular Augmentation. Arthrosc Tech. 2015; 4(2): e127-131.
[32] LOCKS R, CHAHLA J, BOLIA IK, et al. Outcomes following arthroscopic hip segmental labral reconstruction using autologous capsule tissue or indirect head of the rectus tendon. J Hip Preserv Surg. 2018; 5(1): 73-77.
[33] MOYA E, RIBAS M, NATERA L, et al. Reconstruction of nonrepairable acetabular labral tears with allografts: mid-term results. Hip Int. 2016;26 Suppl 1: 43-47.
[34] TEY M, ERQUICIA J, PELFORT X, et al. Allogenic labral transplantation in hip instability following arthroscopic labrectomy. Hip Int. 2011;22: 260-262.
[35] RATHI R, MAZEK J. Arthroscopic acetabular labral reconstruction with fascia lata allograft: clinical outcomes at minimum one-year follow-up. Open Orthop J. 2017; 11: 554-561.
[36] CARREIRA DS, KRUCHTEN MC, EMMONS BR, et al. Arthroscopic labral reconstruction using fascia lata allograft: shuttle technique and minimum two-year results. J Hip Preserv Surg. 2018; 5(3): 247-258.
[37] ENSEKI KR, KOHLRIESER D. Rehabilitation following hip arthroscopy: an evolving process. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2014;9(6): 765-773.
[38] MCCONKEY MO, MOREIRA B, MEI-DAN O. Arthroscopic hip labral reconstruction and augmentation using knotless anchors. Arthrosc Tech. 2015; 4(6): e701-705.
[39] CARREIRA DS, KRUCHTEN MC, EMMONS BR, et al. Arthroscopic labral reconstruction using fascia lata allograft: shuttle technique and minimum two-year results. J Hip Preserv Surg. 2018; 5(3): 247-258.
[40] LEBOURG M, SABATER SERRA R, MÁS ESTELLÉS J, et al. Biodegradable polycaprolactone scaffold with controlled porosity obtained by modified particle-leaching technique. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19(5): 2047-2053.
[41] ANINDYAJATI A, BOUGHTON P, RUYS AJ. Mechanical and cytocompatibility evaluation of uhmwpe/pcl/bioglass((r)) fibrous composite for acetabular labrum implant. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(6). pii: E916.
[42] LI H, CHEN S, WU Y, et al. Enhancement of the osseointegration of a polyethylene terephthalate artificial ligament graft in a bone tunnel using 58S bioglass. Int Orthop. 2012;36(1):191-197.
|