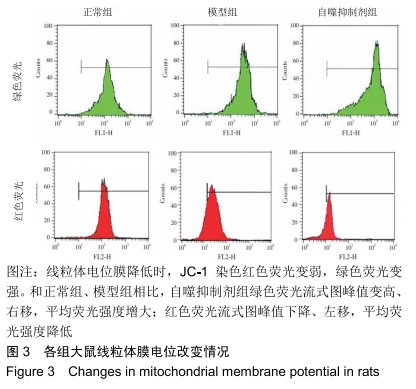
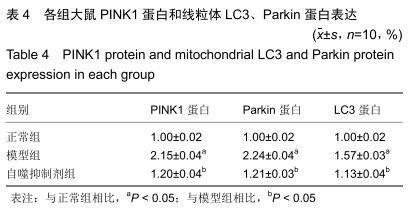
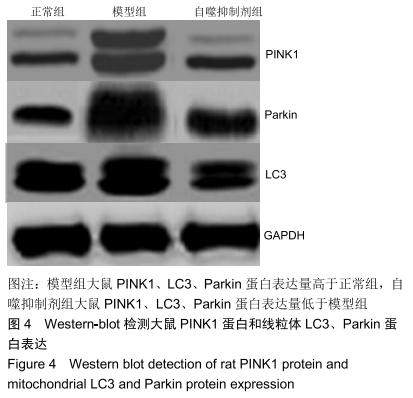
[1] 王琛,刘薇薇, 陈国芳,等. 急性脑出血合并高血压病患者90d预后相关危险因素分析[J].卒中与神经疾病, 2017, 24(3):204-207.
[2] 陆玮,于力.肾小球足细胞线粒体自噬与PINK1/Parkin信号通路研究进展[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2017,33(33):312-315.
[3] 汤友静,牛玉娜,王辉. Pink1/Parkin介导的线粒体自噬分子机制[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报,2017,11(7):101-108.
[4] 石灵,阮云军,冯骞,等.自噬选择性与心脏衰老的关系研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2018,9(15):167-171.
[5] 张春晓,高家昊,张倩倩,等.活性氧在1,4-苯醌诱导的线粒体自噬中的作用[J].浙江预防医学,2018,30(4):334-337.
[6] 梁丹阳,戴汉川. PINK1/Parkin通路在线粒体自噬氧化损伤中的作用[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2018,3(1):116-123.
[7] KANG C, BADR MA, KYRYCHENKO V, et al. Deficit in PINK1-PARKIN mediated mitochondrial autophagy at late stages of dystrophic cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Res. 2018; 114(1):90-102.
[8] 尚画雨,付玉,夏志,等.针刺对运动性骨骼肌损伤大鼠骨骼肌线粒体自噬的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(11):2038-2046.
[9] 郎秀娟,王燕. PINK1/parkin通路调控线粒体自噬机制的研究进展[J].微生物与感染,2018,13(2):102-106.
[10] YUAN B, SHEN H, LIN L, et al.Autophagy Promotes Microglia Activation Through Beclin-1-Atg5 Pathway in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Mol Neurobiol.2017;54(1):115-124.
[11] KUBLI DA, CORTEZ MQ, MOYZIS AG, et al. PINK1 Is Dispensable for Mitochondrial Recruitment of Parkin and Activation of Mitophagy in Cardiac Myocytes. Plos One.2015; 10(6):707-711.
[12] 包新民,舒斯云.大鼠脑立体定位图谱[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1991:21-29.
[13] GONG G, HU L, LIU Y, et al. Upregulation of HIF-1α protein induces mitochondrial autophagy in primary cortical cell cultures through the inhibition of the mTOR pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(4):1133-1136.
[14] HEO JM, ORDUREAU A, PAULO JA, et al. The PINK1-PARKIN mitochondrial ubiquitylation pathway drives a program of TBK1 activation and recruitment of OPTN and NDP52 to promote mitophagy. Molecular Cell.2015; 60(1): 7-11.
[15] VON SS,MARCHESAN E,ZIVIANI E.Mitochondrial quality control beyond PINK1/Parkin.Oncotarget.2018;9(16): 12550-12551.
[16] 金呈强,李金珂,贾彦霞.磷酸酶及张力蛋白同源物诱导的蛋白激酶1/Parkin介导的线粒体自噬的研究进展[J].国际免疫学杂志, 2017,40(1):92-95.
[17] SONG F, GUO C, GENG Y, et al. Therapeutic time window and regulation of autophagy by mild hypothermia after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Brain Res. 2018;1690: 12-22.
[18] SHEFA U, JEONG NY, SONG IO, et al.Mitophagy links oxidative stress conditions and neurodegenerative diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(5):749-756.
[19] ZUO W, ZHANG S, XIA CY, et al. Mitochondria autophagy is induced after hypoxic/ischemic stress in a Drp1 dependent manner: The role of inhibition of Drp1 in ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology. 2014;86:103-115.
[20] IMAI Y, HATTORI N. Chapter 15- Mitophagy Controlled by the PINK1-Parkin Pathway Is Associated with Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis.Autophagy Cancer Other Pathologies Inflammation Immunity Infection Aging, 2014;16(10):227-238.
[21] BARODIA SK, CREED RB, GOLDBERG MS. Parkin and PINK1 functions in oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Brain Res Bull. 2017;133:51-59.
[22] GATLIFF J,EAST D,CROSBY J, et al.TSPO interacts with VDAC1 and triggers a ROS-mediated inhibition of mitochondrial quality control. Autophagy.2014;10(12): 2279-2296.
[23] CAVALLUCCI V, BISICCHIA E, CENCIONI MT, et al.Acute focal brain damage alters mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy in axotomized neurons. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5: e1545.
[24] LI W, DU M, WANG Q, et al.FoxO1 Promotes Mitophagy in the Podocytes of Diabetic Male Mice via the PINK1/Parkin Pathway. Endocrinology. 2017;158(7):2155-2167.
[25] 刘树雄,何建.pink1-prkn PARK2通路与线粒体自噬和肝脏急性缺血再灌注损伤的关联研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2018,22(9): 130-134.
[26] 唐致恒,郑瑞茂. PINK1-Parkin通路与线粒体自噬[J].生理科学进展,2018,5(2):214-217.
[27] STOCKUM SV, MARCHESAN E, ZIVIANI E.Mitochondrial quality control beyond PINK1/Parkin.Oncotarget.2018; 9(16): 12550-12551.
[28] 吴优,卢中秋,姚咏明.线粒体自噬中pink1-parkin途径调控机制的研究进展[J].医学研究杂志,2017,46(3):186-188.
[29] NIU M, DAI X, ZOU W, et al. Autophagy, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and the Unfolded Protein Response in Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Transl Neurosci. 2017;8:37-48.
[30] SHEN X, MA L, DONG W, et al. Autophagy Regulates Intracerebral Hemorrhage Induced Neural Damage via Apoptosis and NF-κB Pathway.Neurochem Int. 2016;96: 100-112.
[31] SHI L, LIANG F, ZHENG J, et al. Melatonin Regulates Apoptosis and Autophagy Via ROS-MST1 Pathway in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11:93.
[32] RITZ M F, GROND-GINSBACH C, KLOSS M, et al. Identification of Inflammatory, Metabolic, and Cell Survival Pathways Contributing to Cerebral Small Vessel Disease by Postmortem Gene Expression Microarray.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2016;13(1):58-67.
[33] SAVERIO M, ELIANA T, MARIANGELA C, et al. Beyond multiple mechanisms and a unique drug: Defective autophagy as pivotal player in cerebral cavernous malformation pathogenesis and implications for targeted therapies. Rare Dis. 2016;4(1):e1142640.
[34] 刘桓,李清华.线粒体功能障碍与神经退行性疾病[J].国际遗传学杂志,2014,37(2):94-98.
[35] 郭倩,王蓓.低氧诱导线粒体自噬的机制及其在相关疾病中的研究进展[J].国际呼吸杂志,2018,38(8):610-614.
[36] GU X, QI Y, FENG Z, et al.Lead (Pb) induced ATM-dependent mitophagy via PINK1/Parkin pathway.Toxicol Lett. 2018;291: 92-100.
|